Kurukshetra Summary: May 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Empowering MSMEs through Science and Technology |

|
| Navigating the Future of MSME Finances |

|
| Technology Adoption by MSMEs in India |

|
| Revitalizing Indian MSMEs |

|
Empowering MSMEs through Science and Technology
 Empowering MSMEs
Empowering MSMEs
MSMEs (Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises) are crucial for India's economic growth. They create jobs, contribute to exports, support rural development, and ensure inclusive growth. MSMEs help distribute income fairly and generate job opportunities, especially in rural and semi-urban areas.
There is an urgent need to connect MSMEs with scientific and technological progress to turn publicly funded research and development into useful products and processes.
Science & Technology Interventions for MSMEs
 Rural Innovation Hub
Rural Innovation Hub
- Government initiatives offer MSMEs resources for research, innovation, and technology, enhancing their global competitiveness and visibility.
- MSMEs are emerging as hubs of indigenous technological innovation in fields like energy-efficient electronics, electric bicycles, drone technology, healthcare devices, and clean technology.
Key Science & Technology Initiatives
Common Research and Technology Development Hub (CRTDH)
- The CRTDH, initiated by the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research (DSIR) in 2014-15, promotes innovation within MSME clusters by fostering collaboration among industry, academia, and government. It offers essential resources such as R&D facilities, testing laboratories, design centres, pilot plants, and prototype development support.
- Presently, 18 CRTDHs operate across various sectors, including electronics, renewable energy, affordable healthcare, environmental technology, and advanced materials. These hubs aim to create a conducive environment for innovation and commercialisation.
CSIR Mega Innovation Complex for MSMEs
- Established in January 2023 in Mumbai by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), the CSIR Mega Innovation Complex for MSMEs provides state-of-the-art incubation laboratories, technical assistance, scientific infrastructure, and networking facilities. This initiative fosters collaboration among MSMEs, startups, CSIR laboratories, deep-tech companies, and public research institutions, offering advanced scientific expertise and business development support.
NIDHI-Technology Business Incubator (NIDHI-TBI) Programme
- Launched by the Department of Science and Technology as part of the NIDHI initiative, this programme supports high-risk, high-potential technology startups through incubators situated in educational and research institutions.
- The programme provides infrastructure, mentorship, legal, financial, and intellectual property consultancy to assist startups in swiftly commercialising their innovations and creating jobs in line with national priorities.
NIDHI-Inclusive Technology Business Incubator (NIDHI-ITBI)
- NIDHI-ITBI promotes innovation and entrepreneurship in emerging startup ecosystems, particularly in rural areas, tier-2, and tier-3 cities. It emphasises social inclusion by targeting women, geographical diversity, and individuals with disabilities.
- The initiative offers grants for proof of concept, prototyping, and early-stage development while nurturing local innovation networks that connect academia, investors, and industry.
Centre for Rural Enterprise Acceleration through Technology (CREATE)
- Established in Leh, CREATE aims to foster rural industrialisation and MSME development in challenging regions like Ladakh. The centre focuses on training and developing local products such as pashmina wool, essential oils, and bio-processing to enhance productivity, quality, economic capacity, and livelihoods in remote areas.
Expansion of Technology Development Centers
 Technology Hubs
Technology Hubs
- The Ministry of MSME currently operates 33 Technology Development Centers that offer support to MSMEs in various sectors, focusing on areas such as design, manufacturing, skill development, and access to advanced technologies.
- To improve the availability of these centers, new ones are being established under a Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model.
- These new centers will provide services including job work, precision production, and the manufacturing of specialized tools.
Scheme for New Technology Centers and Extension Centers
- The objective is to establish 20 Technology Centers and 100 Extension Centers using a hub-and-spoke model.
- This initiative aims to introduce transformative technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Internet of Things (IoT), and Robotics to empower grassroots and remote communities.
- So far, 25 Extension Centers have been set up, providing training to over 72,000 individuals and assisting 1,440 MSMEs.
Overall Impact
- Initiatives in science and technology are enhancing the competitiveness, innovation, and global recognition of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). These initiatives are fostering an environment that promotes innovation, job creation, rural development, and inclusive growth. Consequently, the MSME sector is evolving from basic economic units into centers of innovation. These centers are now crucial contributors to sustainable development within India’s economy.
