Key Concepts: Globalisation & the Indian Economy | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
Globalization
Globalization refers to the process of integrating a country's economy with the global economy, facilitating the unrestricted movement of goods, capital, and people across international borders. 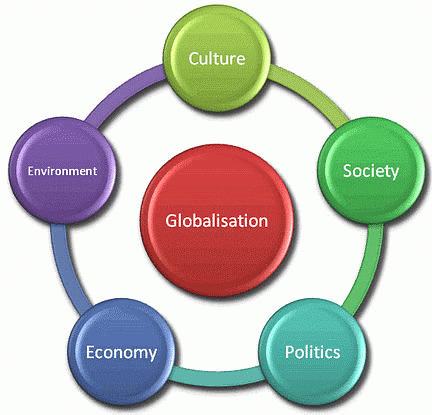
Production Across Countries
Trade has historically been the key link between distant countries, and it is primarily driven by large firms known as Multinational Corporations (MNCs). 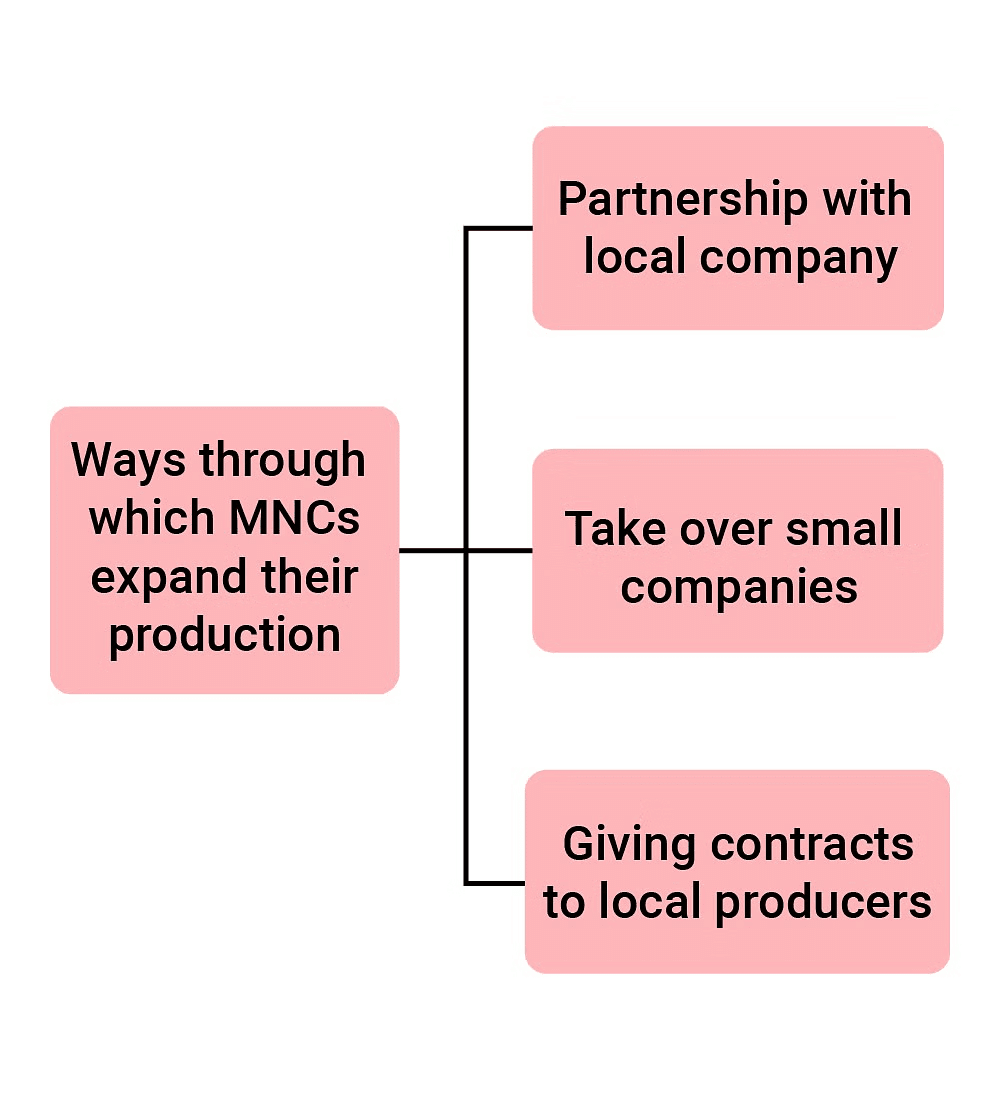
- MNCs are businesses that own or manage production facilities in multiple countries.
- These corporations establish offices and factories in regions where they can access cost-effective labor and resources, aiming to maximize their profits.
Interlinking Production Across Countries 
In some cases, MNCs collaborate with local companies in foreign countries to produce goods. This joint production offers several benefits to the local company:
- Funding for Investment: MNCs can provide financial support for investments, such as acquiring new machinery to enhance production efficiency.
- Introduction of Technology: MNCs may bring in advanced production technology, improving the overall quality and speed of manufacturing.
Investment and Foreign Investment
Investment refers to the expenditure on acquiring assets like land, buildings, machinery, and equipment. Foreign investment, on the other hand, pertains to funds from MNCs or foreign entities directed towards local assets.
