NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 - Money and Credit
Page - 40
Q1: How does the use of money make it easier to exchange things?
Ans: The use of money makes exchanging goods and services much easier by acting as a universally accepted medium of exchange. Here are the key benefits:
- Eliminates Barter Issues: Unlike barter systems, where goods are exchanged directly, money allows transactions without needing a direct match of wants.
- Simplifies Transactions: People can buy what they need without searching for someone who wants what they have to offer.
- Facilitates Pricing: Money provides a clear way to set prices, making it easier to value goods and services.
- Improves Accounting: It simplifies record-keeping in economic transactions.
Q2: Can you think of some examples of goods/services being exchanged or wages being paid through barter?
Ans:In a barter system, goods and services are exchanged directly without using money. Here are some examples:
- A farmer might exchange a portion of their crops for a craftsman's tools.
- A carpenter could build furniture in return for a baker's bread.
- Wages can also be paid in barter; for instance, a painter may receive food from a restaurant owner in exchange for painting the owner's house.
Page - 42
Page - 42
Q1. M. Salim wants to withdraw Rs 20,000 in cash for making payments. How would he write a cheque to withdraw money?
Ans: M. Salim would write a cheque addressed to himself or "Bearer" for Rs 20,000. The cheque would specify the amount to be withdrawn and would need to be signed by Salim. Upon presenting this cheque at his bank, Salim would receive Rs 20,000 in cash.
Q2. Tick the correct answer. After the transaction between Salim and Prem,
(i) Salim’s balance in his bank account increases, and Prem’s balance increases.
(ii) Salim’s balance in his bank account decreases and Prem’s balance increases.
(iii) Salim’s balance in his bank account increases and Prem’s balance decreases.
Ans. (ii) is correct.
When Salim writes a cheque to Prem, Salim's bank account balance decreases by the amount of the cheque (Rs 20,000 in this case). Simultaneously, Prem's balance increases by the same amount once he deposits the cheque into his own bank account.
This is a basic principle of double-entry accounting where one account decreases (Salim's) and another increases (Prem's) by the same amount for the transaction to be balanced.
Q3. Why are demand deposits considered as money?
Ans: Demand deposits are considered as money for several reasons:
- They are funds held in bank accounts that can be accessed on demand.
- Depositors can withdraw these funds using cheques, debit cards, or electronic transfers.
- Demand deposits are highly liquid, meaning they can be quickly converted into cash.
- They are widely accepted as a medium of exchange, similar to cash.
- Due to these characteristics, they are included in broader definitions of the money supply.
Thus, demand deposits play a crucial role in the monetary system.
Page - 44
Page - 44
Q1. Fill the following table:

Ans: 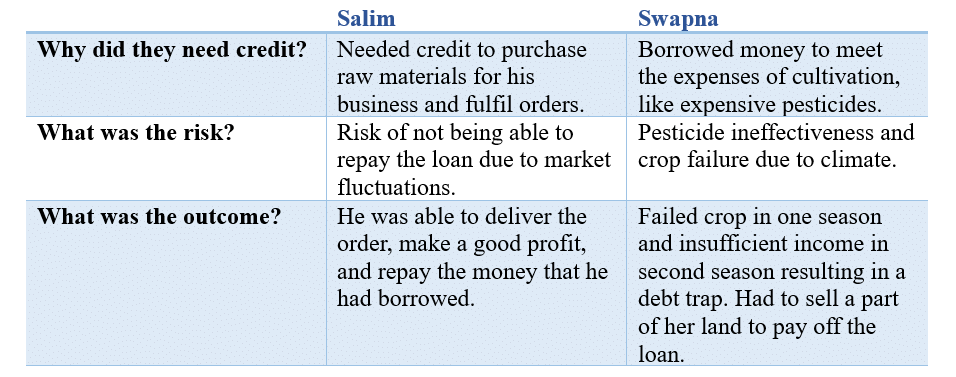
Q2. Supposing Salim continues to get orders from traders. What would be his position after 6 years?
Ans: If Salim continues to receive orders from traders and manages his finances wisely, his business position after six years could be quite strong. Key factors include:
- Consistent orders: Regular demand can lead to growth.
- Expansion: He may be able to broaden his operations and product range.
- Market presence: A strong reputation can enhance his competitiveness.
- Risk management: Success depends on effectively handling challenges like market fluctuations and loan repayments.
Overall, prudent management and sustained orders can significantly improve Salim's business prospects.
Q3. What are the reasons that make Swapna’s situation so risky? Discuss factors – pesticides; role of moneylenders; climate.
