How to Study Ray and Wave Optics for NEET | Physics Class 11 PDF Download
Introduction
Ray and Wave Optics is a foundational chapter in NEET Physics, combining intuitive concepts with high exam relevance. It deals with the geometric behavior of light through reflection and refraction, as well as its wave nature—interference, diffraction, and polarization.
Over the years (2016–2025), this chapter has consistently contributed 4–6 questions, accounting for 8–12 marks in the NEET Physics section. Its conceptual clarity and predictable question patterns make it one of the most scoring areas for students.
This chapter guide focuses on high-frequency topics from both Ray Optics and Wave Optics, offering a structured study plan, targeted revision strategies, and key exam-day tips to help you approach problems with confidence and precision.

Understanding NEET Ray and Wave Optics Syllabus
This chapter covers both geometric and wave aspects of light, making it diverse and application-driven. Here's what you’ll be studying:
Ray Optics (Reflection, Refraction, Lenses, Mirrors)
Wave Optics (Huygens' Principle, Superposition)
Interference
Diffraction
Polarization
Optical Instruments
Dispersion
Young's Double Slit Experiment
Thin Film Interference
Focus on Core Concepts
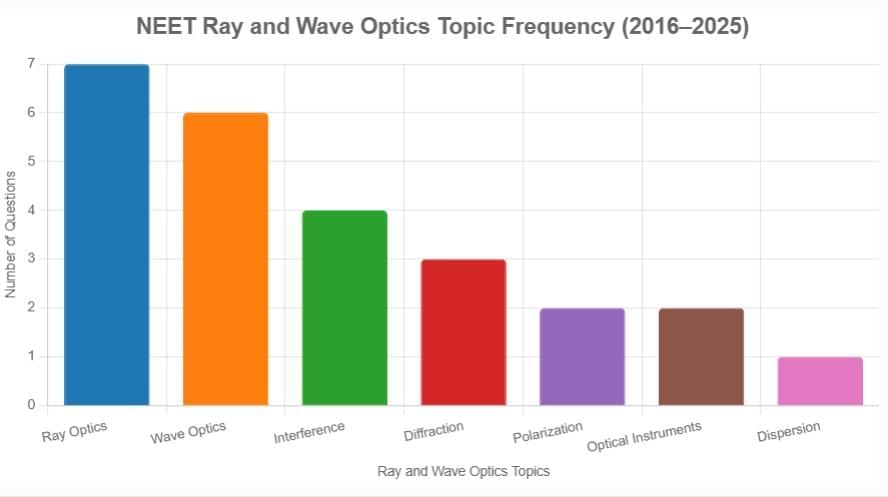
Knowing which topics matter most can supercharge your revision. Based on the 2016 - Present NEET analysis, here’s the topic-wise breakdown of all the core concepts that we should focus on
Ray Optics (7 questions): Lens formula, mirror equation, and refraction.
Wave Optics (6 questions): Huygens' principle and wave nature of light.
Interference (4 questions): Constructive and destructive interference.
Diffraction (3 questions): Single slit and grating patterns.
Polarization (2 questions): Polarization by reflection and Malus' law.
Optical Instruments (2 questions): Microscope and telescope.
Dispersion (1 question): Prism and rainbow formation.
How to Study Important Topics
Once you know what to study, it’s time to understand how to study each topic. Here's how to approach the important topics smartly
Ray Optics
Focus: Master lens formula (1/f = 1/v - 1/u) and mirror equation (1/f = 1/v + 1/u); understand refraction and reflection, often tested with lens and mirror problems.
Method: Solve 10–15 problems daily on focal length, derive equations, and analyze image formation.
Wave Optics
Focus: Grasp Huygens' principle and superposition; frequently tested with wave nature of light in Young's experiment.
Method: Practice 5–10 problems daily on wave propagation, derive v = fλ, and study wavefronts.
Interference
Focus: Learn interference condition (d sinθ = mλ); commonly tested with Young's double slit experiment.
Method: Solve 5–10 problems daily on fringe width, derive the condition, and analyze interference patterns.
Diffraction
Focus: Understand diffraction minimum (a sinθ = mλ); often tested with single slit diffraction.
Method: Practice 5–10 problems daily on diffraction angles, derive the formula, and study grating effects.
