Class 8 Science: Sample Paper Solutions - 3 | Science Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Section – A |

|
| Section – B |

|
| Section – C |

|
| Section – D |

|
Time: 3 hrs
Total Marks: 80
General Instructions
This question paper consists of 31 questions in total and all questions are compulsory.
- Questions 1–7 are multiple-choice questions and each carries 1 mark. Write the correct answer in your answer sheet.
- Questions 8–16 are very short-answer questions and carry 2 marks each.
- Questions 17–26 are short-answer questions and carry 3 marks each.
- Questions 27–31 are long-answer questions and each carries 5 marks.
Section – A
Q1. Which of the following is a good conductor of electricity? (1 mark)
(a) Rubber
(b) Wood
(c) Copper
(d) Plastic
Ans: (c)
Copper allows electric current to pass through it easily, so it is a good conductor. Rubber, wood, and plastic are insulators.
Q2. Separation of salt from seawater is done by: (1 mark)
(a) Evaporation
(b) Sedimentation
(c) Filtration
(d) Decantation
Ans: (a)
Salt is obtained by evaporating seawater in shallow beds. The water evaporates, leaving behind solid salt.
Q3. The smallest unit of life is: (1 mark)
(a) Organ
(b) Cell
(c) Tissue
(d) Organ system
Ans: (b)
The cell is the structural and functional unit of life. Tissues and organs are made up of cells.
Q4. Which property of sound determines its loudness? (1 mark)
(a) Frequency
(b) Amplitude
(c) Speed
(d) Wavelength
Ans: (b)
Loudness of sound depends on its amplitude. Greater amplitude means louder sound. Frequency determines pitch.
Q5. Which gas is produced when zinc reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid? (1 mark)
(a) Oxygen
(b) Carbon dioxide
(c) Hydrogen
(d) Methane
Ans: (c)
Zinc + HCl → Zinc chloride + Hydrogen gas.
Q6. Which of the following is an abiotic component of the environment? (1 mark)
(a) Plants
(b) Animals
(c) Soil
(d) Fungi
Ans: (c)
Soil is a non-living (abiotic) component. Plants, animals, and fungi are biotic (living) components.
Q7. Which instrument is used to measure atmospheric pressure? (1 mark)
(a) Hygrometer
(b) Thermometer
(c) Barometer
(d) Anemometer
Ans: (c)
A barometer is used to measure atmospheric pressure. Hygrometer measures humidity, thermometer measures temperature, and anemometer measures wind speed.
Section – B
Q8. Write two properties of magnetic field lines. (2 mark)
Ans:
- They emerge from the north pole of a magnet and enter the south pole.
- They never intersect each other.
Q9. What is chlorophyll? Why is it important for plants? (2 mark)
Ans:
- Chlorophyll is a green pigment present in the leaves of plants.
- It helps plants to absorb sunlight, which is essential for photosynthesis.
Q10. Differentiate between transparent and opaque objects with examples. (2 mark)
Ans:
- Transparent objects: Allow light to pass through them completely.
Example: glass.- Opaque objects: Do not allow light to pass through them.
Example: wood.
Q11. Why do we see lightning before we hear thunder? (2 mark)
Ans:
- Light travels much faster than sound.
- Hence, we see the flash of lightning before hearing the thunder.
Q12. State two harmful effects of acid rain. (2 mark)
Ans:
- It damages buildings and monuments made of marble (like the Taj Mahal).
- It makes soil and water acidic, harming plants and aquatic life.
Q13. Give two methods of food preservation. (2 mark)
Ans:
- Refrigeration: Slows down the growth of microorganisms.
- Salting or pickling: Prevents spoilage of food by killing microbes.
Q14. Write two advantages of using CNG as fuel. (2 mark)
Ans:
- It produces less pollution compared to petrol and diesel.
- It is cheaper and more efficient than many other conventional fuels.
Q15. Why do bridges have gaps left between sections? (2 mark)
Ans:
- Gaps allow for expansion and contraction of materials due to temperature changes.
- This prevents cracks or damage to the bridge.
Q16. What is a habitat? Name two types. (2 mark)
Ans:
- A habitat is the natural home or environment of an organism where it lives and grows.
- Types: Terrestrial habitat (land) and Aquatic habitat (water).