Ans: Swapna's situation is highly risky due to several factors:
- Pesticides: Relying on pesticides carries risks such as their effectiveness, environmental harm, and high costs. If pesticides fail, it can result in crop failures, affecting her income and loan repayment ability.
- Role of Moneylenders: Borrowing from moneylenders often means facing high interest rates and strict repayment terms. This adds financial stress, especially if her crop yields are low due to external factors like climate.
- Climate: Variability in climate can severely impact agricultural results. Unfavourable weather, such as droughts or floods, can lead to crop failures, directly affecting Swapna's income and her capacity to repay loans.
Page - 45
Page - 45
Q1: Why do lenders ask for collateral while lending?
Ans: Lenders ask for collateral to secure their loans against the risk of borrowers defaulting. This practice helps to:
- Reduce the lender's risk.
- Allow lenders to offer loans at lower interest rates compared to unsecured loans.
- Provide a form of guarantee that the lender can recover funds if the borrower fails to repay.
Common examples of collateral include property, vehicles, and bank deposits.
Q2: Given that a large number of people in our country are poor, does it in any way affect their capacity to borrow?
Ans: Yes, a large number of poor people in the country can greatly affect their ability to borrow. Here are some key points:
- Poverty often leads to limited access to formal financial institutions.
- Many poor individuals lack a credit history, making it hard to qualify for loans.
- They may not have sufficient collateral to secure loans from traditional lenders.
- This situation forces them to rely on informal sources of credit, which usually have higher interest rates and less favourable terms.
Overall, these factors create significant barriers for poor individuals seeking to borrow money.
Q3: Fill in the blanks choosing the correct option from the brackets:
While taking a loan, borrowers look for easy terms of credit. This means __________ (low/high) interest rate, ______________(easy/ tough) conditions for repayment, ___________(less/more) collateral and documentation requirements.
Ans. "While taking a loan, borrowers look for easy terms of credit. This means (low) interest rate, (easy) conditions for repayment, (less) collateral and documentation requirements."
Page - 50
Q1. What are the differences between formal and informal sources of credit?
Ans. Formal sources of credit, such as banks and cooperatives, are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). They offer:
- Lower interest rates
- Loans to various sectors
- Strict requirements for documentation
In contrast, informal sources, like moneylenders and friends, operate without regulation. They tend to:
- Charge higher interest rates
- Have fewer requirements
- Be more accessible, but costly for borrowers
Q2. Why should credit at reasonable rates be available for all?
Ans. Credit at reasonable rates enables people to borrow affordably for essential needs like farming, business, and personal expenses. This accessibility supports economic growth by enabling investments that can enhance income.
Conversely, high-interest rates from informal lenders can lead to:
- Excessive debt
- Reduced income
- Financial difficulties
Therefore, making credit available at reasonable rates is crucial for the development of individuals and the economy.
Q3. Should there be a supervisor, such as the Reserve Bank of India, that looks into the loan activities of informal lenders? Why would its task be quite difficult?
Ans. Yes, a supervisor like the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) should oversee informal lenders to prevent exploitation through high interest rates and unfair practices.
However, this task is challenging due to several factors:
- Informal lenders vary widely in their practices and also operate in many areas, making monitoring difficult.
- Informal lenders lack regulation as they're not bound by strict rules.
- Monitoring requires significant effort and resources.
- Imposing regulations may face pushback from lenders.
Q4. Why do you think that the share of formal sector credit is higher for the richer households compared to the poorer households?
Ans. Richer households have greater access to formal sector credit for several reasons:
- They can provide collateral, which reduces the lender's risk.
- They are viewed as lower risk by banks, making them more likely to receive loans.
- They have a better understanding of banking procedures, allowing them to navigate the loan process more effectively.
In contrast, poorer households often face:
- They can't provide collateral creating higher barriers to accessing formal credit.
- They might not understand bank proceedings for formal credit.
- Therefore they rely on expensive informal loans due to lack of collateral and understanding.
This disparity highlights the need for improved access to formal credit for poorer households.
Page - 52
Page - 52
Q1: In situations with high risks, credit might create further problems for the borrower. Explain.
Ans: In high-risk situations, taking on credit can lead to serious problems for borrowers. This is often referred to as a debt trap. Here’s how it works:
- When a borrower takes out a loan, they must pay back the principal amount plus an interest rate.
- If the borrower fails to repay, they risk losing their collateral, which is an asset pledged as security for the loan.
- In high-risk scenarios, adverse conditions can worsen the borrower's situation, leading to greater losses than if they had not taken the loan.
