Class 8 Science: Sample Paper Solutions - 5 | Science Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
| Section - D |

|
Time: 3 hrs
Total Marks: 80
General Instructions
This question paper consists of 31 questions in total and all questions are compulsory.
- Questions 1–7 are multiple-choice questions and each carries 1 mark. Write the correct answer in your answer sheet.
- Questions 8–16 are very short-answer questions and carry 2 marks each.
- Questions 17–26 are short-answer questions and carry 3 marks each.
- Questions 27–31 are long-answer questions and each carries 5 marks.
Section - A
Q1. Which of the following is a natural fibre? (1 mark)
(a) Nylon
(b) Polyester
(c) Silk
(d) Acrylic
Ans: (c)
Silk is a natural fibre obtained from silkworms, while nylon, polyester, and acrylic are synthetic fibres.
Q2. Which process is used in water treatment plants to remove insoluble impurities? (1 mark)
(a) Evaporation
(b) Sedimentation
(c) Distillation
(d) Filtration
Ans: (b)
Sedimentation allows insoluble impurities to settle down at the bottom, helping in their removal in water treatment plants.
Q3. Which of the following is present only in plant cells? (1 mark)
(a) Nucleus
(b) Mitochondria
(c) Cell wall
(d) Ribosome
Ans: (c)
Cell wall is present only in plant cells, giving them rigidity and shape, while the other organelles are found in both plant and animal cells.
Q4. Which property of sound helps us differentiate between a man’s voice and a woman’s voice? (1 mark)
(a) Loudness
(b) Pitch
(c) Speed
(d) Amplitude
Ans: (b)
Pitch depends on the frequency of sound. A woman’s voice generally has a higher pitch than a man’s voice, helping us differentiate between the two.
Q5. Which gas is released during respiration? (1 mark)
(a) Oxygen
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Carbon dioxide
(d) Hydrogen
Ans: (c)
During respiration, glucose is broken down to release energy, and carbon dioxide is released as a by-product.
Q6. Which one of the following is a decomposer? (1 mark)
(a) Lion
(b) Cow
(c) Mushroom
(d) Goat
Ans: (c)
Mushrooms are decomposers; they break down dead plants and animals into simpler substances, enriching the soil.
Q7. Which device is used to measure temperature? (1 mark)
(a) Hygrometer
(b) Thermometer
(c) Barometer
(d) Ammeter
Ans: (b)
A thermometer is used to measure temperature. Hygrometer measures humidity, a barometer measures air pressure, and an ammeter measures electric current.
Section - B
Q8. Why is petroleum called “black gold”? (2 mark)
Ans: Petroleum is called “black gold” because it is black in colour and very valuable like gold, as it is used to produce fuels, lubricants, and many useful products.
Q9. Name two differences between unicellular and multicellular organisms. (2 mark)
Ans:
- Unicellular organisms have a single cell (e.g., Amoeba), while multicellular organisms are made up of many cells (e.g., humans).
- In unicellular organisms, one cell performs all functions, while in multicellular organisms, different cells perform specialized functions.
Q10. What is corrosion? Give one example. (2 mark)
Ans: Corrosion is the gradual destruction of metals when they react with air, water, or chemicals.
Example: Rusting of iron.
Q11. What is refraction? Give one example from daily life. (2 mark)
Ans: Refraction is the bending of light when it passes from one medium to another.
Example: A pencil appears bent when placed in a glass of water.
Q12. Write two precautions to avoid food spoilage. (2 mark)
Ans:
- Store food in airtight containers or refrigerate it.
- Use preservatives like salt, sugar, or oil to prevent microbial growth.
Q13. Give two harmful effects of using chemical fertilisers. (2 mark)
Ans:
- They reduce soil fertility in the long run.
- They cause water pollution and harm aquatic life.
Q14. Why are summers hotter in urban areas compared to rural areas? (2 mark)
Ans: Urban areas have more concrete buildings, roads, and vehicles that absorb and trap heat. This makes urban areas hotter than rural areas, which have more greenery.
Q15. What is the role of haemoglobin in the blood? (2 mark)
Ans: Haemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to body tissues and transports carbon dioxide back to the lungs.
Q16. State two uses of microorganisms in industry. (2 mark)
Ans:
- Used in making alcoholic beverages like wine and beer (yeast fermentation).
- Used in production of antibiotics like penicillin.