Section – C
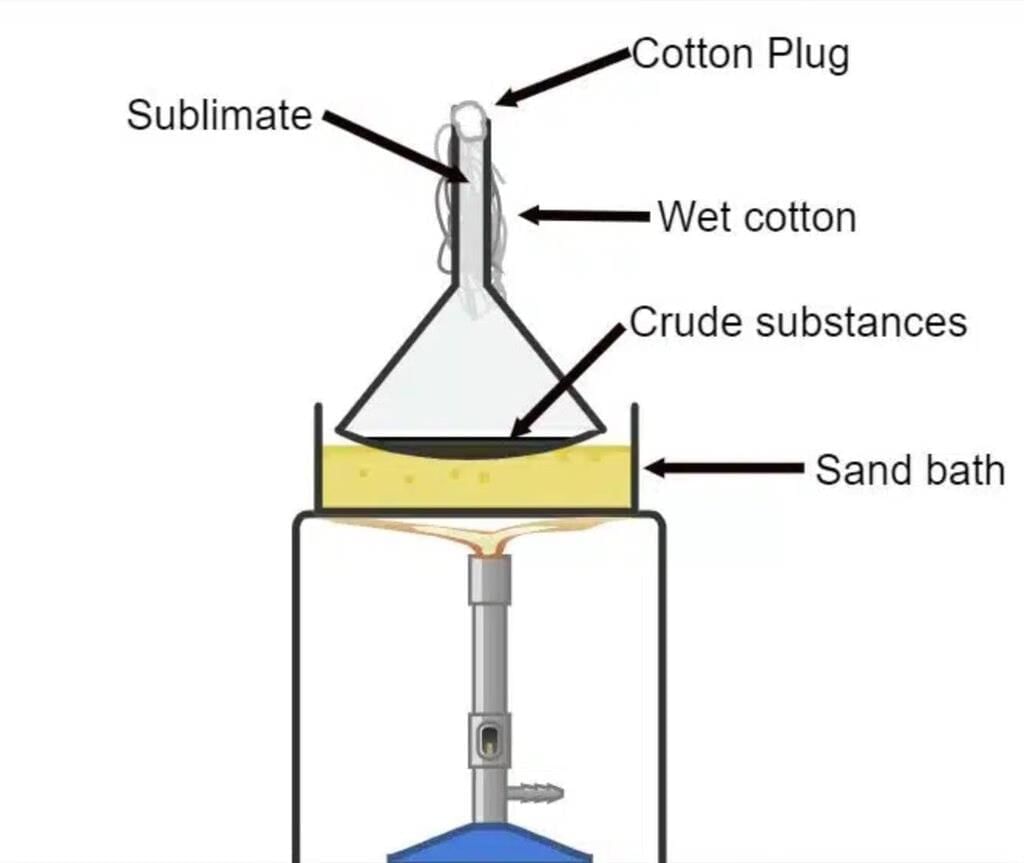
Q17. Explain sublimation with an example and a labelled diagram. (3 mark)
Ans:
- Sublimation: The process in which a solid changes directly into gas without becoming liquid.
- Example: Camphor, dry ice (solid CO2), and naphthalene balls undergo sublimation.
Q18. Why do we wear woollen clothes in winter? (3 mark)
Ans:
- Woollen clothes have fine air trapped between their fibres.
- Air is a poor conductor of heat and prevents loss of body heat.
- Thus, wool keeps us warm in winter.
Q19. Explain how vaccination protects us from diseases. (3 mark)
Ans:
- Vaccines contain dead or weakened germs of a disease.
- When injected, they stimulate the body to produce antibodies.
- These antibodies remain in the body and protect against future infections by the same germ.
