Unit Test (Solutions): How Nature Works in Harmony | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
- 1-mark questions include MCQs.
Q1: A habitat consists of (1 Mark)
(i) only living (biotic) components
(ii) only non-living (abiotic) components
(iii) both living and non-living components interacting together
(iv) only producers and consumers
Ans: (iii)
A habitat is a place where an organism lives and includes biotic (plants, animals, microbes) and abiotic (air, water, soil, light, temperature) components that interact and provide conditions for life.

Q2: In a pond, fish obtain oxygen mainly from (1 Mark)
(i) air above the pond surface only
(ii) dissolved oxygen in water
(iii) plants only
(iv) soil
Ans: (ii)
Fish respire using gills that absorb oxygen dissolved in water; plants and aeration influence dissolved oxygen, but uptake is from the water itself.
Q3: A population refers to (1 Mark)
(i) different species living together in a habitat
(ii) organisms of the same species in a given area and time
(iii) all living and non-living components in an area
(iv) only producers in a habitat
Ans: (ii)
A population is the group of individuals of the same kind (species) living in a defined area at a given time (e.g., 20 grass plants in 1 m×1 m plot).
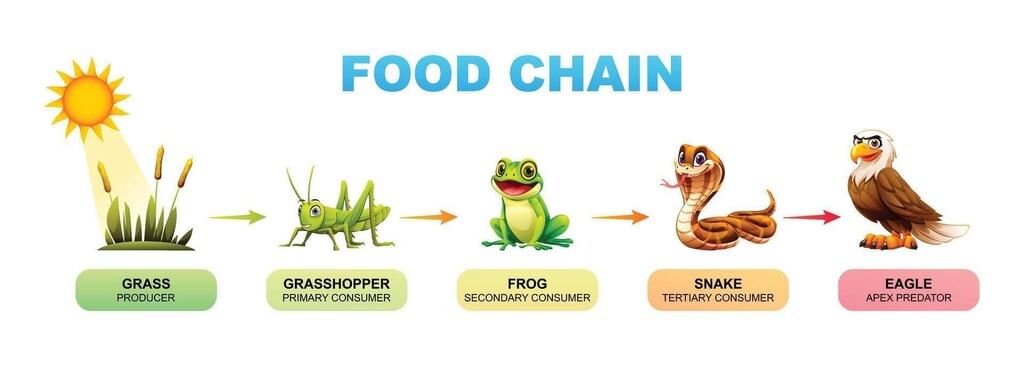
Q4: Which sequence is a correct food chain in a grassland? (1 Mark)
(i) Eagle → Snake → Frog → Grasshopper → Grass
(ii) Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Eagle
(iii) Grasshopper → Grass → Frog → Snake → Eagle
(iv) Grass → Snake → Frog → Grasshopper → Eagle
Ans: (ii)
Producers (grass) → primary consumers (herbivores like grasshopper) → secondary (frog) → tertiary (snake) → top carnivore (eagle).
Q5: Mushrooms growing on dead logs are best classified as (1 Mark)
(i) producers
(ii) herbivores
(iii) decomposers (saprotrophs)
(iv) omnivores
Ans: (iii)
Fungi (mushrooms) decompose dead organic matter, recycling nutrients back to the ecosystem.
Q6: Distinguish between biotic and abiotic components with one example each from a pond. (2 Marks)
Ans:
Biotic: living organisms (e.g., fish, algae, frogs, duckweed).
Abiotic: non-living factors (e.g., water, dissolved oxygen, light, temperature, soil/sediment). Abiotic factors affect biotic life processes; biotic components also modify abiotic conditions (e.g., plants oxygenate water).
Q7: Define community and population, and state how they are related. (2 Marks)
Ans: A population is a group of individuals of the same species in an area at a time (e.g., 5 neem trees in a plot). A community is all the different populations sharing the same habitat (e.g., trees, shrubs, insects, birds in the garden). Multiple populations together constitute a community.
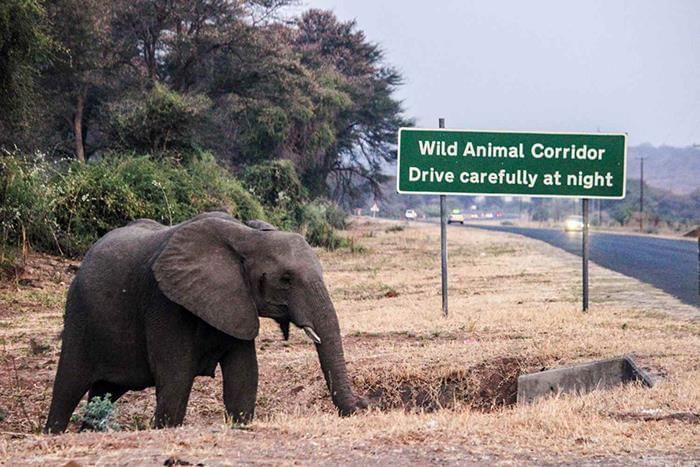
Q8: Why are wildlife corridors (like elephant corridors) important for ecosystem balance? (2 Marks)
Ans: Corridors connect fragmented habitats, allowing safe movement of animals between forest patches to access food, water, and mates; they reduce human–wildlife conflict, maintain gene flow, and help populations adapt to seasonal changes and climate variability.