Section - C
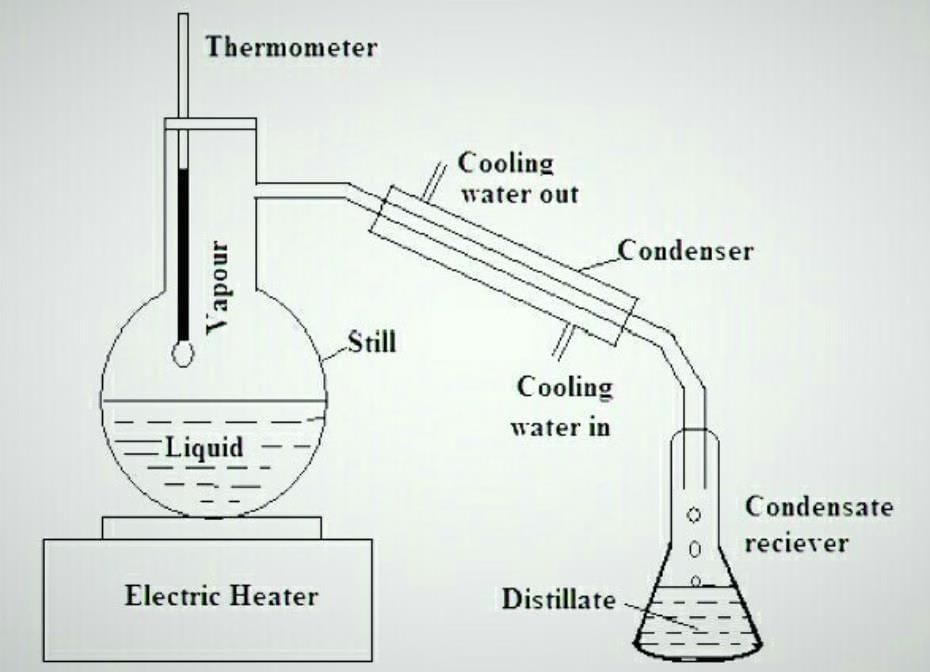
Q17. Explain distillation with a diagram. (3 mark)
Ans: Distillation is the process of separating a mixture of liquids or purifying a liquid by heating it to produce vapour and then condensing the vapour into a liquid.
Example: Distillation of water to obtain pure water from saltwater.
Q18. Why are metals used in making electrical wires? (3 mark)
Ans: Metals are used because they are good conductors of electricity, ductile (can be drawn into thin wires), and strong enough to carry current without breaking.
Q19. What is fermentation? Explain its use in industries. (3 mark)
Ans: Fermentation is a process in which microorganisms like yeast break down sugars to produce energy in the absence of oxygen.
Industrial uses:
- Production of alcohol, wine, and beer.
- Preparation of bread using yeast.
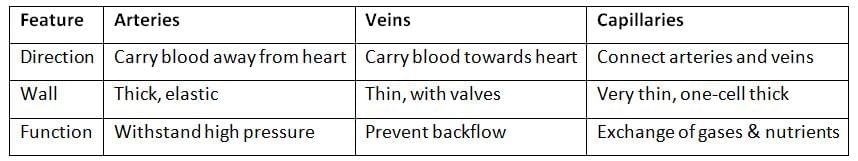
Q20. Write three differences between arteries, veins, and capillaries. (3 mark)
Ans:
Q21. Explain adaptations in desert plants with examples. (3 mark)
Ans: Desert plants have adaptations to conserve water:
- Thick, waxy cuticle on leaves (e.g., cacti) to reduce water loss.
- Spines instead of leaves (e.g., cactus) to prevent transpiration.
- Deep roots to absorb water from underground.
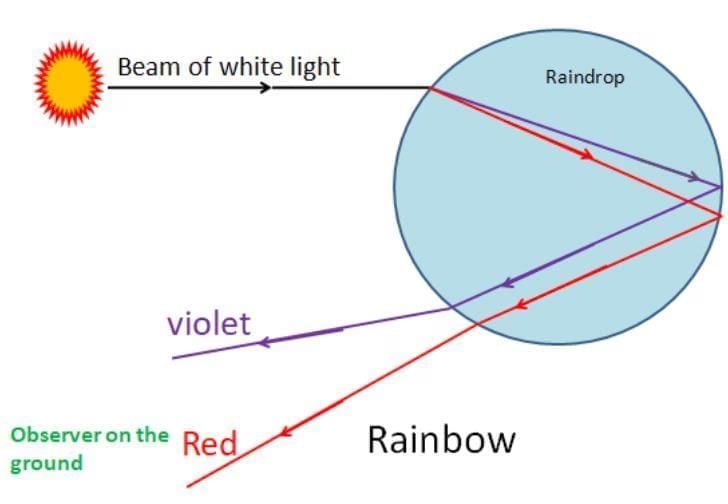
Q22. How does a rainbow form? Explain with a diagram. (3 mark)
Ans: A rainbow forms when sunlight passes through raindrops. The light is refracted, reflected inside the drop, and dispersed into its constituent colours.
