Introduction to Catholic Christianity | Religion, Philosophy & Ethics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Introduction
Christianity serves as the predominant religious tradition in Great Britain. Christianity is a significant monotheistic faith centered on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. As an Abrahamic religion, it shares common origins with Judaism and Islam, the other primary Abrahamic faiths.
Denominations of Christianity
Christianity encompasses a variety of denominations or branches.
The principal branches of the Christian Church include:
- Roman Catholics
- Protestants, encompassing denominations such as Baptists, Methodists, and Pentecostals
- Orthodox Christians
Flowchart of Christian Denominations
The flowchart of Christian denominations includes Orthodox, Roman Catholic, Lutheran, Anglican, Baptist, Methodist, Pentecostal, and other branches.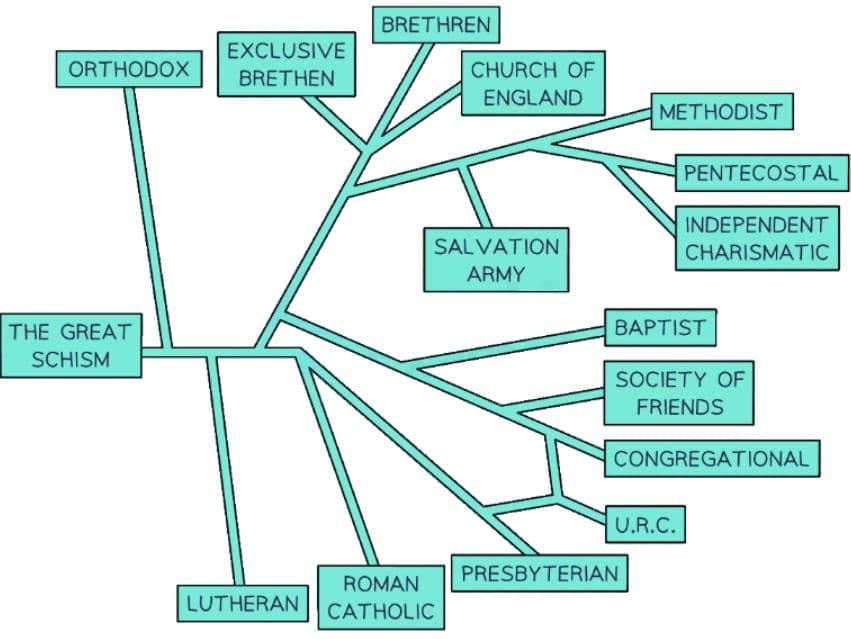
Diversity in Denominations
While these denominations share core beliefs, such as faith in one God, the Incarnation, and the teachings of the Bible, they differ in their interpretations of certain aspects of the faith, resulting in variations in:
- Tradition
- Authority
- Worship
- Teachings
The Church of England, the most prevalent denomination in the UK, blends Catholic and Protestant characteristics. Globally, the Roman Catholic Church represents the largest branch of Christianity.
The Roman Catholic Church
- The Roman Catholic Church boasts over a billion adherents worldwide.
- Like other Christian denominations, Catholics believe in one God, the Trinity, the Incarnation, and the teachings of the Bible.
- The Catholic Church traces its roots to Jesus Christ and his apostles, with Saint Peter regarded as the first Pope.
- The Church upholds the principle of apostolic succession, where the authority granted by Jesus to his apostles has been transmitted through generations to the bishops and the Pope, who governs the Church from Rome.
- Consequently, the authority of the Pope and Church tradition holds significant importance for Catholic Christians.
- Catholic Christianity places strong emphasis on the seven sacraments.
FAQs on Introduction to Catholic Christianity - Religion, Philosophy & Ethics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is the significance of the Roman Catholic Church in Christianity? |  |
| 2. What are the core beliefs of Catholic Christianity? |  |
| 3. How does the Roman Catholic Church view the sacraments, and how many are there? |  |
| 4. What role does the Pope play in the Roman Catholic Church? |  |
| 5. What historical events have shaped the development of the Roman Catholic Church? |  |















