Case Based Questions: Landforms and Life | Social Studies for Class 6 PDF Download
Q1: Read the source and answer the question that follows
Aryan and Meera are hiking in the mountains near their village. Aryan wonders why mountains are so much taller than the surrounding land. Meera explains that mountains are formed by natural forces over millions of years and are much higher than other landforms. She points to the Himalayas and tells Aryan that some mountains still grow taller because natural processes like tectonic movements continue to shape them.
Q1. Why are mountains higher than the surrounding land?
Ans: Mountains are higher because they are formed by natural forces, like tectonic movements, which make them rise over millions of years.
Q2. Why are some mountains still getting taller today?
Ans: Some mountains, like the Himalayas, are still growing taller because the Earth's plates are still moving, pushing them up.
Q3. Which mountain range is still growing taller because of natural movements?
A) The Andes
B) The Himalayas
C) The Alps
D) The Rocky Mountains
Ans: B) The Himalayas
Q2: Read the source and answer the question that follows
Ria and Meera are on a field trip, visiting the Deccan Plateau. Meera explains that plateaus are landforms with a flat top and steep sides, which makes them stand out from the surrounding land. She also points out the rich mineral deposits found on plateaus, making them important for mining. Ria is curious and asks if plateaus are similar to mountains. Meera explains that while both are elevated landforms, plateaus have flat tops, unlike mountains that have sharp peaks. Aryan, who is always interested in the environment, asks about the types of plants and animals that live in plateau regions. Meera adds that plateaus often have unique vegetation, and animals like yaks and mountain goats are commonly found in these regions.

Q1. What is the main difference between a plateau and a mountain?
Ans: Plateaus have flat tops with steep sides, while mountains have pointed peaks.
Q2. Why are plateaus important for mining?
Ans: Plateaus are rich in mineral deposits, making them ideal locations for mining activities.
Q3. What kind of vegetation is typically found on plateaus?
A) Tropical plants
B) Unique vegetation adapted to the environment
C) Forests with tall trees
D) Swampy plants
Ans: B) Unique vegetation adapted to the environment
Q3: Read the source and answer the question that follows
Aryan and Simran are discussing water bodies in their class. They are fascinated to learn that while the Earth is covered mostly by water, only a small portion of it is freshwater, which is essential for drinking, farming, and daily activities. Ria, curious about this, asks why seawater is not suitable for drinking. Aryan explains that seawater is salty, and the high salt content makes it unsafe for humans and animals to drink because it can cause dehydration. Simran adds that freshwater, which is found in rivers, lakes, and glaciers, has very little salt and is therefore safe for consumption. She further explains that even though seawater covers most of the Earth's surface, the limited availability of freshwater makes it a precious resource.
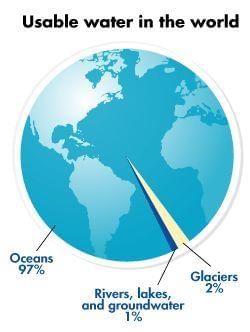
Q1. Why is seawater not safe for drinking?
Ans: Seawater is salty, and the high salt content can cause dehydration, making it unsafe for humans and animals to drink.
Q2. Why is freshwater considered a valuable resource?
Ans: Freshwater is essential for drinking, farming, and daily activities. Since it makes up only a small portion of the Earth's water, it is a precious and a valuable resource.
Q3. Explain the difference between seawater and freshwater and their respective uses.
Ans: Seawater is salty and cannot be consumed due to its high salt content, while freshwater, found in rivers, lakes, and glaciers, has very little salt and is safe for drinking and daily use. Freshwater is vital for agriculture, drinking, and other essential activities.
Q4. Where is freshwater primarily found?
A) Oceans
B) Rivers, lakes, and glaciers
C) Deserts
D) Seas
Ans: B) Rivers, lakes, and glaciers
|
45 videos|310 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Case Based Questions: Landforms and Life - Social Studies for Class 6
| 1. What are the different types of landforms found on Earth? |  |
| 2. How do landforms affect human life and activities? |  |
| 3. What processes lead to the formation of different landforms? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of famous landforms around the world? |  |
| 5. How do landforms impact biodiversity? |  |
