Q9: In a pond study, fish reduced dragonfly numbers; pollinators increased near fish ponds and seed set in plants was higher. Explain the indirect effect of fish on plants. (3 Marks)
Ans: Fish eat dragonfly larvae → fewer dragonflies → less predation on bees/butterflies/flies → more pollinators → improved pollination of nearby flowers → higher seed production. This is a trophic cascade: fish indirectly benefit plants via pollinator release.
Q10: Fill the trophic levels in order and give one example for each from a forest. (3 Marks)
(a) 1st trophic level (Producers): _______
(b) 2nd trophic level (Primary consumers): _______
(c) 3rd trophic level (Secondary consumers): _______
(d) 4th trophic level (Tertiary/top carnivores): _______
Ans:
(a) Producers: green plants/trees (e.g., sal, teak, grasses).
(b) Primary consumers: herbivores (e.g., deer, hare, insects).
(c) Secondary consumers: small carnivores (e.g., frogs, birds like shikra, fox).
(d) Tertiary/top carnivores: large predators/scavengers (e.g., tiger, leopard, vulture).
Q11: Differentiate mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism with one example each from the chapter context. (3 Marks)
Ans: Mutualism: both benefit (bee and flower—bee gets nectar; flower gets pollinated). Commensalism: one benefits, other not affected (orchid on tree—orchid gains support/nutrients trapped on bark; tree largely unaffected). Parasitism: one benefits, other harmed (tick on dog—tick feeds on blood; dog suffers irritation/disease risk).
Q12: Ecosystem functioning and disruption. (5 Marks)
(a) Explain why decomposers are essential to ecosystem health.
(b) Using the “one change leads to another” idea, describe a plausible chain of impacts if pond plants die due to pollution.
(c) Suggest two human actions to prevent such cascades.
Ans:
(a) Decomposers (bacteria, fungi) break down dead matter and wastes into simpler nutrients, returning them to soil/water, sustaining plant growth and closing nutrient cycles. Without them, nutrients would lock in detritus, primary productivity would fall, and wastes would accumulate.
(b) Pollution kills aquatic plants → less photosynthesis → dissolved oxygen drops → fish die → fewer fish predators → some insect populations surge → insects spread to farms → pest outbreaks → increased pesticide use → environmental contamination, soil and water quality decline → further biodiversity loss.
(c) Reduce pollutant discharge (treatment of sewage/industrial effluents), protect riparian buffers and wetlands; restore vegetation; regulate pesticide use through IPM; community monitoring and awareness.
Q13: Sustainable farming and ecosystem services. (5 Marks)
(a) List two drawbacks of overusing synthetic fertilisers and pesticides highlighted by farmers’ experiences.
(b) Propose three eco-friendly practices that enhance soil health and biodiversity in farms.
(c) Explain how natural predators and pollinators support sustainable yields.
Ans:
(a) Overuse can reduce soil organic matter and beneficial microbes, leading to declining soil structure and fertility; pesticide overuse can harm non-target organisms, cause pest resistance, contaminate water, and reduce natural enemies and pollinators.
(b) Practices: add organic manures/compost/green manures (as in Vrikshayurveda’s fermented preparations), diversify crops (rotation/intercropping/millets), conserve soil moisture (mulch), reduce tillage, integrate livestock, plant hedgerows and flowering strips to support natural enemies/pollinators, use rainwater harvesting.
(c) Predators (e.g., beetles, birds) suppress pests biologically, reducing pesticide dependence; pollinators (bees, butterflies) increase fruit/seed set, improving yield and quality—maintaining ecosystem services critical to farm productivity.
|
59 videos|236 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): How Nature Works in Harmony - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the key components of nature that work in harmony? |  |
| 2. How does human activity impact the harmony of nature? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of biodiversity in maintaining ecological balance? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of natural processes that demonstrate harmony in nature? |  |
| 5. How can individuals contribute to preserving the harmony of nature? |  |















