Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Science Class 8 > NCERT Based Activity: Electricity: Magnetic and Heating Effects
NCERT Based Activity: Electricity: Magnetic and Heating Effects | Science Class 8 PDF Download
Activity 4.1: Let us investigate
- Collect a magnetic compass, an electric cell, a cell holder, two drawing pins, a safety pin, two nails, two pieces of connecting wires (one longer and one shorter), and two small pieces of cardboard.
- Using two drawing pins, a safety pin, and a cardboard piece, make a switch (as you made it earlier in the chapter ‘Electricity: Circuits and their Components’ in Curiosity, Grade 7).
- Place the cell in the cell holder.
- Fix two nails to a piece of cardboard as shown in Fig. 4.1a. Fix the middle portion of the longer wire stretched between the nails, such that it is slightly above the surface of the cardboard. Attach one end of that wire to the cell holder and another end to the switch.
- Connect the second wire between the cell holder and the switch.
- Place the magnetic compass beneath the wire between the two nails (Fig. 4.1a).
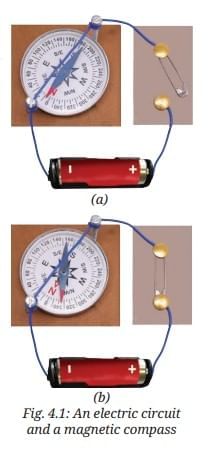
1. While watching the compass needle, move the switch to ‘ON’ position to allow electric current to flow through the wire (Fig. 4.1b). What do you observe?
Ans: The compass needle gets deflected from its original direction.
2. Now again while watching the compass needle, move the switch to ‘OFF’ position. What do you observe this time?
Ans: The compass needle returns to its original direction.
3. Move the switch between ‘ON’ and ‘OFF’ positions a few more times. Carefully observe how the compass needle behaves each time.
Ans: The compass needle deflects when the switch is in the ‘ON’ position and returns to its original direction when the switch is in the ‘OFF’ position.
Activity 4.2: Let us explore
- Take around 50 cm long length of a flexible insulated wire, an iron nail, an electric cell, and few iron paper clips.
- Tightly wrap the wire around the nail in the form of a coil, as shown in Fig. 4.2, and secure it with an adhesive tape.

- Connect the ends of the wire to the cell. Take care to not connect the wires to the cell for more than a few seconds; otherwise, the cell may weaken quickly.
- Bring the nail close to the iron paper clips and lift up. Do the clips hang to the ends of the nail?
Ans: Yes, the clips hang to the ends of the nail when the current flows. - Disconnect the wire from the cell to stop the flow of electric current in the wire. Do the clips fall down?
Ans: Yes, the clips fall down when the current is stopped.
Activity 4.3: Let us experiment
- Take around 100 cm long flexible insulated wire, a piece of chart paper, an iron nail, an electric cell, two magnetic compasses, and few iron/steel paper clips.
- Roll a piece of chart paper to make a cylinder of diameter roughly equal to the width of a pencil. Secure it with an adhesive tape.
- Tightly wind around 50 turns of the insulated wire on the cylinder to form a cylindrical coil as shown in Fig. 4.3a. Secure the wire with an adhesive tape.

- Place the compasses near the two ends of the cylindrical coil (Fig. 4.3b).
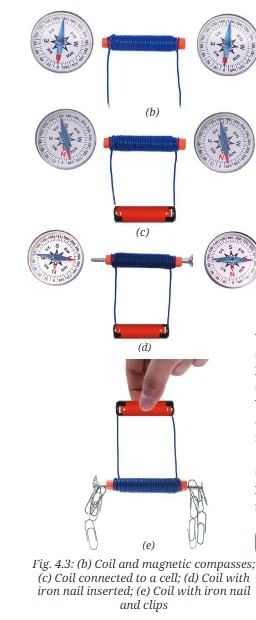
- Connect the two ends of the coil with the terminals of the cell as shown in Fig. 4.3c and observe the magnetic compasses. Do you find any deflection in the needles of the compasses?
Ans: Yes, there is a deflection in the needles of the compasses. - Disconnect the wire from the cell. Do the needles of the compasses come back to their original positions?
Ans: Yes, the needles of the compasses return to their original positions. - Insert an iron nail in the paper cylinder (Fig. 4.3d) and repeat the steps. Is there any difference in the deflection of the compass needles?
Ans: Yes, the deflection of the compass needles is much more with the iron nail inserted. - Place some iron paper clips near the two ends of the nail. Are the clips attracted to the ends of the nail?
Ans: Yes, the clips are attracted to the ends of the nail.
Activity 4.4: Let us investigate
- Take the electromagnet made in Activity 4.3 and a magnetic compass. Label the two ends of the coil as A and B.
- Place the magnetic compass near the end A of the coil as shown in Fig. 4.4a.
- Connect the coil to the cell and observe the compass. Note down which pole of the magnetic compass is attracted to end A.
Ans: The north pole of the magnetic compass is attracted to end A (or south pole, depending on the direction of current flow).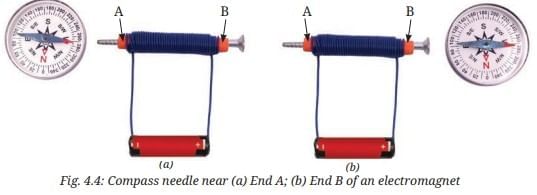
Activity 4.5: Let us observe
- In this activity, we will use a special kind of wire, called a nichrome wire.
