Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Year 8 Physics (Cambridge) > Mnemonics: Exploring Forces
Mnemonics: Exploring Forces | Year 8 Physics (Cambridge) - Class 8 PDF Download
1. Effects of Force on an Object
Mnemonic: "Force Makes Things Move, Change Speed, Change Shape, Change Direction"
- Move: Force can start motion from rest.
- Change Speed: Force can make objects go faster or slower.
- Change Shape: Force can bend, stretch, or squash objects.
- Change Direction: Force can alter the path of motion.
2. Types of Contact Forces
Mnemonic: "My Friend"
- My: Muscular force — force exerted by muscles (e.g., pushing, lifting).
- Friend: Frictional force — opposes motion between surfaces in contact.
3. Types of Non-Contact Forces
Mnemonic: "Mighty Elephants Glide"
- Mighty: Magnetic force — attracts or repels magnetic objects.
- Elephants: Electrostatic force — acts between charged objects.
- Glide: Gravitational force — pulls objects towards each other (e.g., Earth’s pull).
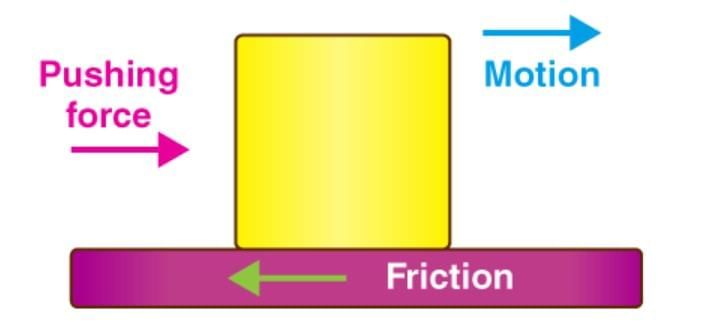
4. Properties of Friction
Mnemonic: "Friction Opposes Rough Airy Waters"
- Opposes: Friction always acts opposite to motion.
- Rough: It is greater on rough surfaces.
- Airy: It exists in air as resistance (air drag).
- Waters: It is also present in water/liquids (fluid resistance).
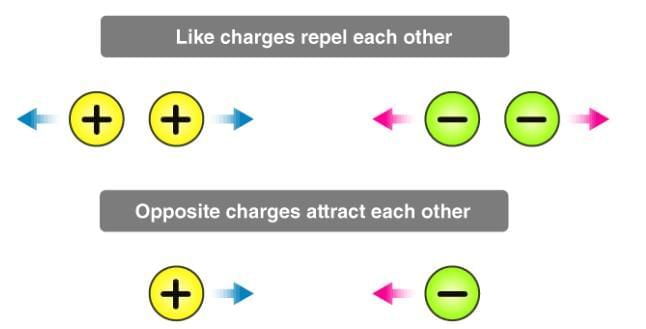
5. Electrostatic Charge Rules
Mnemonic: "Like Repel, Opposites Attract"
- Like: Like charges repel — same charges push away from each other.
- Repel: Repulsion between similar charges — positive repels positive, negative repels negative.
- Opposites: Unlike charges attract — opposite charges pull together.
- Attract: Attraction between opposite charges — positive attracts negative.
6. Floating and Sinking – Force Interaction
Mnemonic: "Gravity Beats Up"
- Gravity: Gravitational force (downwards) — pulls objects towards Earth.
- Beats: Buoyant force (upwards) — pushes objects up in a liquid.
- Up: Upthrust from liquid — determines if an object floats or sinks.
7. Difference Between Weight and Mass
Mnemonic: "Force Pulls, Matter Stays"
- Force: Weight is a force — measured in Newtons, due to gravity.
- Pulls: Weight is pull by Earth (gravity) — varies with location.
- Matter: Mass is the amount of matter — measured in kilograms.
- Stays: Mass stays same everywhere — independent of location.
The document Mnemonics: Exploring Forces | Year 8 Physics (Cambridge) - Class 8 is a part of the Class 8 Course Year 8 Physics (Cambridge).
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
8 videos|39 docs|11 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Exploring Forces - Year 8 Physics (Cambridge) - Class 8
| 1. What are the main effects of force on an object? |  |
Ans. The main effects of force on an object include causing it to start moving, stop moving, change direction, or change its shape. When a force is applied to an object, it can result in acceleration, which is a change in velocity over time. This can lead to various outcomes such as increasing speed, decreasing speed, or altering the object's trajectory.
| 2. What are the different types of contact forces? |  |
Ans. The different types of contact forces include frictional force, normal force, tension force, and applied force. Frictional force opposes the motion of an object sliding over a surface. Normal force acts perpendicular to the surface that supports an object. Tension force is transmitted through a string or rope when it is pulled tight. Applied force is any force that is applied to an object by a person or another object.
| 3. What are some examples of non-contact forces? |  |
Ans. Examples of non-contact forces include gravitational force, electromagnetic force, and nuclear force. Gravitational force is the attraction between two masses, such as the Earth and an object. Electromagnetic force acts between charged particles, influencing their motion and interactions. Nuclear force binds protons and neutrons together in an atomic nucleus.
| 4. What are the properties of friction? |  |
Ans. The properties of friction include that it always acts in the opposite direction of motion, depends on the nature of the surfaces in contact, and is affected by the normal force. Friction can be static (preventing motion) or kinetic (opposing motion in progress) and varies with different materials and conditions, such as surface roughness and lubrication.
| 5. How do weight and mass differ? |  |
Ans. Weight is the force exerted on an object due to gravity and is calculated as the product of mass and gravitational acceleration (Weight = Mass × g). Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object and remains constant regardless of location. Weight can change depending on the gravitational field strength, while mass does not vary.
Related Searches
















