Unit Test (Solutions): Electricity: Magnetic and Heating Effects | Science Class 8 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
- 1-mark questions include MCQs.
Q1: When electric current flows through a straight conductor, the space around it has a (1 Mark)
(i) gravitational field
(ii) electric field only
(iii) magnetic field
(iv) no field
Ans: (iii)
A current-carrying conductor produces a magnetic field around it; this is the magnetic effect of electric current (Oersted’s observation).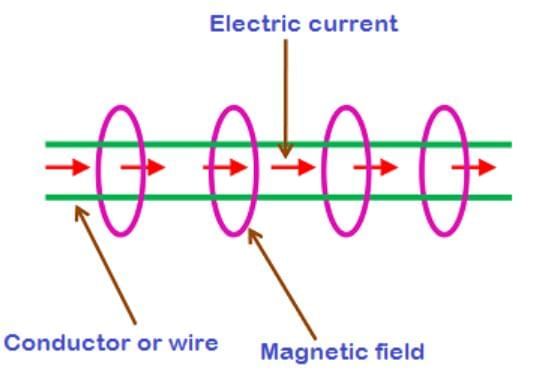
Q2: A current-carrying coil behaves like (1 Mark)
(i) a heater only
(ii) a magnet
(iii) a battery
(iv) an insulator
Ans: (ii)
The coil develops a magnetic field with two poles; with an iron core, it becomes a stronger electromagnet.
Q3: In a nichrome wire, heating is more than in a copper wire of the same size and length for the same current because nichrome has (1 Mark)
(i) lower resistance
(ii) higher resistance
(iii) zero resistance
(iv) infinite resistance
Ans: (ii)
Higher resistance converts more electrical energy to heat (Joule heating) for the same current and time.
Q4: A dry cell is called “dry” because (1 Mark)
(i) it contains dry metal only
(ii) its electrolyte is a moist paste, not a free liquid
(iii) it never leaks
(iv) it cannot supply current
Ans: (ii)
Dry cells use a paste electrolyte inside a zinc container with a central carbon rod.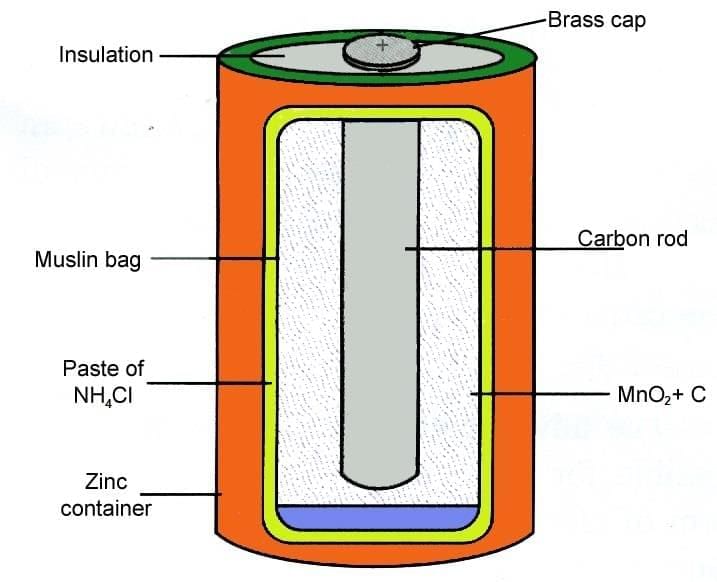 Dry Cell
Dry Cell
Q5: Increasing the number of turns of a coil (keeping current same) makes an electromagnet (1 Mark)
(i) weaker
(ii) unchanged
(iii) stronger
(iv) vanish
Ans: (iii)
Magnetic field strength is proportional to both current and number of turns; more turns strengthen the field.
Q6: State one observation that shows current has a magnetic effect and one that shows current has a heating effect. (2 Marks)
Ans: Magnetic effect: a compass needle placed near a current-carrying wire deflects. Heating effect: a nichrome wire connected in a circuit becomes warm/hot after current flows briefly.