Ultimately, the burden of debt can push borrowers into a cycle of financial distress.
Q2: How does money solve the problem of double coincidence of wants? Explain with an example of your own.
Ans: Money solves the problem of double coincidence of wants by acting as a medium of exchange.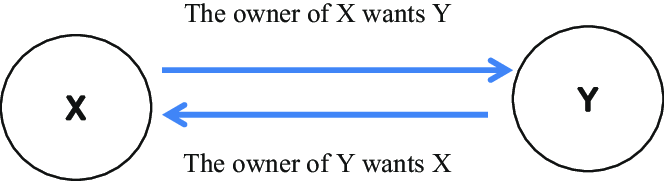
- Double coincidence of wants implies a situation where two parties agree to sell and buy each other’s commodities., i.e., what one party desires to sell is exactly what the other party wishes to buy.
- Money does away with this tedious and complex situation by acting as a medium of exchange that can be used for one and all commodities.
Example: If an ice-cream vendor wants a bicycle, but the bicycle manufacturer wants clothes, and not ice-creams, then the vendor can use the money to obtain a bicycle. - He does need to adhere to the bicycle man’s needs because money acts as the common medium of exchange. Similarly, the bicycle manufacturer can then use the money to buy clothes.
Q3: How do banks mediate between those who have surplus money and those who need money?
Ans: A bank plays a crucial role in connecting those with surplus money to those in need of funds. Here’s how:
- Banks allow individuals to open accounts for deposits and withdrawals.
- They keep only about 15% of cash reserves to meet daily withdrawal demands.
- Depositors earn interest on their surplus funds, encouraging them to invest.
- Banks use the majority of deposits to provide loans to borrowers.
- The difference between the interest charged on loans and the interest paid on deposits is the bank's main source of income.
Q4: Look at a 10 rupee note. What is written on top? Can you explain this statement?
Ans: A ten rupee note features “Reserve Bank of India” at the top, along with the statement “guaranteed by the central government.”
- It is a promissory note and can only be issued by the Reserve Bank of India which supervises all money-related functions in the formal sector, in India.
- The statement on the ten rupee bank note relates to this idea that the RBI is the central organ in the working of money-related activities.
Q5: Why do we need to expand formal sources of credit in India?
Ans: Expanding formal sources of credit in India is essential for several reasons:
- It reduces reliance on informal sources that often charge high interest rates.
- The Reserve Bank of India oversees formal lending, ensuring better regulation.
- Informal loans can lead to a debt trap due to exorbitant interest rates.
- Currently, formal credit meets only about half of the rural population's needs.
- Increasing formal lending, especially in rural areas, can enhance overall economic development.
By expanding formal credit, we can help more people access loans at reasonable rates, promoting financial stability and growth.
Q6: What is the basic idea behind the SHGs for the poor? Explain in your own words.
Ans: The basic idea behind Self Help Groups (SHGs) is to provide financial resources to the poor by organising them, particularly women, into small groups.
There are some main objectives of SHGs, which are as following:
- Organise the rural poor, especially women, into small groups.
- Collect savings from members.
- Provide loans without the need for collateral and offer timely loans for various needs.
- Charge reasonable interest rates with easy repayment terms.
- Serve as a platform to discuss social issues like education, health, and domestic violence.
 Self Help Group
Self Help Group
Q7: What are the reasons why the banks might not be willing to lend to certain borrowers?
Ans: The Banks might not be willing to lend certain borrowers due to the following reasons:
- Banks require proper and legal documents and collateral as security against loans.
- The borrowers who have not repaid previous loans, the banks might not be willing to lend them further.
- For those entrepreneurs, who are going to invest in a business with high risks, the banks might not be willing to lend money.
- One of the main objectives of a bank is to earn more profits after meeting a number of expenses.
- For this purpose, it has to adopt a judicious loan and investment policies that ensure fair and stable return on the funds.
Page - 53
Q8: In what ways does the Reserve Bank of India supervise the functioning of banks? Why is this necessary?
Ans: The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functions of banks in various ways:
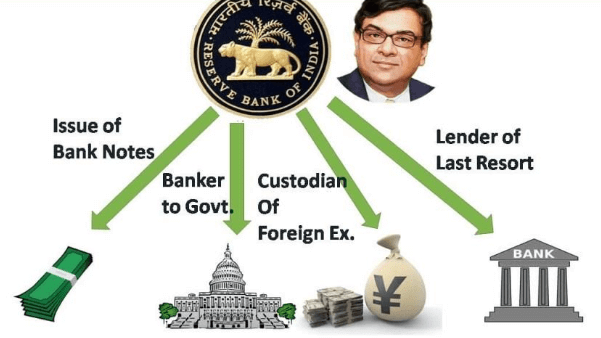 RBI Functioning
RBI Functioning
- RBI holds part of the cash reserve of commercial banks.
