NCERT Based Activity: The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Activity 9.1: Let us investigate
- Take a clean glass tumbler and fill it half with water.
- Add one spoon of salt into it and stir well till it dissolves completely.
- Gradually add a spoonful of salt into the glass tumbler and stir. Observe how many spoons of salt you can add before it stops dissolving completely.
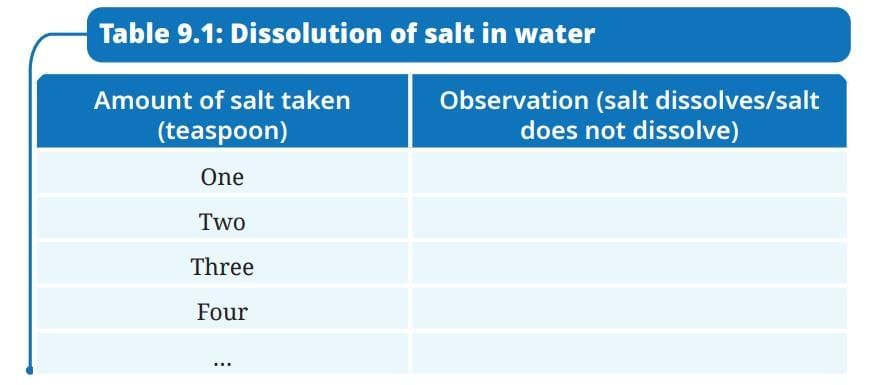
- Record your observations in Table 9.1.
Ans:
Some discussion points and answers:
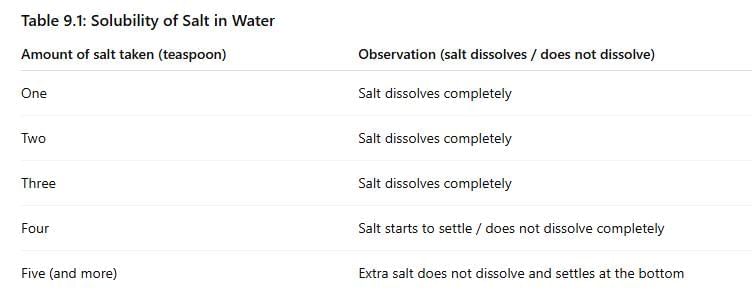
How many spoons of salt were you able to dissolve before some of it remained undissolved?
Answer: The number of spoons varies, typically 2-4 spoons, depending on the water volume and temperature, before undissolved salt remains.What does this indicate about the capacity of water to dissolve salt?
Answer: This indicates that water has a limited capacity to dissolve salt, reaching a saturation point where no more salt can dissolve.What will happen if we keep on adding more salt in a given amount of water?
Answer: If more salt is added beyond the saturation point, it will not dissolve and will settle at the bottom of the tumbler.
Activity 9.2: Let us experiment (Demonstration activity)
- Take about 50 mL of water in a glass beaker and measure its temperature using a laboratory thermometer, say 20 °C.
- Add a spoonful of baking soda (sodium hydrogen carbonate) to the water and stir until it dissolves. Continue adding small amounts of baking soda while stirring, till some solid baking soda is left undissolved at the bottom of the beaker.
- Now, heat the contents to 50 °C while stirring. (Fig. 9.7).
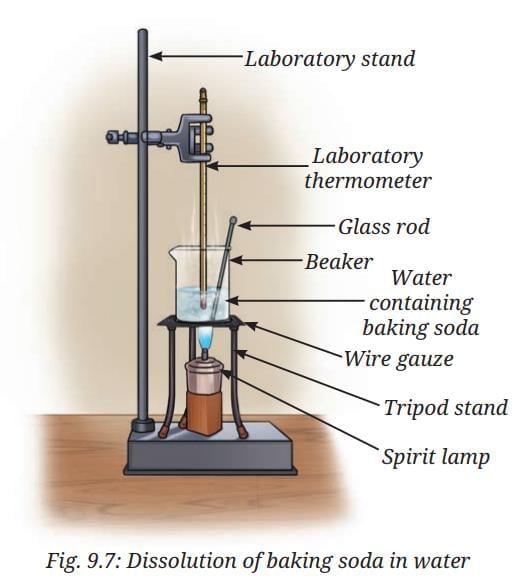
- What happens to the undissolved baking soda?