Q7: Give two ways to increase the strength of an electromagnet made from a coil around an iron nail. (2 Marks)
Ans: (i) Increase the current (use more cells in series),
(ii) Increase the number of turns of the coil. Both increase the magnetic field and lifting ability.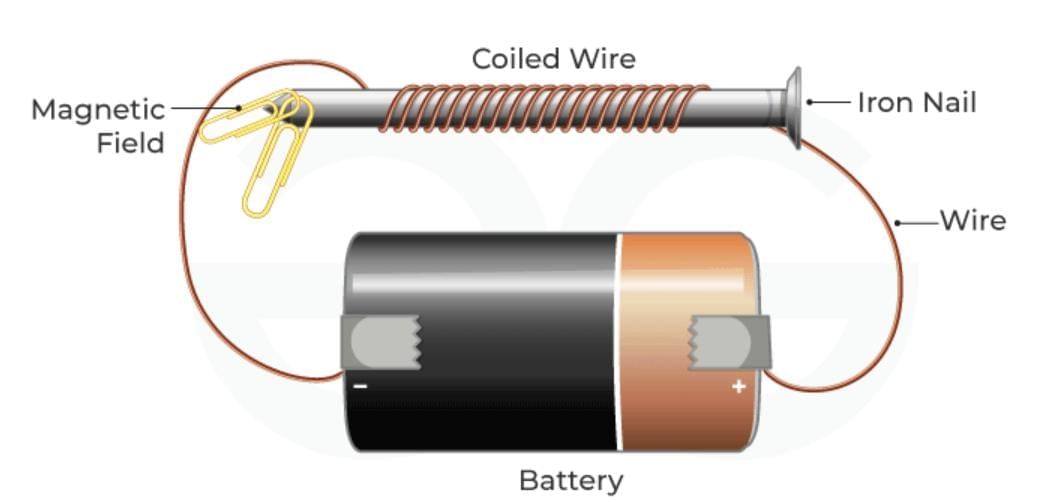 Electromagnet
Electromagnet
Q8: Why is nichrome used as a heating element instead of copper? (2 Marks)
Ans: Nichrome has higher resistivity and high melting point; it heats more for a given current and withstands red-hot temperatures without oxidizing rapidly, unlike copper.
Q9: In a compass-under-wire experiment, the needle deflects when the switch is ON and returns when OFF. Explain what this proves and why the needle returns. (3 Marks)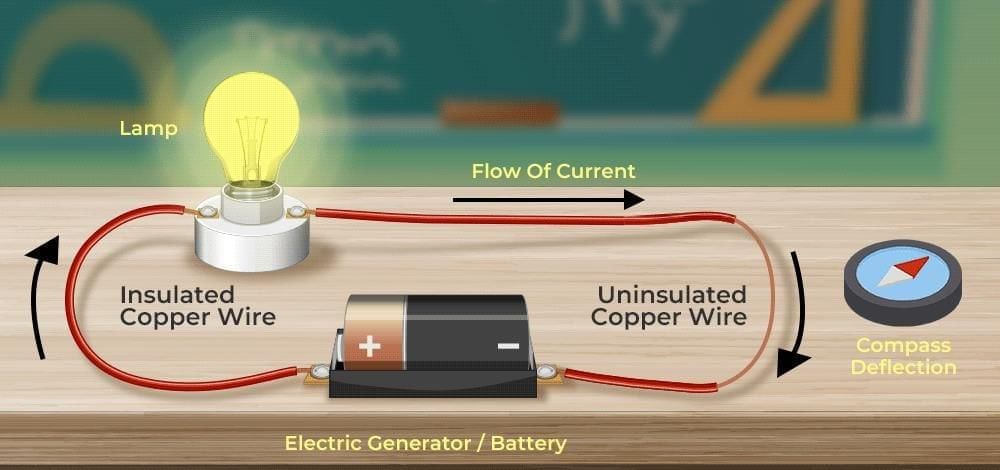
Ans:
- In the compass-under-wire experiment, the needle deflects when the switch is ON because the current flowing through the wire produces a magnetic field around it.
- This field interacts with the compass needle (which is itself a tiny magnet) and makes it turn from its north–south position. When the switch is OFF, the current stops, so the magnetic field disappears.
