Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Religion, Philosophy & Ethics for GCSE/IGCSE > Diversity in Islam
Diversity in Islam | Religion, Philosophy & Ethics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Introduction
In Islamic tradition, the period before Islam in Arabia is known as the Age of Jahiliyyah, often described as a time of ignorance regarding key Islamic concepts such as Tawhid (the oneness of God), Risalah (prophethood), and Akhirah (the afterlife).
Muslims believe:
- Arabia before Islam was a turbulent and perilous society, marked by frequent tribal conflicts and the mistreatment of women.
- The people of Arabia had strayed from the divine messages previously delivered by Allah through the Prophet Ibrahim.
- Ibrahim introduced Islam to Arabia and restored the Ka’aba, which is believed to have been originally constructed by Adam.
- Islam was established as a religion in the 7th century.
- Adherents of Islam are referred to as Muslims.
- Islam is a monotheistic faith, with Muslims worshipping only one God, Allah.
- The Qur’an serves as the sacred text of Islam.
- Muslims also adhere to the teachings and sayings of the Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him), which are recorded in the hadiths.
- Muhammad (peace be upon him) founded Islam, receiving divine revelations of the Qur’an from Allah.
- Islam shares certain principles with other Abrahamic faiths, namely Judaism and Christianity.
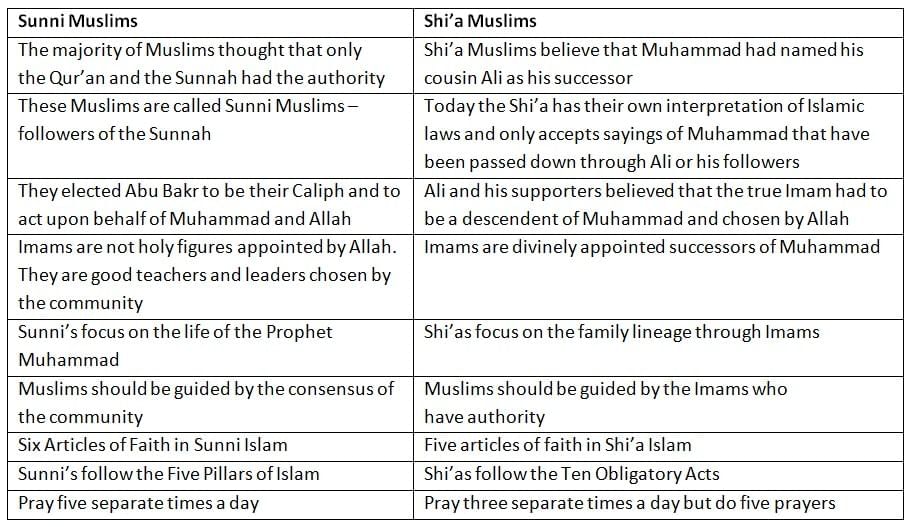
The Two Main Traditions
- Islam is divided into two major branches: Sunni and Shi’a.
- Approximately 85-90% of Muslims worldwide are Sunni, with the majority of the remainder being Shi’a.
- While the core beliefs, or Articles of Faith, differ slightly between Sunni and Shi’a Muslims, there is significant overlap in their fundamental principles.
- Both sects share the following beliefs:
- Allah is the one true God.
- The Qur’an is the ultimate source of religious authority.
- The primary prophets are the same in both traditions.
- Both believe in the Day of Judgment.
- A key point of divergence lies in the historical leadership of the Muslim community following Muhammad’s death.
- Some Muslims supported Ali as the rightful first Caliph, believing the first three Caliphs were unjustly appointed.
- Others believed Ali should not have been considered for the role at all.
The document Diversity in Islam | Religion, Philosophy & Ethics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Religion, Philosophy & Ethics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
FAQs on Diversity in Islam - Religion, Philosophy & Ethics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is the significance of diversity in Islam? |  |
Ans. Diversity in Islam is significant as it reflects the religion's universal message and its ability to transcend cultural, ethnic, and geographical boundaries. Islam promotes the understanding that all human beings, regardless of their backgrounds, can be united under the belief in one God. This diversity enriches the Muslim community (Ummah) and fosters a sense of belonging and cooperation among different groups.
| 2. How does cultural diversity manifest within Islamic practices? |  |
Ans. Cultural diversity within Islamic practices is evident in the various ways Muslims express their faith, including different styles of prayer, dress, and celebration of religious holidays. For instance, while the core tenets of Islam remain the same, the ways of performing prayers (Salah), observing Ramadan, and celebrating Eid can vary widely between cultures, reflecting local customs and traditions.
| 3. What role does language play in the diversity of Islam? |  |
Ans. Language plays a crucial role in the diversity of Islam as it influences the interpretation and practice of Islamic teachings. The Quran is originally in Arabic, but translations exist in many languages, allowing non-Arabic speakers to access its message. Additionally, local languages are often used in religious teachings, community gatherings, and cultural expressions, further enriching the Islamic experience across different regions.
| 4. How has historical migration influenced the diversity of the Muslim community? |  |
Ans. Historical migration has significantly influenced the diversity of the Muslim community by leading to the spread of Islam across various regions. As Muslims migrated due to trade, conquest, or seeking refuge, they carried their beliefs and practices with them, blending with local cultures. This has resulted in a rich tapestry of Islamic traditions, customs, and interpretations that vary from one region to another, enhancing the global Muslim identity.
| 5. What are some common misconceptions about diversity in Islam? |  |
Ans. Common misconceptions about diversity in Islam include the belief that all Muslims share the same culture, practices, and beliefs. Many people may think of Islam as a monolithic religion, overlooking the significant variations across different cultures and societies. These misconceptions can lead to stereotyping and misunderstanding, highlighting the importance of educating others about the true diversity within the Islamic faith.
Related Searches




