- Take a cardboard piece of about 10 cm length and 10 cm width, two nails, a nichrome wire of thickness about 0.3 mm (26–28 gauge) and length of 10 cm, an electric cell, a cell holder, a switch, and connecting wires.
- Mount the nails on the cardboard about 5 cm apart.
- Tie the nichrome wire between these nails and make the connections as shown in Fig. 4.5 with the switch in OFF position. z Touch the nichrome wire. What do you feel?
Ans: The nichrome wire feels normal/cool to touch at room temperature.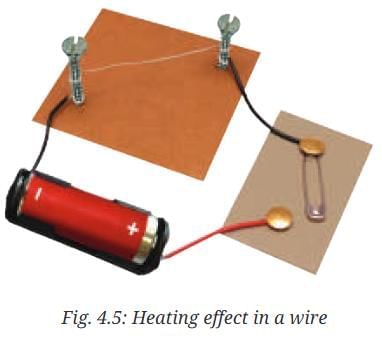
- Move the switch to ON position for about 30 s and then move it back to OFF. Touch the nichrome wire momentarily. (Do not hold the nichrome wire). What difference do you feel?
Ans: The nichrome wire becomes hot after current passes through it. - Repeat the last two steps to confirm the observation.
Ans: Every time the current flows, the nichrome wire gets heated. This confirms that electric current produces a heating effect.
Activity 4.6: Let us construct
- Take five or six juicy lemons, copper wires/ strips (1–2 mm thick) and iron nails. Also take one LED and some connecting wires.
- Insert the copper wire and the iron nail in one of the lemons keeping them apart by a small distance as shown in Fig. 4.8a.
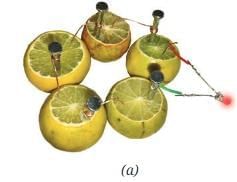
- Repeat the above step for all the remaining lemons.
- Join the copper wires and nails as shown in Fig. 4.8b.
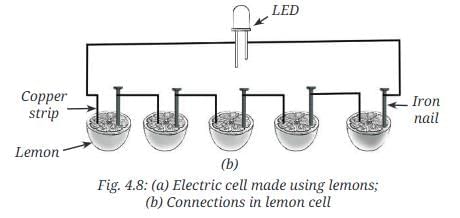
- Connect the LED between the copper wire of the first lemon and the iron nail of the last lemon, using connecting wires.
- What do you observe? Does the LED glow?
Ans: Yes, the LED glows because the lemon juice acts as an electrolyte and produces electricity when connected in series. - If the LED does not glow, reverse its connections. Does the LED glow now?
Ans: Yes, after reversing the connections, the LED glows. This is because an LED glows only when it is connected in the correct direction (polarity).
The document NCERT Based Activity: Electricity: Magnetic and Heating Effects | Science Class 8 is a part of the Class 8 Course Science Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
136 videos|530 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Based Activity: Electricity: Magnetic and Heating Effects - Science Class 8
| 1. What are the magnetic effects of electric current? |  |
Ans. The magnetic effects of electric current refer to the phenomenon where an electric current passing through a conductor generates a magnetic field around it. This effect is demonstrated by the right-hand rule, where if you curl the fingers of your right hand in the direction of the current, your thumb points in the direction of the magnetic field lines. The strength of the magnetic field increases with the amount of current and can be enhanced by coiling the wire into a solenoid.
| 2. How does electricity produce heating effects? |  |
Ans. The heating effect of electricity occurs when an electric current passes through a conductor, causing it to heat up due to the resistance the conductor offers to the flow of current. This phenomenon is known as Joule heating, and it is utilized in various applications such as electric heaters, toasters, and incandescent light bulbs. The amount of heat produced is proportional to the square of the current (I²) and the resistance (R) of the conductor, as described by the formula P = I²R, where P is the power (heat) generated.
| 3. What is the role of fuses in electrical circuits? |  |
Ans. Fuses are safety devices used in electrical circuits to prevent overcurrent, which can lead to overheating and potential fires. A fuse contains a thin wire that melts and breaks the circuit when the current exceeds a certain level, thereby stopping the flow of electricity. This interruption protects electrical appliances and wiring from damage caused by excessive current.
| 4. What are the differences between series and parallel circuits? |  |
Ans. In a series circuit, components are connected end-to-end, forming a single path for current to flow. If one component fails, the entire circuit is interrupted. In contrast, a parallel circuit has multiple paths for current to flow, so if one component fails, the others can still operate. Additionally, in a series circuit, the total resistance increases, while in a parallel circuit, the total resistance decreases as more components are added.
| 5. How can we demonstrate the magnetic field around a conductor? |  |
Ans. To demonstrate the magnetic field around a conductor, you can perform a simple experiment using a copper wire, a battery, and iron filings. Connect the copper wire to the battery, ensuring that current flows through the wire. Place a piece of cardboard or paper over the wire and sprinkle iron filings on top. Gently tap the cardboard to allow the filings to align with the magnetic field lines, which will form a pattern around the wire, visually demonstrating the magnetic field generated by the electric current.
Related Searches
