- The needle then returns to its original position, aligning itself again with the Earth’s magnetic field. This proves that a current-carrying conductor produces a magnetic field.
Q10: Match the following: (3 Marks)
(i) Voltaic cell ——— (a) works on heating effect of current
(ii) Electromagnet ——— (b) chemical reactions produce electricity
(iii) Electric iron ——— (c) works on magnetic effect of current
Ans:
(i) Voltaic cell — (b) Chemical reactions produce electricity
(ii) Electromagnet — (c) Works on magnetic effect of current
(iii) Electric iron — (a) Works on heating effect of current
Explanation:
A voltaic cell changes chemical energy into electrical energy, an electromagnet uses current to produce magnetism, and an electric iron converts electrical energy into heat.
Q11: A student uses one cell to power an electromagnet and later switches to two identical cells in series. Predict and explain two observable changes in the setup. (3 Marks)
Ans: When two identical cells are connected in series instead of one:
- The compass placed near the coil will show more deflection, because the stronger current produces a stronger magnetic field.
- The electromagnet will lift more paper clips or heavier objects, due to increased magnetic strength.
Reason: With two cells in series, the voltage increases, which increases the current in the coil. A higher current makes the magnetic field stronger and may also make the wire heat up faster.
Q12: (a) Describe how you would make a simple lemon cell to glow an LED.
(b) Why might the LED glow only after reversing its terminals?
(c) Will pure distilled water work as electrolyte instead of lemon juice? Explain. (5 Marks)
Ans: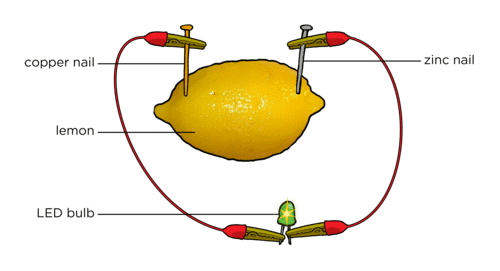
(a) Insert two dissimilar metals (e.g., copper strip and iron nail) into a lemon (electrolyte: acidic juice). Connect several lemons in series by linking copper of one to iron of the next. Connect LED between the free copper (first lemon) and the free iron (last lemon) using wires.
(b) LEDs are polarized components; current passes only when LED’s longer lead (anode, +) is connected to the positive side of the lemon-battery chain and the shorter lead (cathode, –) to the negative. Reversing may be needed to match polarity.
(c) Pure distilled water is a very poor conductor; the cell will not work effectively. Lemon juice contains ions (acid) that conduct electricity; similarly, salt solutions work as electrolytes, but pure water lacks sufficient ions.
Q13: (a) Explain the heating effect of electric current with four factors it depends on.
(b) List two safety concerns arising from unwanted heating and two household measures/devices that address them.
(c) Give two societal advantages of using electric heating devices over burning wood/charcoal. (5 Marks)
Ans:
(a) As current flows through a resistance, electrical energy converts to heat (Joule heating). Heat produced depends on: material (resistance), length (longer → more heat), thickness (thinner → more heat for same material), magnitude of current and duration (higher current or longer time → more heat).
(b) Safety concerns: overheating may melt plugs/sockets, damage insulation, or cause fires. Measures/devices: use correctly rated wires/plugs/sockets; fuses/MCBs in circuits; proper ventilation/clearances for heaters; avoid overloading sockets.
(c) Advantages: cleaner (less indoor/outdoor air pollution), safer and easier to control; reduces deforestation from fuelwood; more efficient, adjustable, and convenient in urban settings.
|
136 videos|530 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Electricity: Magnetic and Heating Effects - Science Class 8
| 1. What are the main concepts covered in the topic of Electricity, specifically regarding Magnetic and Heating Effects? |  |
| 2. How does the heating effect of electric current work, and what is its significance? |  |
| 3. What is electromagnetism and how is it applied in real-life situations? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the difference between static electricity and current electricity? |  |
| 5. What safety precautions should be taken while working with electrical devices to prevent hazards? |  |






















