Key Concepts: Sectors of the Indian Economy | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Sectors of Economic Activities |

|
| Comparing the three Sectors |

|
| Division of Sectors as Organised and Unorganised |

|
| Sectors in terms of Ownership |

|
Sectors of Economic Activities
All activities that give an income in return are called economic activities.
Example: People going to work in factories, banks, schools, etc.
Economic activities can be classified into different sectors on the basis of the nature of work.
Primary Sector
- Goods which are produced by exploiting natural resources come under the category of the primary sector.
- This sector is also called the agriculture and related sector.
Example: Cotton cultivation
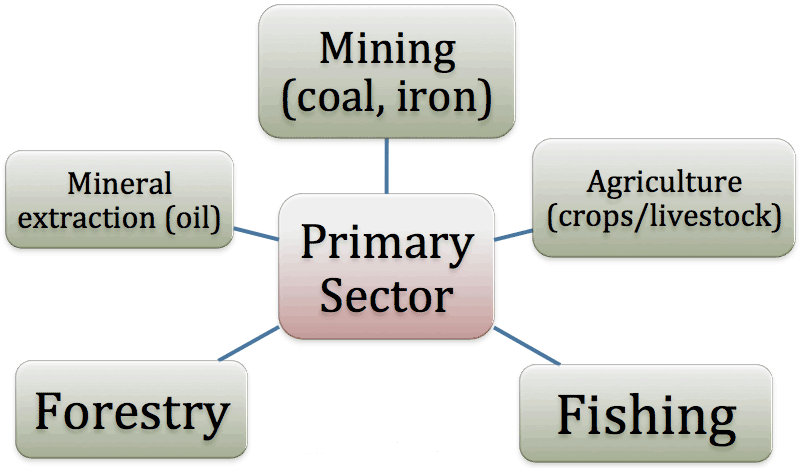 Primary Sector of Economy
Primary Sector of Economy
Secondary Sector
- Transformation of one good into another comes under the category of the secondary sector.
- Manufacturing is one of the important components of this sector.
Example: Transformation of sugarcane into sugar.
Tertiary Sector
- All production units that provide services to support the development of primary and secondary sectors fall under the tertiary sector category. This is also known as the service sector.
Example: Services given by doctors, teachers, lawyers, etc.
Comparing the three Sectors
These three sectors are highly interdependent on one another.
This can be explained with the help of an example:
- Farmers buy goods such as tractors, pump sets, fertilisers (manufacturing sector) to produce agricultural goods (primary sector).
- This shows the dependence of the primary sector on the secondary sector.
- Now farmers want to sell their output. For this, they need transport facilities. It shows the dependence of the primary sector on the tertiary sector.
 The Dependency of 3 Sectors on Each Other
The Dependency of 3 Sectors on Each Other
- There are thousands of goods and services produced in an economy. We cannot add different types of goods in practice. So the value of these goods and services should be used rather than adding up the actual numbers. Comparisons are made among these three sectors on the basis of the value of final goods and services produced.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP)The value of final goods and services produced in each sector during a particular year provides the total production of the sector for that year. The sum of production in these sectors gives us the gross domestic product (GDP) of a country.
- The tertiary sector has emerged as the largest sector because it helps in the development of the primary and secondary sectors.
- Several services, such as hospitals, banks, insurance companies, transport, and educational institutions, are the basic services required by the primary and secondary sectors for their normal functioning.
Division of Sectors as Organised and Unorganised
Organised Sector
- The organised Sector covers those enterprises or places of work where the terms of employment are regular.
- They are registered by the government and have to follow its rules and regulations.
- Therefore, people have job security.
