Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 10 > Key Concepts: Water Resources
Key Concepts: Water Resources | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
1. Earth's Water Composition
- 71% of Earth’s surface is covered with water.
- Of this: 97% is saltwater, unsuitable for direct human use.
- Only 3% is freshwater, available in limited forms like glaciers, groundwater, and surface water.
2. Sources and Cycle of Freshwater
- Freshwater comes primarily from surface runoff and groundwater—both part of the hydrological cycle.
The hydrological cycle is a continuous process: Water evaporates from oceans and lakes. Forms clouds, falls as precipitation, and returns to surface or underground sources. This makes water a renewable resource.
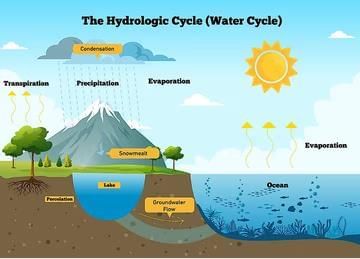 Hydrological Cycle
Hydrological Cycle
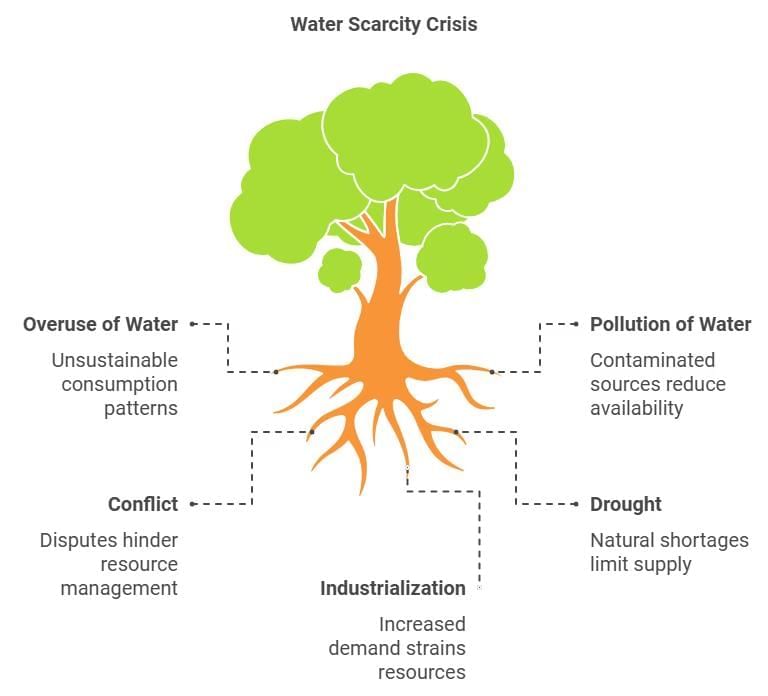
3. Water Scarcity: Causes and Challenges
Despite abundance, water scarcity persists due to:
- Unequal access, overuse, and pollution rather than just natural shortages.
- Regions like Rajasthan experience both low rainfall and overexploitation.
- Growing population and industrialization have amplified demand for water.
Key Issues:
- Overuse in agriculture, especially irrigated farming.
- High water demand from industries and urban areas.
- Pollution from domestic and industrial waste, pesticides, and fertilizers.
- Quality issues make even available water unsafe for consumption.
4. Government Initiatives
Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM)
- Aims to provide 55 litres/person/day of clean piped water to every rural household.
- Focuses on: Quality and regular supply of water. Reducing health hazards from polluted water.
Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY)
- Improve irrigation infrastructure.
Promote water-use efficiency ("more crop per drop").
Encourage sustainable farming and water-saving technologies.
5. Traditional & Modern Water Management Systems
A. Ancient Hydraulic Structures
Historical records show water systems like:
- Dams, lakes, and canals in Mauryan and Sultanate periods.
- Bhopal Lake, Hauz Khas tank, and systems in Kalinga and Kolhapur.
B. Dams as Multi-Purpose Projects
Dams serve for:
- Irrigation
- Hydroelectric power
- Water supply (domestic and industrial)
- Flood control, navigation, and recreation
Examples:
- Bhakra–Nangal Project: irrigation + electricity
- Hirakud Dam: flood control + conservation
Disadvantages of Dams:
- Sedimentation, disrupted aquatic life, displacement of people.
- Ecological imbalance from commercial crops.
- Social disputes and inter-state conflicts.
- Sometimes fail in flood control during extreme rainfall.
C. Cropping Pattern Shift
Irrigation encourages water-intensive commercial crops.
Leads to:
- Soil salinisation
- Social inequality (rich landowners vs. landless poor)
- Increased water stress
6. Water Conservation Techniques
A. Rainwater Harvesting (RWH)
- Involves collecting rainwater from rooftops or other surfaces.
- Stored in underground tanks, cisterns, or aquifers.
- Effective in both urban and arid rural areas.
Case Studies:
- Rajasthan: Underground tankas used to store drinking water.
- Shillong: Despite heavy rainfall nearby, faces shortages—houses use rooftop RWH.
- Gendathur (Karnataka): Community harvesting yields 1,00,000 litres annually.
- Tamil Nadu: First state to make RWH legally mandatory in all homes.
B. Bamboo Drip Irrigation (Meghalaya)
- Traditional system using bamboo pipes to channel spring water to crops.
- Water-saving and eco-friendly; supplies precise water drops directly to plant roots.
Conclusion
While Earth's water seems abundant, freshwater availability is limited and threatened by human activities. Sustainable management through:
- Government initiatives
- Technological solutions
- Traditional practices
is essential to ensure equitable and long-term access to water for all.
The document Key Concepts: Water Resources | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
66 videos|798 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Key Concepts: Water Resources - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What are the main sources of water? |  |
Ans. The main sources of water include surface water (rivers, lakes, and reservoirs), groundwater (aquifers), rainwater, and desalinated water from oceans. Each source plays a crucial role in meeting the water needs of communities and ecosystems.
| 2. What are the primary causes of water scarcity? |  |
Ans. The primary causes of water scarcity include over-extraction of water resources, population growth, pollution, climate change, and inefficient water management practices. These factors can lead to a significant imbalance between water supply and demand.
| 3. How can water resources be effectively managed? |  |
Ans. Effective water resource management can be achieved through strategies such as sustainable water use practices, improved irrigation techniques, investment in water infrastructure, watershed management, and policy regulations aimed at protecting water sources.
| 4. What are multi-purpose river projects and their benefits? |  |
Ans. Multi-purpose river projects are large-scale initiatives aimed at utilizing river systems for various purposes, including irrigation, hydroelectric power generation, flood control, and recreation. These projects can enhance water availability, improve agricultural productivity, and support economic development.
| 5. What is rainwater harvesting and why is it important? |  |
Ans. Rainwater harvesting is the collection and storage of rainwater for later use. It is important because it helps to conserve water, reduce dependence on traditional water sources, mitigate flooding, and recharge groundwater supplies, making it a sustainable solution for water scarcity.
Related Searches

