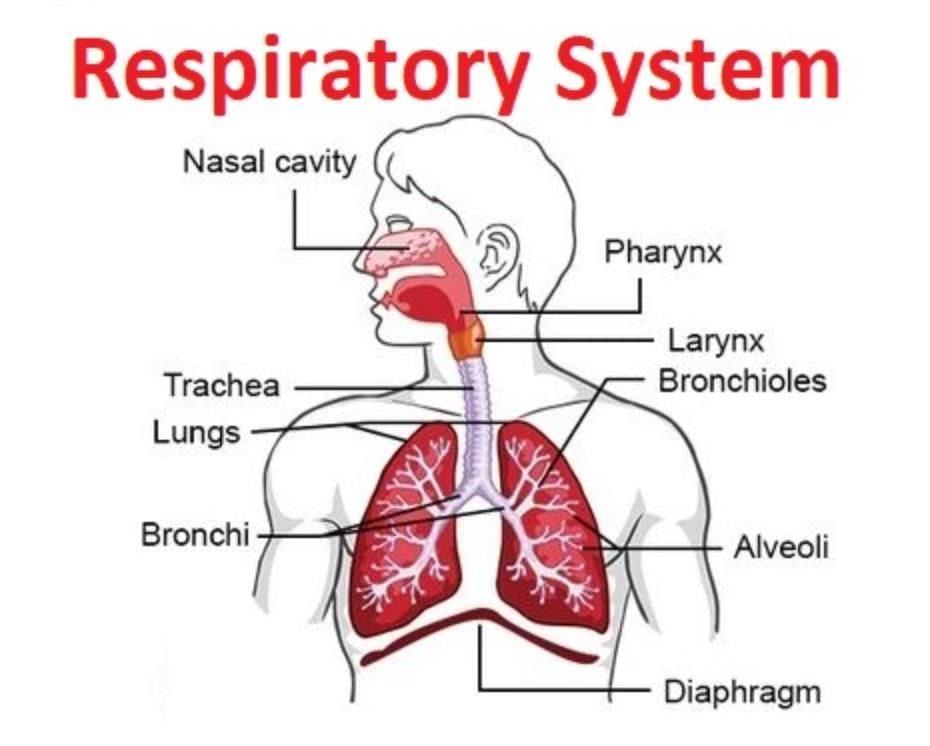
Q20. Draw a neat labelled diagram of the human respiratory system. (3 mark)
Ans:
Q21. What are asteroids and comets? State two differences. (3 mark)
Ans:
- Asteroids: Small rocky objects orbiting the Sun, mostly found between Mars and Jupiter.
- Comets: Made of ice, dust, and gas; they have a glowing tail when near the Sun.
Differences:
- Asteroids are mainly rock/metal, while comets are icy.
- Asteroids orbit mainly in the asteroid belt, while comets come from outer regions of the solar system.
Q22. What are adaptations in plants? Explain with two examples. (3 mark)
Ans: Adaptations: Special features that help plants survive in their habitats.
Examples:
- Cacti have spines instead of leaves to reduce water loss in deserts.
- Lotus has broad leaves that float and stomata on the upper surface to exchange gases in water.
Q23. Describe the construction and working of an electric bell. (3 mark)
Ans: Construction: An electric bell consists of an electromagnet, soft iron armature, hammer, gong, and a switch.
Working:
- When the switch is on, current passes through the coil, making the electromagnet attract the armature.
- The hammer hits the gong, producing sound.
- The circuit breaks, the armature returns, and the process repeats rapidly.
Q24. Why is forest conservation important? Give two methods. (3 mark)
Ans: Importance: Forests provide oxygen, maintain ecological balance, prevent soil erosion, and support biodiversity.
Methods:
- Afforestation — planting more trees.
- Preventing deforestation and promoting sustainable use of forest resources.
Q25. What is electrolysis? Give one daily-life example. (3 mark)
Ans:
- Electrolysis: The process of chemical decomposition of a substance by passing electric current through it.
- Example: Electrolysis of water splits it into hydrogen and oxygen gases.
Q26. Explain the importance of reducing, reusing, and recycling. (3 mark)
Ans:
- Reducing: Minimising the use of resources (e.g., using less plastic) reduces pollution.
- Reusing: Using items multiple times (e.g., glass bottles) saves energy and resources.
- Recycling: Processing waste materials (e.g., paper, metals) into new products conserves raw materials and reduces waste.
Section – D
Q27. (a) Define irrigation. (5 mark)
(b) Explain two traditional methods of irrigation.
(c) Mention two drawbacks of traditional methods.
Ans: (a) Irrigation is the process of supplying water to crops at regular intervals for their proper growth.
(b) Two traditional methods of irrigation:
- Moat (well system): Water is drawn from a well and used for irrigation.
- Chain pump: Uses a chain of buckets to lift water from a source and pour it onto fields.
(c) Drawbacks of traditional methods:
- They require a lot of human and animal labour.
- They lead to uneven distribution and wastage of water.
Q28. (a) What are contact and non-contact forces? (5 mark)
(b) Explain magnetic force with an experiment.
(c) Mention one advantage and one disadvantage of friction.
Ans: (a) Contact forces are those that require physical contact (e.g., friction, muscular force).
Non-contact forces act from a distance without contact (e.g., magnetic force, gravitational force).
(b) Magnetic force experiment:
Place a magnet near iron filings. The filings are attracted and arrange along magnetic field lines, showing that a magnet exerts force without contact.
(c) Advantage of friction: Helps us walk without slipping.
Disadvantage of friction: Causes wear and tear of machine parts.
Q29. (a) What is acid rain? (5 mark)
(b) State three causes of acid rain.
