Short and Long Answer Questions: Health: The Ultimate Treasure | Science Class 8 PDF Download
Short Answer Questions
Q1. What are the three main dimensions of health and why must they be balanced?
Answer: The three dimensions are physical, mental, and social health, and balancing them helps the body work well, keeps the mind calm, and supports healthy relationships.
Q2. How did the student’s story show a link between screen time and health?
Answer: Too much screen time increased loneliness and stress, which led to headaches, weight loss, and poor sleep, showing how habits affect both mind and body.
Q3. How does Ayurveda suggest we maintain daily health?
Answer: Ayurveda recommends following a daily and seasonal routine, eating fresh food suited to your body type, and practicing yoga, cleanliness, and good sleep.
Q4. Why are clean surroundings important for health?
Answer: Clean surroundings reduce germs and vectors like flies and mosquitoes, improve air and water quality, and lower the risk of diseases.
Q5. What is the difference between symptoms and signs of illness?
Answer: Symptoms are what we feel, such as pain or tiredness, while signs are what others can observe or measure, like fever or a rash.
Q6. How do communicable diseases spread through air and water?
Answer: They spread when infected droplets are breathed in or when people eat or drink contaminated food and water containing pathogens.
Q7. What simple habits help prevent communicable diseases?
Answer: Washing hands with soap, covering your mouth when coughing, keeping food and water clean, and using mosquito nets help prevent infection.
Q8. What are non-communicable diseases and one key reason they are increasing?
Answer: Non-communicable diseases do not spread between people and are rising due to unhealthy lifestyles, such as poor diet and low physical activity.
Q9. How do vaccines protect both individuals and communities?
Answer: Vaccines train the immune system to fight specific germs and, when many people are vaccinated, they reduce disease spread, protecting those who are unvaccinated.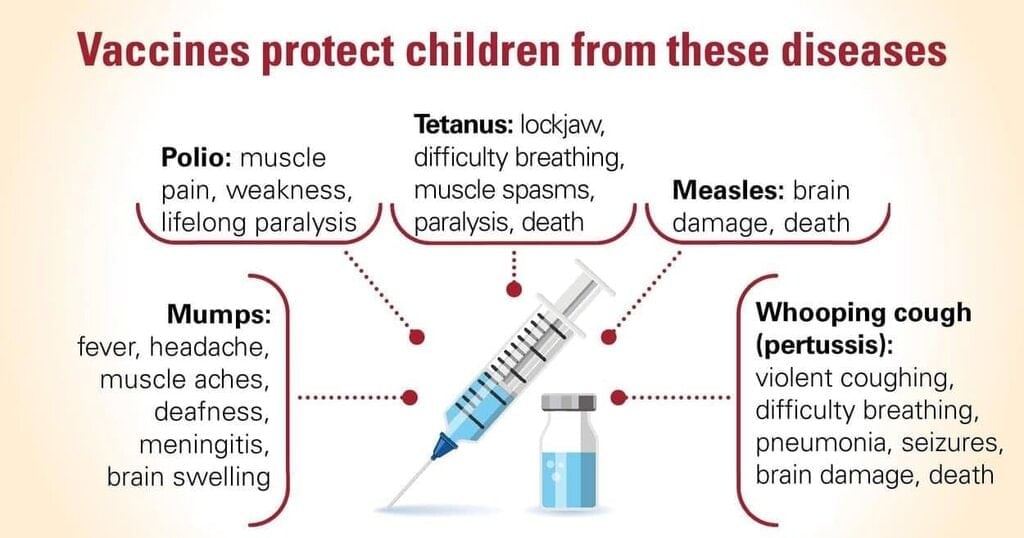
Q10. Why should antibiotics not be used for colds and flu?
Answer: Colds and flu are caused by viruses, and antibiotics only kill bacteria, so using them is useless and can promote antibiotic resistance.
Q11. What practices help prevent antibiotic resistance?
Answer: Only take antibiotics when prescribed, complete the full course, don’t use leftovers, and avoid buying them without a prescription.
Q12. How can lifestyle changes help prevent and manage NCDs?
Answer: Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, getting enough sleep, avoiding tobacco and alcohol, and managing stress help prevent and control NCDs.
Q13. Why are vaccines important?
Ans.
- Vaccines produce antibodies in our body to fight against disease-causing microbes entering our body.
- Diseases like cholera, tuberculosis, smallpox, and hepatitis can be prevented by vaccination.
- Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV) is administered as drops to children.
 Oral Polio Vaccine
Oral Polio Vaccine
Q 14. List all possible ways by which pathogens can enter our body.
Ans.
- Pathogens are disease-causing microbes, which invade our body through openings including the eyes, nose, and mouth through open wounds, urogenital openings, and also through mosquito bites.
- These pathogens invade the cell and tissue of a host and cause severe infectious disease.
 Pathogens
Pathogens
Q 15. Define communicable diseases with examples.
Ans.
- There are some microbial diseases that can spread from an infected person to a healthy person through the air, water, food, or physical contact.
- Such a kind of disease is called communicable disease.