Navigating the Future of MSME Finances

Role of MSMEs in the Economy
- MSMEs (Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises) are vital for economic growth, especially in driving various industries in rural and underdeveloped areas.
- Globally, MSMEs represent about 90% of businesses, generate 60-70% of jobs, and contribute nearly 50% to GDP.
- In India, as of April 2023, there are 6.23 crore registered MSMEs employing 26.66 crore people.
- MSMEs contribute to around one-third of India’s GDP and account for over 45% of exports.
- This sector encompasses a wide range of industries, including food processing, textiles, auto parts, hospitality, and manufacturing, such as components for Chandrayaan.
- About 70% of MSMEs are service-based, with micro-enterprises being the most common.
Evolving Definition of MSME
 MSME Growth
MSME Growth
- Effective April 1, 2025, the definitions for MSMEs were broadened, with turnover limits doubled and investment ceilings raised by providing clear numerical values.
- Previously, classifications relied only on investment figures; since 2020, MSMEs are classified based on two criteria: investment and turnover.
- The government has made the registration process easier through the Udyam Registration Portal (URP) and Udyam Assist Platform (UAP), helping smaller businesses to register formally.
- This formalisation led to an increase in MSME registrations from 1.65 crore (April 2023) to 6.23 crore (April 2025).
- The states with the most MSME registrations are Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu.
Strengthening MSMEs: Government Initiatives
- MSMEs depend on various factors like skill development, affordable finance, technology, marketing, and infrastructure for their growth.
- In the 2025 Budget, the government raised the classification limits for MSMEs. This change aims to avoid penalizing growth and to extend MSME benefits to larger firms.
- By expanding the MSME classification, the government promotes inclusivity, competitiveness, and overall development.
MSME Finance Framework
- MSMEs play a crucial role in Priority Sector Lending (PSL). Banks are required to allocate 40% of Adjusted Net Bank Credit (ANBC) for PSL, with 7.5% specifically for Micro Enterprises.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) aims for a 20% year-on-year credit growth target for Micro and Small Enterprises (MSEs) and seeks to improve their access to lending.
- Loans of up to ₹10 lakh for MSEs are offered without collateral.
- The RBI is considering the removal of foreclosure charges on floating-rate loans. This change would allow MSMEs to switch lenders more easily and benefit from lower interest rates.
Credit Guarantee Scheme (CGS)
The Credit Guarantee Scheme (CGS) supports lenders by providing guarantees through the Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE).
- In April 2023, the guarantee limit increased from ₹5 crore to ₹10 crore.
- The coverage varies based on specific criteria: 90% for women-owned businesses, 85% for SC/ST entrepreneurs, 80% for firms in the North-East and Jammu & Kashmir, and 75% for other businesses.
- Since its inception in 2000, CGS has issued 71 lakh guarantees totaling ₹4.27 lakh crore. Between 2023 and 2025, an additional 44 lakh guarantees worth ₹5.02 lakh crore were granted.
- The reduction of guarantee fees by 50% in 2023 significantly increased the utilization of the scheme.
Important Schemes for MSMEs
- Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP): This scheme encourages self-employment by supporting small businesses in non-farming areas. It offers substantial financial assistance, covering up to 95% of bank financing with subsidies for starting businesses, which can go up to 35%. Since its inception, PMEGP has facilitated the establishment of over 1 million businesses and the creation of 8.3 million jobs.
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY): PMMY provides collateral-free loans for income-generating activities. Since 2015, the scheme has disbursed over 516.7 million loans, amounting to ₹32.61 trillion, helping to promote entrepreneurship and small businesses across the country.
- PM Vishwakarma Scheme: Launched in 2023, this scheme aims to support traditional craftsmen by offering skills development, tools, digital support, and low-interest loans. In a short span of 18 months, nearly 3 million beneficiaries have enrolled, and 400,000 loans have been approved. The scheme offers loans up to ₹300,000 at a low-interest rate of 5%, with government backing.
- Self Reliant India Fund: This fund was established under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative, with a ₹10,000 crore contribution from the government and ₹50,000 crore from private equity. It aims to provide equity funding to growth-oriented MSMEs through venture capital, supporting their expansion and development.
- MSMEs (Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises) are crucial for India’s growth, job creation, and exports.
- Recent policy changes have expanded the definition of MSMEs, allowing more businesses to benefit from government support.