- RBI mainly ensures that the banks maintain a minimum cash balance out of the deposits they receive.
- The commercial banks have to submit information to RBI on how much they are lending, to whom, and at what interest rate, etc.
- RBI observes that the Banks are not only providing loans to profitable businesses but also to traders and small cultivators, small-scale industries, small borrowers, etc.
Q9: Analyse the role of credit for development.
Ans: Credit plays a crucial role in a country’s development. By sanctioning loans to developing industries and trade, banks provide them with the necessary aid for improvement.
- This leads to increased production, employment, and profits. However, caution must be exercised in the case of high risks so that losses do not occur.
- This advantage of loans also needs to be manipulated and kept under an administrative hold because loans from the informal sector include high interest rates that may be more harmful than good.
- For this reason, it is important that the formal sector gives out more loans so that borrowers are not duped by moneylenders, and can ultimately contribute to national development.
Q10: Manav needs a loan to set up a small business. On what basis will Manav decide whether to borrow from the bank or the moneylender? Discuss.
Ans: Manav will decide whether to borrow from the bank or the moneylender based on several key factors:
- Interest Rate: He will consider which option offers a more suitable rate.
- Collateral: Availability of collateral required by the bank is crucial.
- Documentation: The amount of paperwork needed by the bank can influence his choice.
- Repayment Terms: The mode and ease of repayment are significant factors.
Ultimately, these factors will help Manav choose the most beneficial option for his business needs.
Q11: In India, about 80 percent of farmers are small farmers, who need credit for cultivation.
(a) Why might banks be unwilling to lend to small farmers?
(b) What are the other sources from which the small farmers can borrow?
(c) Explain with an example how the terms of credit can be unfavorable for the small farmer.
(d) Suggest some ways by which small farmers can get cheap credit.
Ans:(a) Banks often hesitate to lend to small farmers due to the following reasons:
- They require proper documentation and collateral as security for loans.
- But there is the situation where small farmers frequently lack the necessary documents and assets to secure loans.
- Many small farmers struggle to repay loans on time, especially after crop failures.
(b) Apart from banks, the small farmers can borrow from local money lenders, agricultural traders, big landlords, cooperatives, SHGs, etc.
(c) For example, Gopal, a small farmer, borrowed money from a local moneylender at a high interest rate of 3% to cultivate rice. Unfortunately, a drought caused his crops to fail, forcing him to sell part of his land to repay the loan. This illustrates how unfavourable terms can severely impact small farmers.
(d) The small farmers can get cheap credit from different sources like Banks, Agricultural Cooperatives, and SHGs.
Q12: Fill in the blanks
(i) Majority of the credit needs of the __________households are met from informal sources.
(ii) __________costs of borrowing increase the debt-burden.
(iii) __________issues currency notes on behalf of the Central Government.
(iv) Banks charge a higher interest rate on loans than what they offer on __________.
(v) __________is an asset that the borrower owns and uses as a guarantee until the loan is repaid to the lender.
Ans:
(i) Majority of the credit needs of the poor households are met from informal sources.
(ii) High costs of borrowing increase the debt-burden.
(iii) Reserve Bank of India issues currency notes on behalf of the Central Government.
(iv) Banks charge a higher interest rate on loans than what they offer on deposits.
(v) Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns and uses as a guarantee until the loan is repaid to the lender.
Q13: Choose the most appropriate answer.
(i) In a SHG, most of the decisions regarding savings and loan activities are taken by:
(a) Bank
(b) Members
(c) Non-government organisation
Ans: (i) (b)
In a Self-Help Group (SHG), most decisions about savings and loans are made by the members of the group. They collectively manage the group's finances and decide on savings, loans, and other activities.
(ii) Formal sources of credit do not include
(a) Banks
(b) Cooperatives
(c) Employers
Ans (ii): (c)
Formal sources of credit typically include banks and cooperatives, while employers are not considered a formal source of credit.
|
66 videos|798 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 - Money and Credit
| 1. What is the definition of money in the context of economics? |  |
| 2. How does credit function in the economy? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of credit available to consumers? |  |
| 4. What role do banks play in the money and credit system? |  |
| 5. How can individuals manage their credit effectively? |  |






