- Continue adding more baking soda while stirring at this temperature until some solid baking soda remains undissolved.
- Again, heat the contents further to 70 °C while continuing to stir. What do you observe?
- What do you infer from this experiment?
Answer:
What happens to the undissolved baking soda?
Answer: The undissolved baking soda dissolves when heated to 50 °C.What do you observe?
Answer: At 70 °C, the previously undissolved baking soda also dissolves, and more can be added until it again becomes saturated.What do you infer from this experiment?
Answer: Water at 70 °C dissolves more baking soda than at 50 °C or 20 °C, indicating that solubility of solids like baking soda generally increases with an increase in temperature.
Activity 9.3: Let us measure
- Switch ON the digital weighing balance.
- Observe the initial reading on the digital weighing balance display.
- It should show a zero reading. If not, then we must bring it to zero by pressing the tare or reset button (Fig. 9.12a).
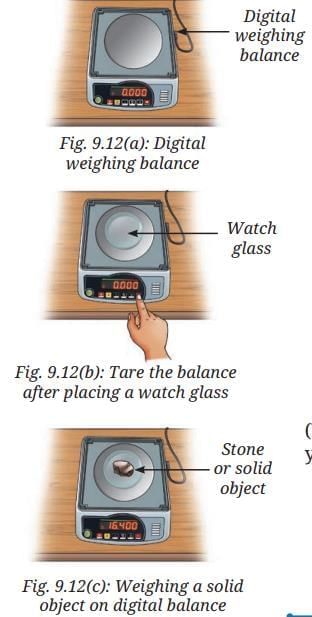
- Place a dry and clean watch glass or butter paper on the pan.
- Note the reading on the digital weighing balance.
- Reset the digital weighing balance reading to zero by pressing the tare or reset button as shown in Fig. 9.12b.
- Now, carefully place the solid object, such as stone, on the watch glass (Fig. 9.12c).
- Note the reading displayed on the balance, which gives the mass of the stone, say 16.400 g.
Answer: The mass of the stone is measured as 16.400 g using the digital weighing balance after taring with the watch glass.
Activity 9.4: Let us observe and calculate
Take a measuring cylinder and observe it carefully. Note down the following:
- What is the maximum volume it can measure?
- What is the smallest volume it can measure? Look at the measuring cylinder again.
- How much is the volume difference indicated between the two bigger marks (for example, between 10 mL and 20 mL)?
- How many smaller divisions are there between the two bigger marks?
- How much volume does one small division indicate?

Answer:
What is the maximum volume it can measure?
Answer: For the 100 mL measuring cylinder, it can measure up to 100 mL.What is the smallest volume it can measure?
Answer: The smallest volume is 1 mL, as calculated from the divisions.How much is the volume difference indicated between the two bigger marks?
Answer: 10 mL (e.g., between 10 mL and 20 mL).How many smaller divisions are there between the two bigger marks?
Answer: 10 divisions.How much volume does one small division indicate?
Answer: 1 mL (10 mL ÷ 10 divisions).
Activity 9.5: Let us measure 50 mL of water
- Place a clean, dry measuring cylinder on a flat surface.
- Pour water slowly into the measuring cylinder up to the required mark, as shown in Fig. 9.17.
- If required, adjust the level of water in the measuring cylinder by adding or removing a small amount of water using a dropper.
- On careful observation, you will notice that the water inside the measuring cylinder forms a curved surface called the meniscus. (Fig. 9.18).
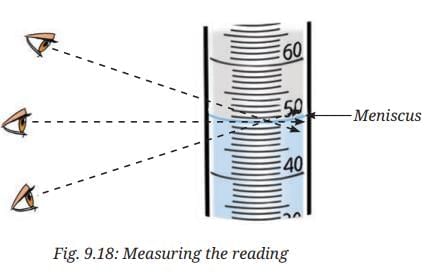
- Read the mark on the measuring cylinder that coincides with the bottom of the meniscus for water or other colourless liquids.
- Make sure that the eyes are at level with the bottom of the meniscus while noting the readings as shown in Fig. 9.18.
- Once it reaches the required level—that is, 50 mL—transfer this water to the required container.
Q: Why are measuring cylinders always designed narrow and tall instead of wider and short like a beaker?