(c) Mention two preventive measures.
Ans: (a) Acid rain is rainwater that becomes acidic due to the dissolution of acidic gases like SO₂ and NO₂ from the atmosphere.
(b) Causes of acid rain:
- Burning of fossil fuels (coal, petroleum).
- Emission of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides from industries.
- Vehicle exhaust releasing harmful gases.
(c) Preventive measures:
- Use of cleaner fuels like CNG, LPG.
- Installation of scrubbers in factories to reduce gas emissions.
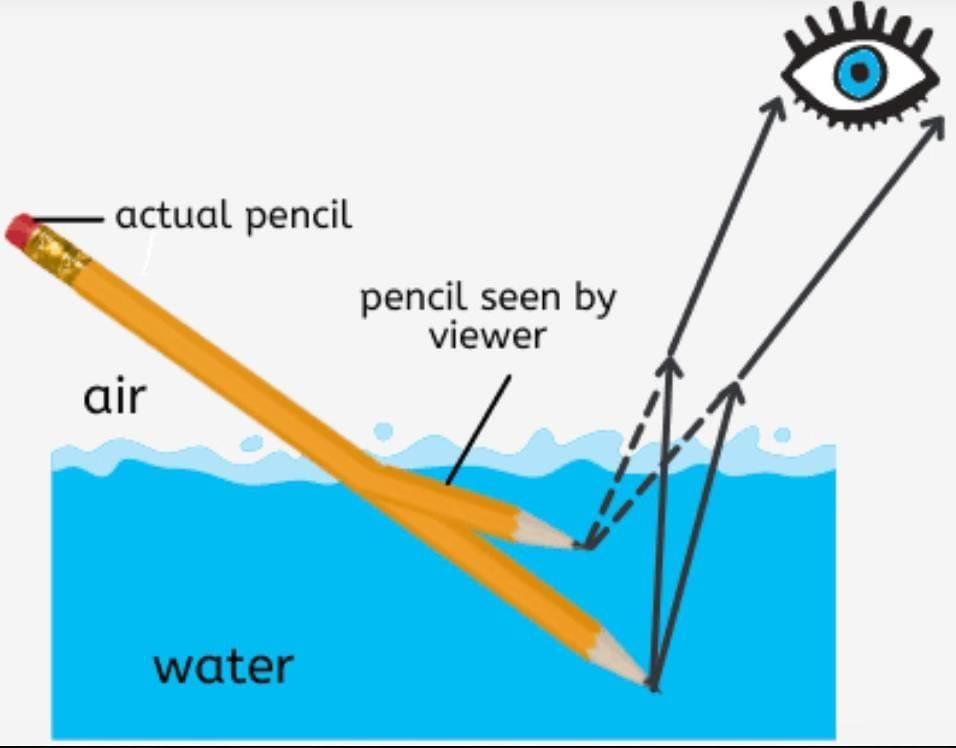
Q30. (a) Define refraction of light. (5 mark)
(b) State laws of refraction.
(c) Explain one daily-life example of refraction.
Ans: (a) Refraction of light is the bending of light rays when they pass from one medium to another due to a change in speed.
(b) Laws of refraction:
- The incident ray, the refracted ray, and the normal at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
- The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant (Snell’s law).
(c) Example: A pencil partly immersed in water appears bent or broken at the surface due to refraction of light.
Q31. (a) What are microorganisms? (5 mark)
(b) Write three useful and two harmful effects of microorganisms.
(c) Mention one method to prevent microbial spoilage of food.
Ans: (a) Microorganisms are tiny living organisms that cannot be seen with the naked eye, such as bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and viruses.
(b) Useful effects:
- Bacteria like Rhizobium fix nitrogen in soil.
- Yeast is used in baking and fermentation.
- Some microorganisms produce antibiotics (e.g., Penicillium).
Harmful effects:
- Cause diseases in humans, animals, and plants (e.g., malaria, cholera).
- Spoil food, making it unfit for consumption.
(c) Prevention of food spoilage: Food can be preserved by refrigeration or pickling to prevent microbial growth.
|
92 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Science: Sample Paper Solutions - 3 - Science Class 8
| 1. What is the structure of the Class 8 Science sample paper? |  |
| 2. How can students prepare effectively for the Class 8 Science exam? |  |
| 3. What types of questions are typically included in Section B of the Class 8 Science paper? |  |
| 4. How important is practical knowledge in the Class 8 Science curriculum? |  |
| 5. What strategies can be used to tackle long-answer questions in Section C? |  |