Resources for Important Topics
Core Materials: NCERT Physics Class 12 (Chapter 9: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, Chapter 10: Wave Optics), HC Verma's Concepts of Physics (Optics), DC Pandey's Objective Physics for NEET.
Supplementary Resource: EduRev app (EduRev) for video lectures, practice questions, and mock tests tailored to NEET preparation.
Memorize and Understand Formulas
Memorizing all the formulas can certainly give you an edge in the main exam. The following is a list of formulas that are essential for solving both conceptual and numerical questions with speed and accuracy.
Essential Formulas

Learning Approach
Develop a formula sheet and derive equations (e.g., lens formula) to deepen understanding.
Use flashcards for quick recall.
Apply formulas in numerical problems to reinforce concepts and avoid rote learning.
Numerical Practice
- Daily Objective: Solve 20–30 numerical problems daily, prioritizing high-frequency topics: Ray Optics, Wave Optics, Interference, and Diffraction.
- Problem Sources: DC Pandey's Objective Physics, past NEET question papers, and EduRev app question banks.
- Focus Areas: Lens and mirror calculations, wave speed problems, interference fringe analysis, and diffraction patterns.
- Strategy: Time practice sessions to 1–2 minutes per question and maintain an error log to address recurring mistakes.
Analysis of Previous Years' Papers
- Purpose: Identify patterns and difficulty levels in Ray and Wave Optics questions.
- Scope: Review NEET Physics papers from 2016–2025, focusing on Ray Optics (e.g., lens systems), Wave Optics (e.g., Young's experiment), and Interference (e.g., fringe spacing).
- Expectation: Anticipate 4–6 questions, with a strong likelihood of Ray Optics and Wave Optics problems.
- Resource: Utilize EduRev app (EduRev) for past papers.
Mock Test Practice
- Objective: Simulate exam conditions to improve time management and accuracy.
- Goal: Aim for 1–2 minutes per question during timed mock tests.
- Resource: Use EduRev app (EduRev) for mock tests and analyze performance on high-priority topics.
Exam Day Tips
Quick Formula Review: Before the exam, glance at your formula sheet for Ray Optics, Wave Optics, and Interference to reinforce key equations.
Prioritize High-Weightage Questions: Start with Ray Optics and Wave Optics questions, as they are more likely to appear and often solvable with clear formulas.
Time Allocation: Spend 1–2 minutes per question; skip complex numericals initially and return if time permits.
Check Units and Calculations: Ensure units are consistent (e.g., meters for wavelength) and double-check multi-step calculations, especially for Interference.
Stay Calm: If stuck on a diffraction or polarization problem, take a deep breath and break it into smaller steps (e.g., use diffraction formula).
Additional Preparation Strategies
Consistency: Maintain a daily commitment of 2 hours to Ray and Wave Optics for steady progress.
Precision: Verify calculations in multi-step numericals (e.g., Ray Optics, Interference) to minimize errors.
Time Management: Allocate 1–2 minutes per question initially, revisiting complex problems as needed.
Well-being: Prioritize 6–8 hours of sleep, incorporate 5-minute breaks hourly, and maintain a balanced diet to support focus and stamina.
Motivation: Set achievable short-term goals (e.g., mastering Ray Optics) and acknowledge progress to sustain momentum.
This structured guide, grounded in NEET trends and enriched with targeted strategies, is your ultimate roadmap to conquer Ray and Wave Optics. Focus on Ray Optics, Wave Optics, Interference, and Diffraction to maximize your Physics score. Best wishes for your NEET preparation!
|
119 videos|494 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on How to Study Ray and Wave Optics for NEET - Physics Class 11
| 1. What are the core concepts included in the NEET Ray and Wave Optics syllabus? |  |
| 2. How can I effectively memorize and understand the formulas related to Ray and Wave Optics for NEET? |  |
| 3. What strategies can I use for numerical practice in Ray and Wave Optics for NEET? |  |
| 4. How can analyzing previous years' papers help in preparing for the Ray and Wave Optics section of NEET? |  |
| 5. What are some effective exam day tips for tackling the Ray and Wave Optics section in NEET? |  |





