- Access to affordable, collateral-free finance and credit guarantees is essential for driving MSME growth and formalisation.
- Government initiatives such as PMEGP, PMMY, and PM Vishwakarma offer significant support, including credit and skill development for MSMEs.
- Upcoming RBI guidelines on foreclosure fees could improve credit flexibility for MSMEs.
- The expansion of the Credit Guarantee Scheme reflects the government’s commitment to reducing financial barriers for MSMEs.
Technology Adoption by MSMEs in India
Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) play a vital role in India’s economy, with over 4 crore enterprises employing nearly 18 crore people. They contribute around 30% to the GDP and nearly 50% of exports, earning them the title of the engine of inclusive growth. However, these enterprises face significant challenges in adopting technology, which impacts their productivity, innovation, and global competitiveness.
Key Points
- MSMEs are crucial for providing employment and contributing to the national income.
- They are a major source of exports, highlighting their importance in the global market.
- Despite their contributions, the sector struggles with technology adoption, which is essential for improving efficiency and staying competitive.
- Addressing these challenges is crucial for enhancing the overall productivity and global standing of MSMEs in India.
Present Situation of Technology in MSMEs
- The technology ecosystem for MSMEs in India is currently fragmented and not fully developed.
- A significant number of MSMEs are still relying on outdated machinery.
- These enterprises do not have adequate in-house research and development (R&D) capabilities.
- MSMEs face challenges in commercialising innovations.
- Despite the existence of government-supported R&D and innovation programmes, the absence of structured connections between MSMEs and technology institutions hampers the effective absorption and integration of new technologies.
Major Challenges in Embracing Technology
- Financial Limitations: Access to affordable credit is limited, and there are high capital expenses along with narrow profit margins. This situation makes it difficult for businesses to invest in new technologies and machinery for the long term.
- Awareness and Digital Literacy Deficiencies:. significant number of owners and workers in Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) are unaware of relevant technologies and their benefits. Additionally, low levels of digital skills further impede the use of digital tools and platforms.
- Insufficient Market Intelligence: The lack of access to data regarding consumer behaviors, demand trends, and global market insights restricts innovation and competitiveness for MSMEs.
- Skill Shortages and Workforce Limitations: There is a noticeable shortage of workers skilled in emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), automation, and data analysis. Furthermore, inadequate practical training hampers workforce development in these areas.
- Outdated Equipment and Low Efficiency: Many MSMEs depend on outdated or second-hand machinery because modern equipment is prohibitively expensive. This reliance adversely affects efficiency and product quality.
- Insufficient Infrastructure: Poor internet connectivity, unreliable power supplies, and lacking digital infrastructure, particularly in rural and semi-urban regions, pose significant barriers to technology adoption.
- Misalignment and Complexity of Technological Solutions: Numerous off-the-shelf technologies are not tailored to the needs of MSMEs. Additionally, the absence of in-house expertise hampers effective customization and integration of these technologies.
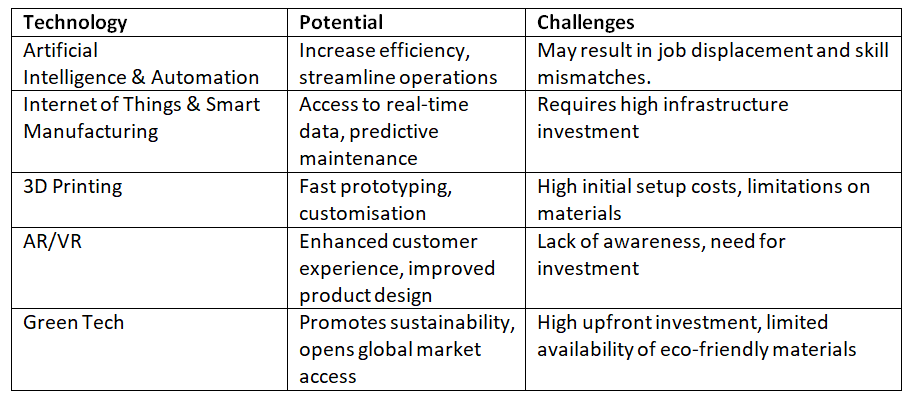
- Low Adoption of Emerging Technologies: Advanced solutions such as AI, the Internet of Things (IoT), Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), 3D printing, and Industry 4.0 are underutilized. This underutilization is due to high costs, complexity, and a lack of awareness regarding these technologies.