By partnering with local companies, sourcing supplies from them, competing with them, or even acquiring them, MNCs significantly impact production processes in various regions around the world.
Foreign Trade and Market Integration
Foreign trade enables producers to reach customers beyond their local areas.
Effects of Foreign Trade
- Producers can sell their goods in local markets and also compete in international markets.
- Buyers have the chance to select from a wider range of products that are not just limited to local production.
- This results in the integration of markets across different countries.
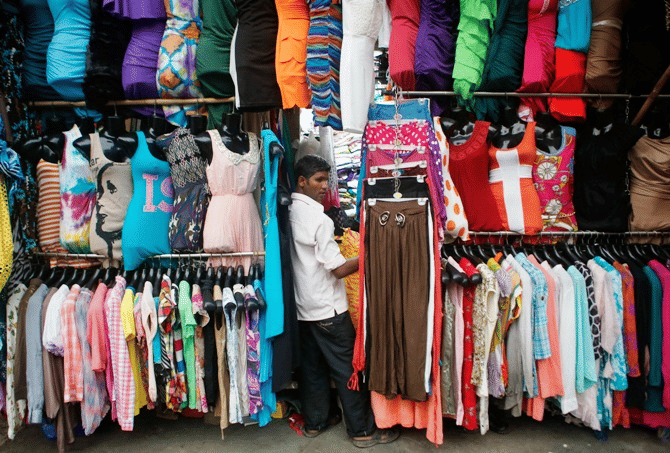 Small traders of readymade garments facing stiff competition from both the MNC brands and imports.
Small traders of readymade garments facing stiff competition from both the MNC brands and imports.
Understanding Globalisation
Globalisation is about how countries are being rapidly integrated and connected, mainly due to the activities of multinational corporations (MNCs). There is a growing exchange of goods, services, investments, and technology between nations.
Factors Driving Globalisation
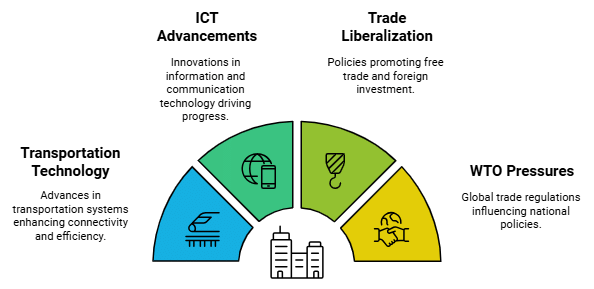
Several key factors have enabled globalisation:
- Transportation Technology: Improvements in how we transport goods have made it easier and faster to move products across borders.
- Information and Communication Technology: Advances in technology related to information and communication have facilitated better and quicker interactions between countries, supporting global trade and investment.
- Liberalisation of Trade and Investment Policies: Many countries have relaxed their rules regarding foreign trade and investment, making it easier for businesses to operate across borders.
- Influence of the World Trade Organisation (WTO): The WTO has played a significant role in promoting and regulating international trade, encouraging countries to engage more openly in global commerce.
World Trade Organization (WTO)
- The World Trade Organization (WTO) aims to facilitate and simplify international trade.
- As of now, there are 164 member countries in the WTO. The organization has established rules to promote free trade among all its member nations.

Impact of Globalization in India
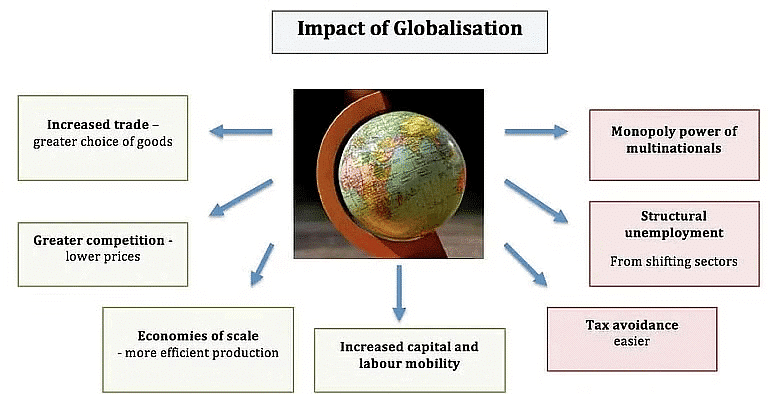
Globalization has enhanced consumer options, resulting in superior product quality at reduced prices, thereby elevating living standards.
The Struggle for Fair Globalization
Key Considerations
- Ensuring proper implementation of labor laws to safeguard workers' rights.
- Supporting small producers to improve their performance and competitiveness.
- Utilizing trade and investment barriers when necessary to protect local interests.
- Negotiating at the World Trade Organization (WTO) for fairer trade rules and practices.
- Aligning with other developing countries to counterbalance the influence of developed nations in WTO discussions.
- Considering both the positive and negative impacts of globalization on various sectors, such as agriculture and industry, for a balanced perspective.
|
66 videos|798 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Key Concepts: Globalisation & the Indian Economy - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What is globalisation and how does it affect economies? |  |
| 2. What are the main factors that have enabled globalisation? |  |
| 3. What is the role of the World Trade Organisation (WTO) in global trade? |  |
| 4. How has globalisation impacted India’s economy? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges in achieving fair globalisation? |  |






















