Important Diagrams: Health: The Ultimate Treasure | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Q1: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
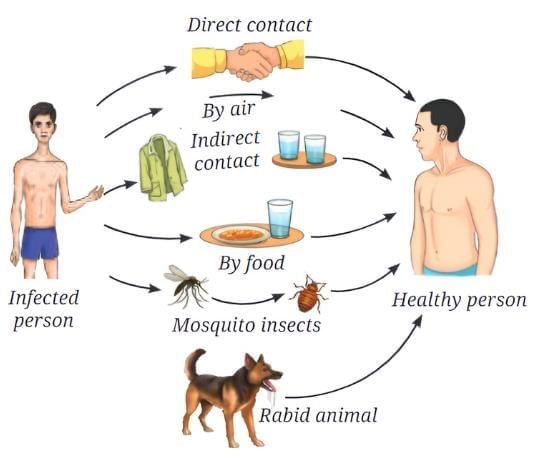
Common methods of transmission of diseases:
(i) What are the different methods shown in the diagram for the transmission of communicable diseases?
Ans: The diagram shows communicable diseases being transmitted through air (e.g., coughing or sneezing), direct contact (e.g., shaking hands), indirect contact (e.g., sharing personal items), contaminated food or water, vectors (e.g., mosquitoes), and animal bites (e.g., rabid animals).
(ii) Define communicable diseases.
Ans: Communicable diseases are illnesses caused by pathogens, such as bacteria or viruses, that spread from an infected person to a healthy person through methods like air, direct or indirect contact, contaminated food or water, or vectors.
(iii) What is the role of vectors in disease transmission?
Ans: Vectors, such as mosquitoes, transfer pathogens from an infected person to a healthy person through bites. Diseases like malaria and dengue spread this way, where the mosquito acts as a carrier.
(iv) Which of the following is an example of a disease transmitted through the air?
(a) Malaria
(b) Common cold
(c) Cholera
(d) Typhoid
Ans: (b)
The diseases like the common cold are transmitted through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes, spreading pathogens to a healthy person.
(v) What is the significance of understanding the methods of disease transmission?
Ans: Understanding these methods helps identify how pathogens spread, enabling preventive measures like handwashing, covering the mouth while sneezing, using mosquito nets, and ensuring clean food and water to reduce the risk of communicable diseases.
Q2: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
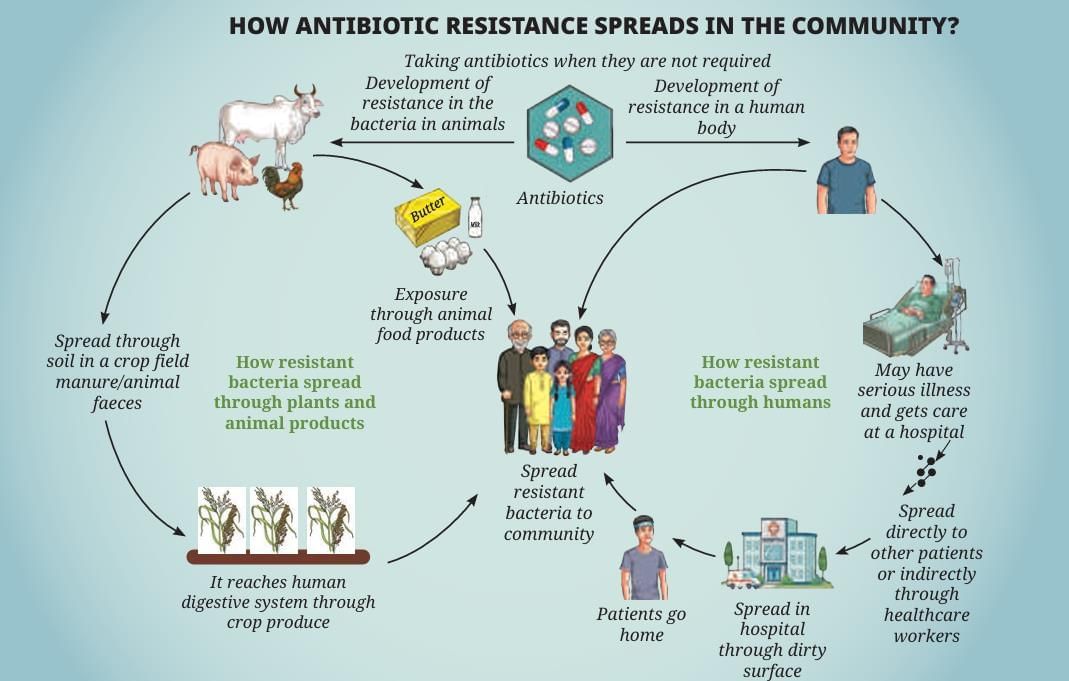
(i) What are the main pathways shown in the diagram for the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria?
Ans: The diagram shows antibiotic-resistant bacteria spreading through hospitals (via dirty surfaces or healthcare workers), human communities (from patients going home), animal food products (via resistant bacteria in animals), and soil or crops (via manure or animal feces).
(ii) Define antibiotic resistance.
Ans: Antibiotic resistance is when bacteria survive and multiply despite treatment with antibiotics, spreading through communities, hospitals, or food chains, as illustrated in the diagram, making infections harder to treat.
(iii) What is the role of unnecessary antibiotic use in resistance?
Ans: The diagram shows that taking antibiotics when not needed contributes to the development of resistant bacteria in humans and animals, which then spread to the community or through food products.
(iv) Which of the following is a consequence of antibiotic resistance?
(a) Easier treatment of infections
(b) Increased risk of complications
(c) Reduced need for vaccines
(d) Improved hygiene practices
Ans: (b)
Antibiotic resistance leads to harder-to-treat infections, increasing the risk of complications, prolonged illness, and even death.
(v) What is the significance of controlling antibiotic use, as highlighted by the diagram?
Ans: Controlling antibiotic use, as shown in the diagram, prevents the development and spread of resistant bacteria, ensuring antibiotics remain effective for treating infections and reducing health risks in communities.
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Important Diagrams: Health: The Ultimate Treasure - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the essential components of a healthy lifestyle according to the article? |  |
| 2. How does physical activity contribute to health as mentioned in the article? |  |
| 3. Why is nutrition considered the foundation of health in the article? |  |
| 4. What role does mental health play in overall well-being according to the article? |  |
| 5. How can individuals effectively manage stress based on the insights from the article? |  |
