- Example: Cholera, Chickenpox, Tuberculosis.
Q 16. Why we should keep a handkerchief on the nose and mouth while sneezing?
Ans.
- Sneezing releases fine droplets of moisture into the air, which can contain thousands of viruses.
- These droplets can easily spread infectious agents, particularly in crowded or enclosed spaces.
- If a person with a cold sneezes without covering their mouth and nose, the viruses can become airborne.
- Healthy individuals can inhale these viruses, increasing the risk of them becoming sick.
- Using a handkerchief or tissue while sneezing helps to:
- Contain the droplets and minimize their spread in the air.
- Protect others from inhaling infectious agents.
- Promote good hygiene practices to prevent the transmission of illnesses.
Q 17. How do houseflies spread diseases?
Ans.
- Houseflies sit on the garbage and animal excreta where pathogens stick to their bodies.
- These pathogens get transferred to uncovered food when these flies sit on uncovered food items and the person consuming these food falls sick.
Q 18: Neha went to a party and she ate a variety of foodstuff there, on reaching home she started vomiting and had stomach ache. What do you think why it is so?
Ans: It is because of food poisoning. Food poisoning could be due to the consumption of food spoilt by some microorganisms.
Q 19. What are viruses? Name some common diseases in humans caused by viruses.
Ans. Viruses are microscopic organisms. They, however, reproduce only inside the cells of the host organism, which may be a bacterium, plant or animal. Some diseases like cold, influenza (flu), polio and chicken pox are caused by viruses.
Q 20. What are antibiotics? Explain with the help of examples.
Ans. The medicines which are used to kill or stop the growth of the disease-causing microorganisms are called antibiotics. The first antibiotic is Penicillin. It was discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1929. These days, a large number of antibiotics are produced by bacteria and fungi. For example: Streptomycin, Tetracycline and Erythromycin.
Q 21. Explain how a vaccine works.
Ans. A vaccine works by training the immune system to recognise and combat disease-causing microbes. Here’s how it functions:
- When a microbe enters the body, the immune system produces antibodies to fight it.
- The body remembers how to produce these antibodies for future encounters.
- If a vaccine containing dead or weakened microbes is introduced, the body responds by creating the necessary antibodies.
- These antibodies remain in the body, providing long-term protection against the disease.
This process helps prevent various diseases, including cholera, tuberculosis, and polio.
Q 22. What do you mean by food poisoning?
Ans.
- Some microorganisms settle on food. They release toxic substances into the foodstuff. This makes the food contaminated and unfit for use. This is called food poisoning.
- If anyone consumes this food, it can produce fatal results. Serious illness is caused, and the patient gets frequent vomiting and loose motion.
- This physical condition can even lead to death. So it is very important that we preserve food to prevent it from being spoilt.
Long Answer Questions
Q.1. What are the major precautions one should follow while taking antibiotics?
Ans. The following precautions must be taken while taking antibiotics:
- Antibiotics should be taken only on the advice of a qualified doctor. And one must finish the course prescribed by the doctor.
- Antibiotics must be avoided when not needed or in the wrong doses.
- Antibiotics taken unnecessarily may kill beneficial bacteria in the body.
Q.2. What are carriers of disease-causing microbes? Explain with the help of two examples.
Ans. There are some insects and animals that carry disease-causing microorganisms like a housefly and mosquitoes. Such insects and animals are called carriers of disease-causing microbes.
Examples:
(i) Housefly: The housefly is a carrier of microorganisms. They sit on the garbage and animal excreta. The pathogens stick to their bodies. When these flies sit on uncovered food, they may transfer the pathogens. Whoever eats the contaminated food is likely to get sick. So, we should not consume uncovered food.
(ii) Female Anopheles Mosquito: It is the carrier of the parasite of malaria. Female Aedes mosquito acts as a carrier of the dengue virus. We can control malaria by keeping the surroundings clean and dry.  Female Anopheles Mosquito
Female Anopheles Mosquito
Q3. Explain how health includes physical, mental, and social well-being with examples from daily life.
Answer:
- Health means more than not being sick; it includes a strong body, a calm mind, and good relationships. Physical health is supported by balanced food, exercise, and sleep, like playing outdoors and eating fruits and vegetables.
- Mental health involves managing stress and screen time, such as taking breaks from phones and practicing deep breathing. Social health means having supportive friends and family, like spending time together and talking about feelings.
- When all three stay balanced, we work better, feel happier, and recover faster from problems.
Q4. Describe how lifestyle choices affect non-communicable diseases and suggest practical ways to reduce risk.
Answer: 
- Non-communicable diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and cancer are linked to habits such as poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and little sleep.
- Eating processed, sugary foods and sitting for long hours increases risk over time. We can lower risk by following a balanced diet, moving for at least 60 minutes a day, and sleeping 8–9 hours.
- Avoiding tobacco and alcohol and managing stress with yoga or meditation also help. Regular check-ups and early diagnosis make these conditions easier to manage.
Q5. Discuss how clean surroundings and community action prevent disease, using the Odisha example.
