UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 3rd August 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Environment
Thar Desert Wind Farms Record World’s Highest Bird Mortality Rate
 Why in News?
Why in News?
A recent study has revealed alarming findings regarding wind farms in India’s Thar Desert, which have recorded the world’s highest bird mortality rates. This discovery raises significant concerns about the environmental implications of expanding renewable energy sources.
Key Takeaways
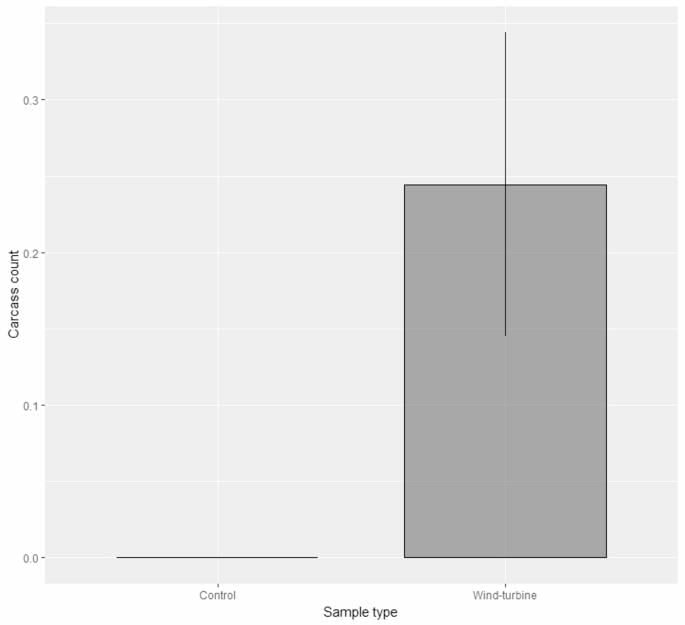
- The Thar Desert wind farms have an estimated bird mortality rate of 4,464 birds per 1,000 sq. km.
- Critically endangered species, including the Great Indian bustard, are particularly at risk.
- Control sites away from turbines registered zero bird deaths, confirming the turbines' role in bird fatalities.
Additional Details
- About the Study: Conducted by the Wildlife Institute of India (WII), the research spanned 3,000 sq. km in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, involving 900 wind turbines and over 270 bird species. The study included seven multi-season surveys which found 124 bird carcasses around selected turbines.
- Species at Risk: The Thar Desert is part of the Central Asian Flyway, crucial for migratory birds. Raptors, which have long lifespans and reproduce slowly, are particularly vulnerable due to their flight patterns that increase collision risks with turbine blades.
- Proposed Mitigation Measures: Strategies such as blade painting for visibility, timed shutdowns during migration seasons, and careful site assessments using tools like the Avian Sensitivity Tool for Energy Planning (AVISTEP) have been recommended.
- Despite the findings, current regulations do not mandate environmental impact assessments (EIAs) for onshore wind energy projects in India, highlighting a critical gap in regulatory oversight.
As India shifts focus to offshore wind energy, which is less land-intensive, it must also consider potential impacts on marine biodiversity. The country aims to install 30 GW of offshore wind capacity by 2030, but concerns about ecological assessments in biodiverse areas persist.
GS2/International Relations
Impact of Trump’s Tariffs on India
Why in News?
U.S. President Donald Trump has implemented a 25% tariff along with an additional penalty on Indian imports, creating uncertainty around the potential for a bilateral trade agreement between India and the U.S. This development complicates future trade negotiations.
Key Takeaways
- 25% tariff imposed on Indian imports, potentially raising the effective tariff to 35% with additional penalties.
- Estimated reduction of India's GDP growth by 0.2%, impacting key sectors like garments and electronics.
- Ongoing tensions related to India's energy dealings with Russia and agricultural protectionism.
Additional Details
- Impact on Economy: The tariffs are expected to lower India's GDP growth forecasts from 6.6% to 6.4%, affecting sectors such as garments, precious stones, and auto parts, which may struggle against competitors from countries like Vietnam and South Korea.
- Trade Negotiations: Following the tariffs, India and the U.S. had planned to finalize a bilateral trade deal by fall 2025. However, tensions, including India's reluctance to open its agricultural sector, have complicated these discussions.