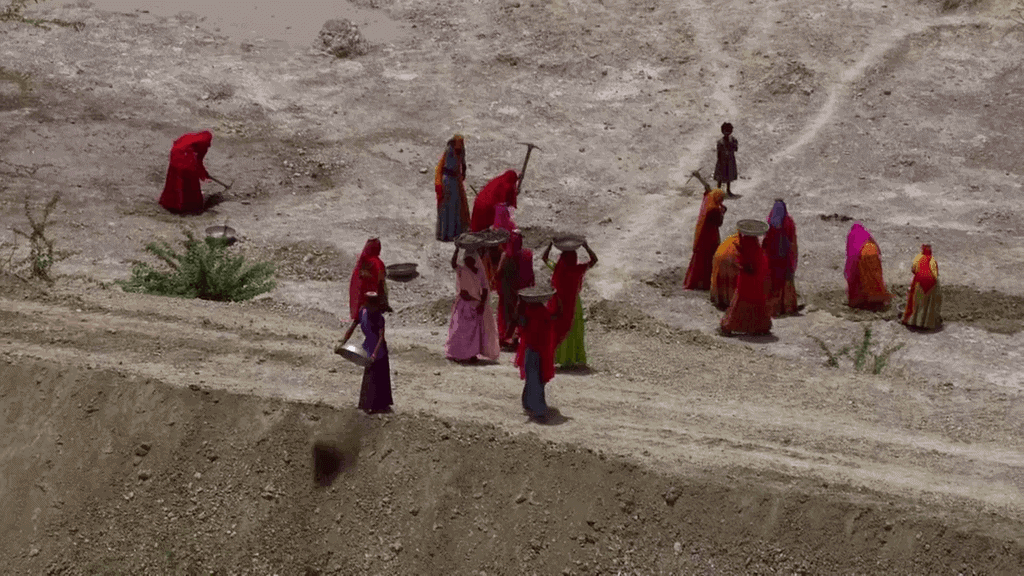
Unorganised Sector
- The unorganised sector covers small and scattered units that are largely outside the control of the government.
- There are rules and regulations, but they are generally not being implemented by the unorganised sector.
- Employment is not secure in the unorganised sector.
How to Protect Workers in the Unorganised Sector?
In the unorganised sector, protection and support are required for the workers for their economic and social development. Besides getting irregular and low-paid work, they also face social discrimination.
Sectors in terms of Ownership
- The public sector is the sector that is owned, controlled, and managed by the government. Activities in the government sector are guided by the motive of social welfare and not to earn profit.
- In the private sector, ownership of production units is in the hands of private individuals. Activities in the private sector are mainly guided by the motive to earn profit.
Example: Tata Iron and Steel Company (TISCO) and Reliance Industries Limited (RIL). - Employment is an activity from which a person earns the means of living, i.e. income in cash or in kind.
- Unemployment refers to a situation where persons who can work and are willing to work fail to secure work.
- Underemployment is a situation in which a worker gets work for less time than the time he can work. In other words, he remains unemployed for some months in a year or some hours every day.
There was a big change in the share of three sectors in G.D.P. (from 1973 to 2000), but the data show that a similar shift has not taken place in terms of employment.
- In the secondary sector, output went up by 8 times, but it rose only 2.5 times in terms of employment.
- In the tertiary sector, output went up 11 times, whereas employment rose 3 times.
The government can create more employment opportunities by providing better: - Infrastructure such as roads, dams, canals, etc.
- Further, this can be enhanced by providing services like banks, transport and communication.
- Set up industries that process vegetables and agricultural products such as potatoes, rice, wheat, tomatoes, and fruits, which can be sold in outside markets.
- This will be employed in industries located in semi-rural areas.
Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act-2005 (NREGA -2005)
- This act is implemented as “Right to Work” in all the districts of India.
- Under this act, all those who can work and need work have been guaranteed 100 days of employment in a year by the government.

|
66 videos|798 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Key Concepts: Sectors of the Indian Economy - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What are the three sectors of economic activities in India? |  |
| 2. How can we compare the three sectors of the Indian economy? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between organised and unorganised sectors in India? |  |
| 4. How can we classify the sectors of the Indian economy based on ownership? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the sectors of the Indian economy? |  |
