Answer:
- Clean surroundings reduce germs, insects, and pollution that cause many illnesses. In Bhadrak district, Odisha, a sanitation campaign encouraged families to build and use toilets, which reduced open defecation.
- As hygiene improved, cases of diarrhoea and infections fell, showing how community steps protect everyone. Proper waste disposal, safe water, and clean public spaces also cut disease spread. When communities act together, public health improves faster and stays better.
Q.6. Explain causative microorganisms, mode of transmission, and preventive measures of human diseases like Tuberculosis, Measles, Chickenpox, Polio, Cholera, Typhoid, Hepatitis B Malaria etc.
Ans. Some of the common diseases affecting humans, their mode of transmission, and few general methods of prevention are given in the following table: 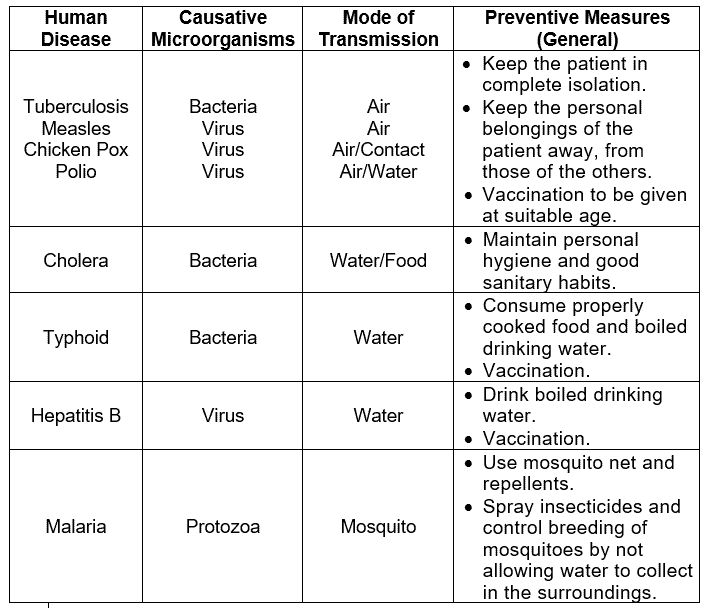
Q7. Compare communicable and non-communicable diseases in terms of causes, spread, and prevention.
Answer:
- Communicable diseases are caused by pathogens like bacteria and viruses and can spread through air, water, contact, or insects. Non-communicable diseases are not caused by germs, do not spread between people, and are linked to lifestyle, environment, or body functions.
- Communicable diseases are prevented by hygiene, safe food and water, masks in crowds, and mosquito control. Non-communicable diseases are prevented by healthy eating, exercise, enough sleep, and avoiding harmful substances. Both types benefit from awareness, early diagnosis, and proper treatment.
Q8. Explain how the immune system and vaccines protect us, with examples of acquired immunity.
Answer:
- The immune system is the body’s defense team that recognises and fights harmful germs. Vaccines train this system by safely showing it how to identify specific pathogens before we meet the real ones.
- After vaccination, the body remembers the germ and responds quickly, which is called acquired immunity. Examples include tetanus shots that protect against a bacterial toxin and childhood vaccines like polio and measles. When many people are vaccinated, diseases spread less, protecting the whole community.
Q9. Describe antibiotics, their correct use, and why antibiotic resistance is dangerous.
Answer:
- Antibiotics are medicines that kill bacteria and are used for illnesses like typhoid or tuberculosis. They do not work against viruses such as colds, flu, or COVID-19, so using them wrongly causes harm.
- If antibiotics are overused or not taken as prescribed, bacteria can change and become resistant. Resistant infections are harder to treat, can last longer, and may spread to others. To prevent this, take antibiotics only with a doctor’s advice and always finish the full course.
Q10. Explain the role of habits like diet, exercise, sleep, and screen time in maintaining overall health.
Answer:
- Healthy habits build strong bodies and minds and keep relationships positive. A balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains gives energy and protects against disease.
- Daily exercise strengthens the heart, lungs, and muscles, while 8–9 hours of sleep helps the brain and body recover. Limiting screen time reduces eye strain, stress, and poor sleep, improving mood and focus. Together, these habits prevent illness and help us feel our best every day.
Q11. Describe how traditional systems like Ayurveda support wellness and how they can work with modern medicine.
Answer:
- Ayurveda promotes balance of body, mind, and environment through routines, seasonal habits, and food suited to your body type. Practices like yoga, pranayama, cleanliness, and restful sleep support daily wellness.
- These methods can help prevent illness, reduce stress, and improve digestion and immunity. For serious or advanced diseases, modern medicine provides tests, quick treatment, and life-saving care. Using safe traditional practices with modern medical advice gives a balanced approach to health.
|
136 videos|530 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Short and Long Answer Questions: Health: The Ultimate Treasure - Science Class 8
| 1. What are the main components of good health? |  |
| 2. How can lifestyle choices impact health? |  |
| 3. What role does mental health play in overall health? |  |
| 4. Why is preventive healthcare important? |  |
| 5. How can a balanced diet contribute to better health? |  |
















