Practice Question - 32 (Quant Based DI) | 100 DILR Questions for CAT Preparation PDF Download
The following table represents addition of two six-digit numbers given in the first and the second rows, while the sum is given in the third row. In the representation, each of the digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 has been coded with one letter among A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, J, K, with distinct letters representing distinct digits.
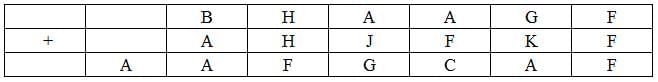
Q1: Which digit does the letter A represent?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 1
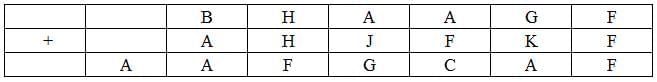
The value of F can only be 0 as F+F=F can only hold if F=0.
Also, A can only be 1(in the second column) because to get a carry of more than 1, B has to be a double-digit number which is not possible. (A carry is a digit that is transferred from one column of digits to another column of more significant digits.)
So the data can be tabulated as follows:
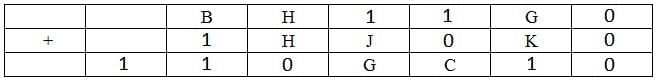
Since the last row in the third column is 0, the carry to the second column must have been 1, Hence B+1+1=11 => B=9
In the 4th column, H+H = 10 since a carry 1 has gone to the 3rd column. Hence H=5.
G+K must be 11 and the carry 1 goes to the next column, so C=1+1=2.
Now, G,K can take values (3,8), (4,7) and (5,6) in any order.
From 5th column G=J+1 => J=G-1
Case: G=3 and K=8, here J =2 which is not possible as C =2
Case: G=8 and K=3, J=7, a possible case.
Case: G=4 and K=7, J=3 possible
Case: G=7 and K=4, J=6 possible
Case: G=5 and K=6, J=4 not possible as H =5.
Case: G=6 and K=5, J=5 both J and K are same, not possible.
Hence the cases can be tabulated as follows:
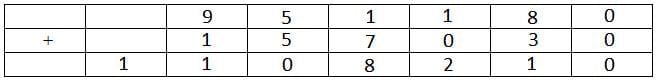
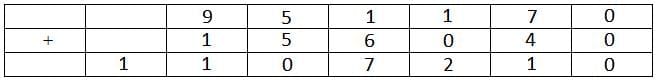
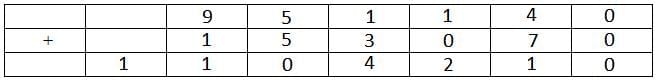
The letter A represents 1.
 View Answer
View Answer 
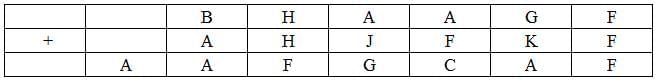
The value of F can only be 0 as F+F=F can only hold if F=0.
Also, A can only be 1(in the second column) because to get a carry of more than 1, B has to be a double-digit number which is not possible. (A carry is a digit that is transferred from one column of digits to another column of more significant digits.)
So the data can be tabulated as follows:
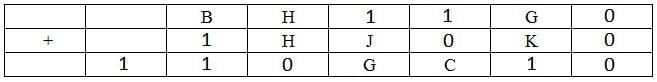
Since the last row in the third column is 0, the carry to the second column must have been 1, Hence B+1+1=11 => B=9
In the 4th column, H+H = 10 since a carry 1 has gone to the 3rd column. Hence H=5.
G+K must be 11 and the carry 1 goes to the next column, so C=1+1=2.
Now, G,K can take values (3,8), (4,7) and (5,6) in any order.
From 5th column G=J+1 => J=G-1
Case: G=3 and K=8, here J =2 which is not possible as C =2
Case: G=8 and K=3, J=7, a possible case.
Case: G=4 and K=7, J=3 possible
Case: G=7 and K=4, J=6 possible
Case: G=5 and K=6, J=4 not possible as H =5.
Case: G=6 and K=5, J=5 both J and K are same, not possible.
Hence the cases can be tabulated as follows:
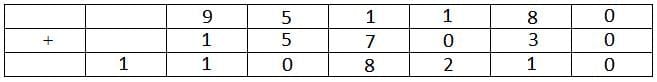
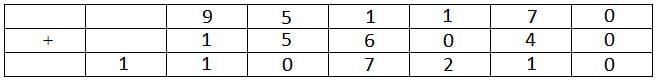
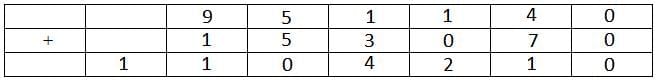
The letter B represents 9.
