Resources: Water, Mineral and Human | Social Science Olympiad Class 4 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| 1. Water Resources |

|
| 2. Mineral Resources |

|
| 3. Human Resources |

|
| Remember! |

|
1. Water Resources
1.1 Why Water Is Important?
Our body needs water: a 100 kg animal has about 65 kg of water, and some plants can be 99 % water!
Water is as essential as air—you can’t go a day without it!
Water is used for:
Drinking and cooking
Cleaning, flushing toilets, and carrying away waste
Factories and industries
Fishing and caring for forests
Generating electricity with dams (hydropower)
Growing crops on farms
1.2 Where Water Comes From
Surface Water
Rivers, lakes, ponds, and streams filled by rain.
Groundwater
Rainwater that seeps into the ground, collected in wells and tube-wells.
Atmospheric Water
Rain and snow from clouds (in India, monsoons bring most rain).
Ocean Water
Evaporates into the air, forms clouds, and returns as rain.
1.3 Using Water on Farms and in Power Plants
Irrigation: Canals and pumps bring water to fields so crops can grow.
Hydropower: Waterfalls turn turbines to make electricity.
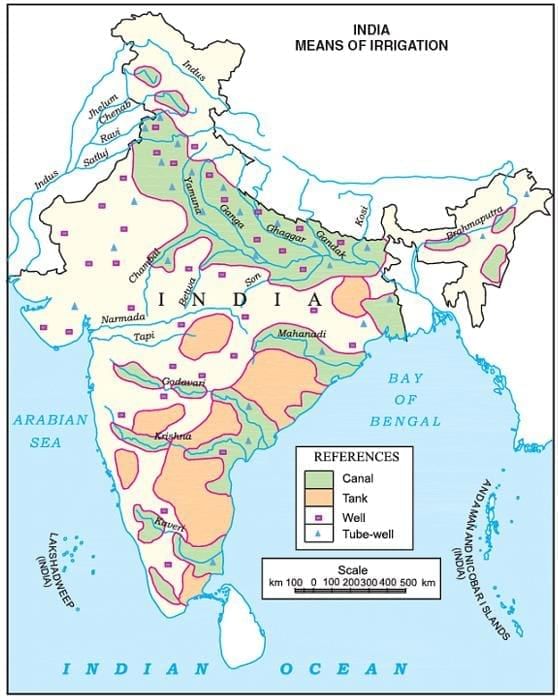
1.4 Big Challenges with Water
Uneven Rainfall: Some areas flood, others stay very dry.
Wasting Water: When water seems plenty, we often waste it.
Pollution: Dirty water can make people and animals sick.
1.5 How We Manage Water
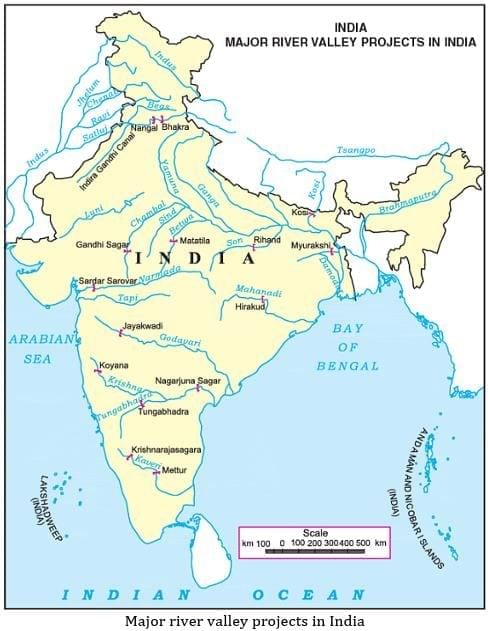
Too Much Water: Build dams to store rain and prevent floods; plant trees to stop soil washing away.
Too Little Water: Collect rainwater, dig deeper wells, and build canals.
Cleaning Water: National programs work to keep rivers clean, even when traditions make it hard.
2. Mineral Resources
2.1 What Are Minerals?
Ores are rocks dug from deep underground (mines).
Ores are refined to get pure metals (like iron, copper, aluminium) or other materials (like coal and petroleum).
 Coal Railway Engine
Coal Railway Engine
2.2 Important Minerals in India
Iron Ore: Found in Odisha, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, and Goa. Made into steel at Jamshedpur, Bhilai, Rourkela, Durgapur, and Bokaro.
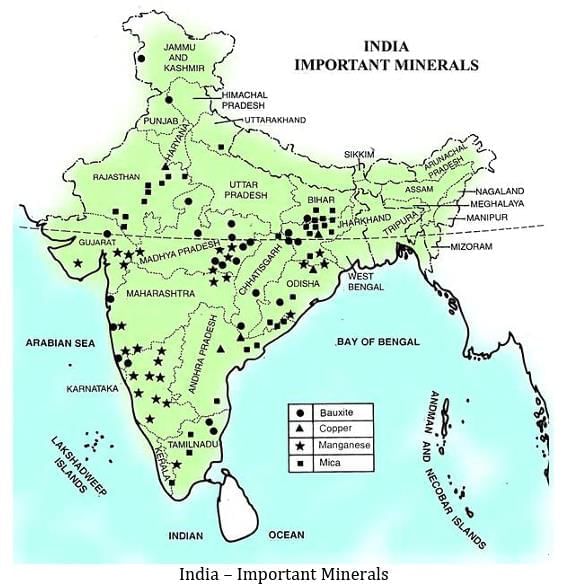
Coal: Fuels steel mills and power stations.
Petroleum: Piped from wells in Assam, Gujarat, and Bombay High; refined into petrol, diesel, kerosene, LPG, and more.
Copper: First metal used by humans; makes electric wires.
Manganese: Makes steel harder.
Mica: Insulates electrical machines.
Aluminium: Builds aircraft bodies.
Limestone: Used in cement.
Gold: Mined in Kolar, Karnataka.
2.3 Why We Must Conserve Minerals
Minerals are limited—one day they will run out.
We must avoid waste and look for renewable energy (wind, solar) to reduce pollution.
3. Human Resources

3.1 Who Are Human Resources?
Every person—pilots, soldiers, actors, musicians, engineers, doctors, teachers—helps society.
Together, skilled people form our country’s human resources.
3.2 Why Skills and Education Matter
If a country has too few trained people, it cannot grow well.
Education builds knowledge and skills for jobs and keeps roads, hospitals, and communications running smoothly.
3.3 Other Factors That Help Development
Good transport and clear roads
Strong communication (phones, internet)
Accessible healthcare (hospitals, clinics)
All these depend on educated and skilled workers.
Remember!
Water is everywhere but not always where we need it—protect and share it.
Minerals lie under the ground—use them wisely and explore clean energy alternatives.
People are our greatest resource—learn well and help build a better nation.
|
26 docs|22 tests
|
FAQs on Resources: Water, Mineral and Human - Social Science Olympiad Class 4
| 1. What are the main types of water resources available on Earth? |  |
| 2. How do mineral resources impact the economy? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of human resources in sustainable development? |  |
| 4. How can water resources be conserved effectively? |  |
| 5. What are some renewable and non-renewable mineral resources? |  |