Ans: Measuring cylinders are made narrow and tall so that the liquid level rises higher and the markings are farther apart. This makes it easier to read the exact volume accurately. If the cylinder were wide and short like a beaker, the markings would be too close together, and the reading would be less precise.
Activity 9.6: Let us calculate
- Collect various objects with a cuboid shape, such as a notebook, a shoe box, or a dice.
- Measure the length (l), width (w), and height (h) of the objects using a scale. Suppose the length of the notebook is 25 cm, the width is 18 cm, and the height is 2 cm.
- Calculate the volume by using the following formula: Volume = l × w × h.
Answer: Volume = 25 cm × 18 cm × 2 cm = 900 cm³. - Record in your notebook
Activity 9.7: Let us measure
- Collect various objects from your surroundings, such as a stone, metal keys, and so on.
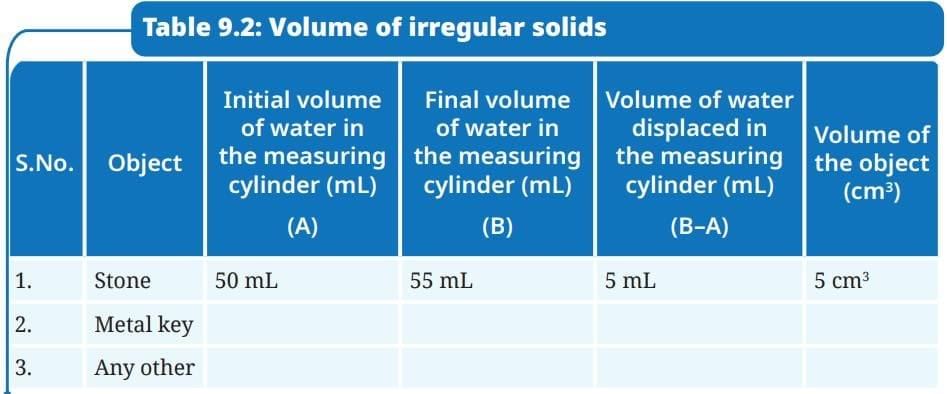
- Fill a measuring cylinder with water up to any desired volume, say 50 mL,(Fig. 9.19a) and record the initial volume taken in Table 9.2.
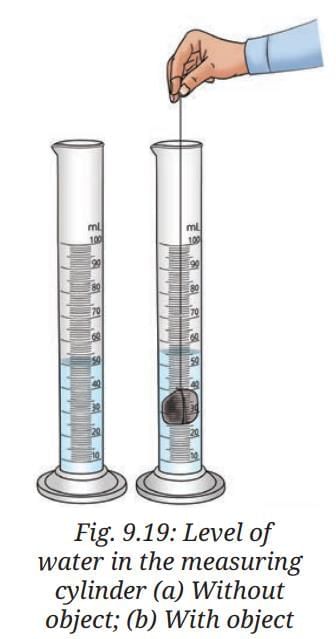
- Tie the object, say a stone, with a thread and slowly lower it into the measuring cylinder.
- What do you notice?
- Record the final volume after the level rises, say 55 mL, as shown in Fig. 9.19b.
- Subtract the initial volume from the final volume after the object is put into the measuring cylinder. This is the volume of the object.
- Record your observations in Table 9.2.
Ans: 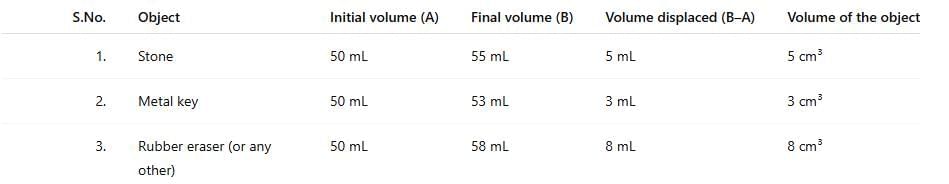
What do you notice?
Answer: The water level rises from 50 mL to 55 mL when the stone is submerged.Volume of the object:
Answer: 5 cm³ (55 mL - 50 mL).
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Based Activity: The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are solutes, solvents, and solutions? |  |
| 2. How can we measure the volume of water accurately in experiments? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of calculating concentration in solutions? |  |
| 4. How can we observe the properties of solutions? |  |
| 5. What experiments can demonstrate the concept of solubility? |  |