Q23. What is an electromagnet? How is it made? Mention two uses. (3 mark)
Ans: An electromagnet is a magnet produced by passing electric current through a coil of wire.
Making: Coil a copper wire around an iron core and connect it to a battery.
Uses:
- Used in electric bells.
- Used in cranes to lift heavy metallic objects.
Q24. Why should we protect wildlife? Write three reasons. (3 mark)
Ans:
- To maintain ecological balance.
- To preserve biodiversity.
- To prevent extinction of species.
Q25. What is an electromagnet? How is it made? Mention two uses. (3 mark)
Ans: An electromagnet is a temporary magnet that produces a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it. It is made by winding insulated copper wire around a piece of soft iron and then passing electric current through the wire.
Uses:
- Electromagnets are used in electric bells and telegraphs.
- They are used in cranes to lift and move heavy loads of iron and steel.
Q26. What are greenhouses? State two advantages and one disadvantage. (3 mark)
Ans: Greenhouses are structures with transparent walls and roofs used to grow plants in a controlled environment.
Advantages:
- Protect plants from extreme weather.
- Help in faster growth of plants.
Disadvantage:
- Expensive to construct and maintain.
Section - D
Q27. (a) What is soil erosion? (5 mark)
(b) Name three causes of soil erosion.
(c) Suggest three preventive measures.
Ans: (a) Soil erosion: The removal of the top fertile layer of soil by water, wind, or human activities.
(b) Causes:
- Deforestation
- Overgrazing by animals
- Heavy rainfall or wind
(c) Preventive measures:
- Planting trees and grasses to hold the soil.
- Contour ploughing and terrace farming.
- Avoiding overgrazing and deforestation.
Q28. (a) Define respiration. (5 mark)
(b) Differentiate between breathing and respiration.
(c) Explain anaerobic respiration with an example.
Ans: (a) Respiration: The process by which living organisms release energy from food in the form of ATP.
(b) Difference between breathing and respiration: (To be explained properly).(c) Anaerobic respiration: Respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen.
Example: Glucose → Lactic acid + Energy (in muscles during vigorous exercise).
Q29. (a) What is photosynthesis? (5 mark)
(b) Explain the role of chlorophyll, water, and sunlight in photosynthesis.
(c) State its importance for life on Earth.
Ans: (a) Photosynthesis: The process by which green plants make food using carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.
(b) Role of components:
- Chlorophyll: Absorbs sunlight and initiates photosynthesis.
- Water: Provides hydrogen and oxygen for glucose formation.
- Sunlight: Provides energy needed to drive the chemical reaction.
(c) Importance:
- Produces oxygen necessary for life.
- Provides food (glucose) for plants and animals.
- Maintains ecological balance by reducing carbon dioxide.
Q30. (a) What are synthetic materials? (5 mark)
(b) Write three uses of plastics.
(c) Suggest three ways to reduce plastic pollution.
Ans: (a) Synthetic materials: Materials that are artificially made by humans from chemical substances. Examples: Nylon, polyester, plastics.
(b) Uses of plastics:
- Making containers, bottles, and packaging materials.
- Manufacturing toys, furniture, and household items.
- Insulation in electrical wires and pipes.
(c) Ways to reduce plastic pollution:
- Use cloth bags instead of plastic bags.
- Recycle and reuse plastic materials.
- Avoid single-use plastics like straws and cutlery.
Q31. (a) How do ciliary muscles affect the functioning of eye? (5 mark)
(b) How can night birds see in the dark?
Ans: (a) Ciliary muscles can contract and relax. Because of this they can change the thickness of eye lens which also changes its focal length. With change in focal length eye lens can make image of near by objects and also far away objects. So power of accommodation of eye is due to the function of the ciliary muscle.
(b) Night birds can see very well through darkness, but they cannot see during day. The night birds have a large cornea and a large pupil, to allow more light to come in. These birds have more rods, which are sensitive to dim light, so they can see well through darkness.
|
136 videos|530 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Science: Sample Paper Solutions - 5 - Science Class 8
| 1. What are the key topics covered in Class 8 Science? |  |
| 2. How can students effectively prepare for their Class 8 Science exams? |  |
| 3. What types of questions can students expect in their Class 8 Science exams? |  |
| 4. Why is conducting experiments important in Class 8 Science? |  |
| 5. How can students improve their understanding of scientific concepts in Class 8? |  |