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact on MSMEs
 Emerging Technologies
Emerging Technologies
Government Initiatives to Support MSMEs
- MSME Technology Centres (TCs): The government has set up 15 new MSME Technology Centres with the support of the World Bank. These centres provide essential tools, assist in product development, and offer skill training to help MSMEs enhance their capabilities.
- ZED Certification Scheme: This scheme encourages manufacturers to adopt practices that ensure Zero Defects and Zero Effects in their production processes. It aims to promote high-quality manufacturing while minimising environmental impact.
- PRISM Scheme: The PRISM (Promoting Innovations in Small and Medium Enterprises) Scheme supports grassroots innovation by helping individuals, startups, and MSMEs commercialise their innovative ideas and solutions.
- Extension Centres (ECs): The government is establishing 100 Extension Centres across the country to provide Technology Centre services directly to MSMEs at the grassroots level. This initiative aims to reach last-mile MSMEs and offer them the necessary support and services.
- CGTMSE (Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises): The CGTMSE scheme facilitates easier access to credit for micro and small enterprises by providing credit guarantees for collateral-free loans. This helps reduce the risk for lenders and encourages them to extend loans to these businesses.
- Digital MSME Scheme: This initiative promotes the adoption of cloud computing and Information and Communication Technology (ICT) tools among MSMEs. The aim is to enhance their competitiveness and digital readiness in an increasingly digital economy.
- MSME Champions Portal: The MSME Champions Portal serves as a comprehensive platform for MSMEs to resolve complaints, access various government schemes, and receive real-time advisory support. It aims to streamline services and provide necessary assistance to MSMEs efficiently.
Future Directions
- Strengthening the Technology Ecosystem: Foster collaborations between industry and academia, and establish innovation hubs focused on specific sectors to co-create and implement scalable tech solutions for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
- Ensuring Access to Affordable Finance: Promote fintech and alternative lending platforms, along with subsidized credit options aimed at enhancing technology adoption.
- Capacity Building and Skill Development: Increase the number of tool rooms and training centers, especially in underdeveloped regions, while emphasizing skill enhancement in digital technologies, smart manufacturing, and sustainable practices for the workforce.
- Upgrading Infrastructure: Improve internet connectivity, ensure a reliable power supply, and develop digital infrastructure in rural and semi-urban areas to facilitate industrial growth.
- Promoting Green and Sustainable Manufacturing: Offer subsidies for the adoption of green technologies and establish certification and branding for eco-friendly MSMEs to enhance their market competitiveness.
Conclusion
 MSME Digital Growth
MSME Digital Growth
- The foundation laid by various government initiatives is commendable.
- However, a more focused, inclusive, and cooperative approach is essential to address the existing challenges.
- Key areas that require improvement include:
- Enhancing access to finance
- Building robust digital infrastructure
- Upskilling the workforce effectively
- Fostering innovation ecosystems
- By concentrating on these areas, India can fully harness the potential of its MSME sector.
- This focus will be instrumental in achieving global competitiveness in the digital age.
Revitalizing Indian MSMEs
The Union Budget for 2025-26 marks a crucial shift in India's growth strategy by prioritizing Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises ( MSMEs. as a central element of economic transformation.
- MSMEs are recognized as one of the four fundamental pillars of the economy, alongside agriculture, exports, and private investment. They play a vital role in India's industrial landscape and job market.
- With over 6.3 crore registered businesses employing more than 250 million people, MSMEs contribute 45.73% to India's total exports in FY 2025-26. They are the second-largest source of jobs after agriculture and are key to fostering decentralized industrial growth.
Revised MSME Classification for Growth
- The Budget introduces a significant change by increasing the classification limits for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) to address the "fear of graduation."
- Micro Enterprises can now invest up to ₹2.5 crore with turnover limits raised to ₹10 crore.
- Small Enterprises can invest up to ₹25 crore with turnover up to ₹100 crore, and Medium Enterprises can go up to ₹125 crore in investment and ₹500 crore in turnover.
- This 2.5x increase in investment and 2x rise in turnover limits aims to help enterprises grow without losing crucial financial and institutional benefits.
- The adjustment also seeks to address the "missing middle" in the industrial framework, facilitating smoother growth for businesses.
Credit Empowerment: Strengthening Financial Access
- The Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE) has significantly improved credit access.