- Retaliatory Measures: India has signaled its intention to impose retaliatory tariffs in response to the U.S. tariffs on Indian steel and aluminum products, further straining bilateral relations.
In summary, Trump's tariff imposition has significant implications for India, affecting its economy, export competitiveness, and ongoing trade negotiations with the U.S. The situation remains fluid, and both countries are committed to resolving these issues, despite the complexities introduced by recent tariffs.
GS2/Polity
Assam’s Eviction Drives - The Ripple Effect in Northeast India
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Assam government's intensified eviction drive, targeting alleged encroachments on forest and government lands, particularly affecting Bengali-speaking Muslims, has sparked political controversy and heightened regional tensions. This situation is significantly influencing inter-State relations within Northeast India.
Key Takeaways
- The eviction drives have their roots in a long-standing political narrative.
- Recent incidents have raised concerns over human rights violations and political motivations.
- The actions are affecting not just the targeted communities but also neighboring states.
Additional Details
- Genesis of Eviction Drives: The current government, which came to power in Assam in 2016, has been committed to protecting the interests of the local community, land, and heritage. The first eviction drive was initiated in September 2016 following a Gauhati High Court order to reclaim forestlands.
- Major Incidents: A significant event occurred in 2021 in Darrang district, resulting in two fatalities and amplifying concerns regarding human rights. The eviction drives resumed in June 2025 amid corruption allegations against the government.
- Socio-Political Context: The eviction policy is rooted in an anti-infiltration narrative targeting Bengali-speaking Muslims, often labeled derogatorily. Historical events like the Assam Agitation (1979–1985) and the Assam Accord have shaped current political attitudes.
- Regional Impact: Neighboring states such as Nagaland, Manipur, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh, and Mizoram are on high alert due to the eviction drives, which have led to increased border vigilance and accusations of Assam pushing evictees into their territories.
- Inter-State Border Disputes: The eviction actions are linked to unresolved border disputes, with allegations of encroachment by migrants leading to tensions between Assam and its neighbors. Judicial interventions have been called for to address these issues.
In conclusion, the eviction drives in Assam are not merely administrative actions but reflect a complex interplay of political motivations, regional sensitivities, and human rights concerns. They underscore the critical balance between land rights, environmental conservation, identity politics, and governance in the Northeast.
GS2/International Relations
UK’s Palestine Shift: A Tipping Point in Global Diplomacy
 Why in News?
Why in News?
British Prime Minister Keir Starmer announced that the UK will recognize the State of Palestine at the upcoming UN General Assembly in September unless Israel agrees to a Gaza ceasefire, facilitates more humanitarian aid, and commits to a two-state peace process.
Key Takeaways
- Growing global support for Palestinian statehood recognition.
- UK's potential recognition marks a significant shift in diplomatic relations.
- Major Western powers are re-evaluating their stance on Palestinian statehood.
Additional Details
- Current Palestine Recognition Drive: The UK's announcement follows similar intentions expressed by France, Canada, and Portugal, indicating a broader shift in Western diplomatic support towards Palestine amidst ongoing conflicts.
- The Balfour Declaration: Issued in 1917, this declaration marked Britain's support for a Jewish homeland in Palestine, significantly impacting the geopolitical landscape of the region.
- Historically, 147 out of 193 UN member states have recognized Palestine, though major Western nations had previously resisted recognition, tying it to the need for a conclusive Israel-Palestine peace settlement.
The UK's intention to recognize Palestine, 108 years after the Balfour Declaration, signifies a historic policy shift. As global scrutiny of Israel grows, particularly regarding humanitarian crises in Gaza, Western nations, including the UK, are facing increasing pressure to adopt a more balanced approach towards the Palestinian cause.
|
57 videos|5393 docs|1142 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 3rd August 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the main environmental concerns associated with wind farms in the Thar Desert? |  |
| 2. How have Trump's tariffs impacted trade relations between the United States and India? |  |
| 3. What are the implications of eviction drives in Assam for the broader Northeast India region? |  |
| 4. In what ways has the UK’s shift in policy towards Palestine influenced global diplomatic relations? |  |
| 5. What steps can be taken to reduce bird mortality rates at wind farms? |  |
