 View Answer
View Answer 
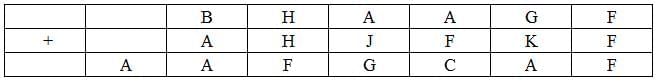
The value of F can only be 0 as F+F=F can only hold if F=0.
Also, A can only be 1(in the second column) because to get a carry of more than 1, B has to be a double-digit number which is not possible. (A carry is a digit that is transferred from one column of digits to another column of more significant digits.)
So the data can be tabulated as follows:
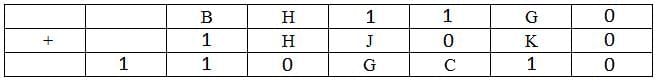
Since the last row in the third column is 0, the carry to the second column must have been 1, Hence B+1+1=11 => B=9
In the 4th column, H+H = 10 since a carry 1 has gone to the 3rd column. Hence H=5.
G+K must be 11 and the carry 1 goes to the next column, so C=1+1=2.
Now, G,K can take values (3,8), (4,7) and (5,6) in any order.
From 5th column G=J+1 => J=G-1
Case: G=3 and K=8, here J =2 which is not possible as C =2
Case: G=8 and K=3, J=7, a possible case.
Case: G=4 and K=7, J=3 possible
Case: G=7 and K=4, J=6 possible
Case: G=5 and K=6, J=4 not possible as H =5.
Case: G=6 and K=5, J=5 both J and K are same, not possible.
Hence the cases can be tabulated as follows:
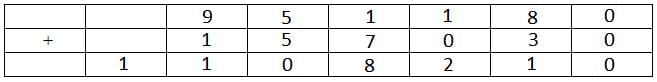
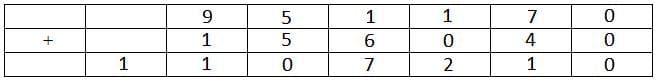
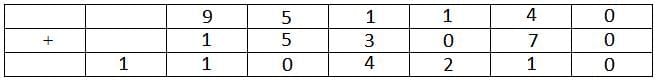
In all possible cases 7 is already represented by a letter other than D. Hence 7 is the answer.
 View Answer
View Answer 
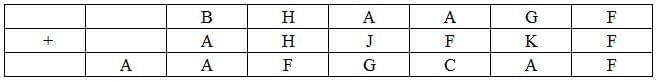
The value of F can only be 0 as F+F=F can only hold if F=0.
Also, A can only be 1(in the second column) because to get a carry of more than 1, B has to be a double-digit number which is not possible. (A carry is a digit that is transferred from one column of digits to another column of more significant digits.)
So the data can be tabulated as follows:
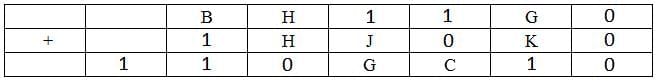
Since the last row in the third column is 0, the carry to the second column must have been 1, Hence B+1+1=11 => B=9
In the 4th column, H+H = 10 since a carry 1 has gone to the 3rd column. Hence H=5.
G+K must be 11 and the carry 1 goes to the next column, so C=1+1=2.
Now, G,K can take values (3,8), (4,7) and (5,6) in any order.
From 5th column G=J+1 => J=G-1
Case: G=3 and K=8, here J =2 which is not possible as C =2
Case: G=8 and K=3, J=7, a possible case.
Case: G=4 and K=7, J=3 possible
Case: G=7 and K=4, J=6 possible
Case: G=5 and K=6, J=4 not possible as H =5.
Case: G=6 and K=5, J=5 both J and K are same, not possible.
Hence the cases can be tabulated as follows:
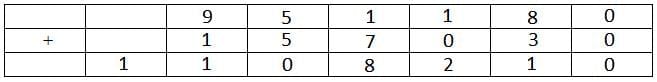
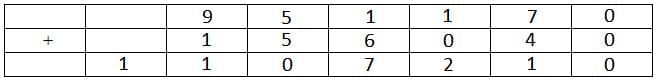
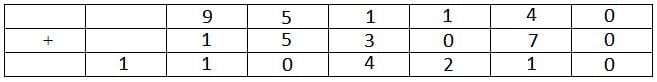
From the table it is clear that 6 cannot be represented by G.
|
102 videos|123 docs|121 tests
|
FAQs on Practice Question - 32 (Quant Based DI) - 100 DILR Questions for CAT Preparation
| 1. What is the format of the Quant Based Data Interpretation (DI) section in the exam? |  |
| 2. How can I effectively prepare for the Quant Based DI section? |  |
| 3. What types of questions are commonly found in the Quant Based DI section? |  |
| 4. Are there specific strategies for solving DI questions quickly? |  |
| 5. How important is accuracy in the Quant Based DI section? |  |