- The credit guarantee limit for micro and small enterprises has been raised from ₹5 crore to ₹10 crore, unlocking ₹1.5 lakh crore in credit over five years. For innovative startups, the guarantee cap has increased to ₹20 crore with reduced fees for loans in 27 priority sectors.
- Export-oriented MSMEs can now access term loans of up to ₹20 crore, enhancing India’s global market position.
- The introduction of a specialized MSME Credit Card, offering up to ₹5 lakh in credit support, will facilitate digitized, collateral-free access to working capital, with 10 lakh cards planned for issuance in the first year.
Promotion of Startups and Inclusive Entrepreneurship
- To foster grassroots innovation and ensure inclusive growth, the Budget proposes a ₹10,000 crore Fund of Funds aimed at supporting startups across various sectors, with a particular focus on Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities.
- Additionally, a special scheme is introduced to offer term loans of up to ₹2 crore over a period of five years to 500,000 first-time entrepreneurs belonging to Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs), women, and rural youth. This scheme will also provide supplementary assistance such as seed capital, interest subvention, technical mentoring, and connections to institutions.
- These initiatives are an extension of the Stand-Up India programme and aim to make entrepreneurship more accessible across various social and geographical segments, supported by relevant metrics and examples.
Focusing on Labour-Intensive Industries for Employment and Exports
- The Government's Budget aims to modernise and globalise employment-intensive sectors such as footwear, leather, and toys.
- The Focus Product Scheme for the footwear and leather industry emphasises design innovation, component manufacturing, and growth in the non-leather segment, with the potential to create 22 lakh jobs and generate ₹4 lakh crore in turnover.
- The toy sector will receive targeted support for cluster development, modernisation, and skill building, aiming to establish India as a leading global hub for toys.
- Additionally, a National Institute of Food Technology, Entrepreneurship, and Management will be established in Bihar to enhance food processing in eastern India.
Manufacturing and Clean Tech: Driving Future-Readiness
- Under the newly launched National Manufacturing Mission, MSMEs will receive policy support and targeted strategies to integrate into broader industrial value chains.
- There is a particular emphasis on clean technology manufacturing, offering incentives for the domestic production of solar PV cells, EV batteries, wind turbines, and high-voltage transmission equipment.
- These initiatives are in line with India’s green development goals and aim to position MSMEs as vital contributors to the global shift towards clean energy, reducing import dependence and enhancing long-term industrial resilience.
Consistent Financial Support for Growth
- The Budget allocates ₹23,168.15 crore to the Ministry of MSME for FY 2025–26, a slight increase from ₹22,137.95 crore in FY 2024–25.
- Funding has varied in previous years, with a decrease to ₹17,306.70 crore in the Revised Estimate for 2024–25 and a peak of ₹23,628.73 crore in 2022–23. This year's budget reflects a steady policy commitment.
- The sector's Gross Value Added (GVA) increased from 27.3% of GDP in 2020–21 to 30.1% in 2022–23, indicating growing economic strength and influence.
Export-Led Growth and Global Integration
- MSMEs have become a significant driver in India's export growth. Their exports increased from ₹3.95 lakh crore in 2020–21 to a projected ₹12.39 lakh crore in 2024–25. The number of exporting MSMEs rose from 52,849 to 1,73,350 during this time.
- The sector’s share of exports grew from 43.59% in 2022–23 to 45.79% as of May 2024. This rise has been aided by trade facilitation, digital marketplaces, and product standardisation, helping MSMEs align with India's global trade goals.
- India’s MSMEs are not merely involved in economic development; they are essential for inclusive and sustainable growth. The 2025–26 Budget outlines a transformative plan to strengthen scale, competitiveness, and access for MSMEs across various sectors and regions. As India aims for its $5 trillion economy target, MSMEs will continue to play a crucial role in job creation, innovation, and decentralisation of industry.
|
38 videos|5167 docs|1089 tests
|
FAQs on Kurukshetra Summary: May 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC
| 1. How can MSMEs benefit from the adoption of science and technology? |  |
| 2. What are the common challenges faced by MSMEs in adopting technology? |  |
| 3. How is the government supporting MSMEs in India to navigate their finances? |  |
| 4. What role does technology play in revitalizing Indian MSMEs? |  |
| 5. What trends are emerging in the technology adoption landscape for MSMEs in India? |  |















