Geometry Chapter Notes | Mathematics for Grade 5 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Basic Geometrical Terms |

|
| Angles |

|
| Symmetry in 2D Shapes |

|
| Symmetry in 3D Shapes or Solids |

|
| Nets |

|
Introduction
Geometry is like a treasure map that helps us explore the world of shapes, lines, and angles around us! Imagine looking at the straight edges of your notebook, the curves of a round plate, or the way a door swings open to form an angle. Geometry is all about understanding these patterns and how they fit together. In this chapter, we’ll dive into the exciting world of points, lines, angles, symmetry, and 3D shapes, discovering how they appear in everyday objects like books, balls, and even buildings. Get ready to see the world through a geometric lens!
Basic Geometrical Terms
Point
- A point is a tiny dot on paper with no shape or size, like a pinpoint on a map.
- Denoted by letters like A, B, or C.
- Example: Points A, B, and C are marked as dots on a page.
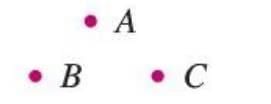
Line
- A line stretches endlessly in both directions with no start or end point.
- Denoted as
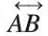 with an arrow showing it extends forever.
with an arrow showing it extends forever. - Cannot be measured as it has no fixed length.
- Example: Line
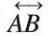 shown as a straight line extending both ways.
shown as a straight line extending both ways.
Types of Lines
Lines can be straight or curved.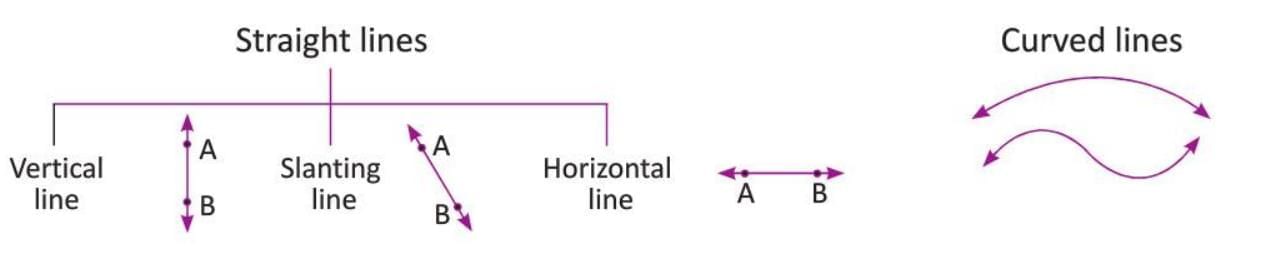
- Straight lines: Like the sides of a page.
- Curved lines: Like the edge of a bangle.
Example: The side of a page is a straight line, while a bangle’s edge is a curved line.
Line Relationships
Lines can interact in different ways.
- Intersecting Lines: Lines that cross at a common point, called the point of intersection, forming angles.
Example: Lines l and m meet at point O, forming angles at O.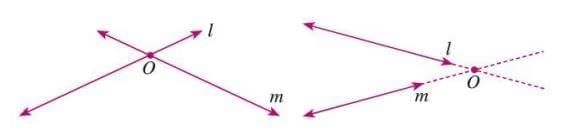
- Parallel Lines: Lines that stay the same distance apart and never meet. Denoted as l || m.
Example: Railway tracks are parallel lines, like l || min a diagram.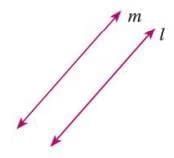
- Perpendicular Lines: Lines that meet at a right angle (90°). Denoted as l ⊥ m.
Example: An addition (+) sign shows perpendicular lines.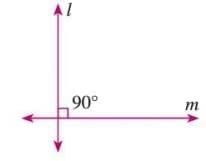
Line Segment
- A part of a line with two endpoints, measurable with a ruler.
- Denoted as
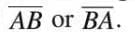 with a bar (¯) above it.
with a bar (¯) above it. - Example: Line segment
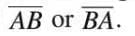 joins points A and B with a fixed length.
joins points A and B with a fixed length.
Ray
- A line with one endpoint that extends infinitely in one direction.
- Denoted as
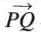 with an arrow showing the direction of extension.
with an arrow showing the direction of extension. - Example: Ray PQ starts at P and extends indefinitely through Q.

Angles
An angle forms when two rays meet at a common point, called the vertex.
- The rays are called the arms of the angle.
- Denoted with the symbol ∠, like ∠CAB or ∠BAC.
- Example: In a figure, rays AB and AC meet at vertex A, forming ∠CAB or ∠BAC.
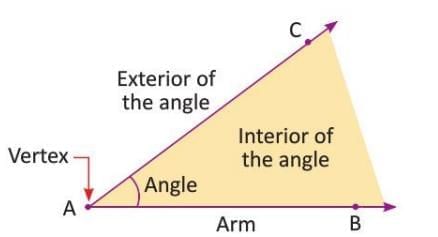
Interior and Exterior
- The space between the rays is the interior, and the outside is the exterior.
Angle as Rotation
- An angle measures the amount of turn between two rays at their vertex.
- Example: The angle between the arms of a hand fan changes as it opens or closes.
Classification of Angles
- Right Angle: Measures exactly 90°, formed by a vertical and horizontal line.
- Example: The corner of a book forms a right angle.

- Example: The corner of a book forms a right angle.
- Acute Angle: Measures more than 0° but less than 90°.
- Example: The angle in a slice of pizza is often acute.

- Example: The angle in a slice of pizza is often acute.
- Obtuse Angle: Measures more than 90° but less than 180°.
- Example: The angle of a reclining chair’s backrest is obtuse.

- Example: The angle of a reclining chair’s backrest is obtuse.
- Straight Angle: Measures exactly 180°, forming a straight line.
- Example: A fully open book forms a straight angle.

- Example: A fully open book forms a straight angle.
Measure of an Angle
An angle’s measure is the amount of rotation between its two arms.
- Measured in degrees (°), the standard unit for angles.
- The gap between arms affects the angle size, not the arm length.
- Example: A hand fan’s angle increases as its arms open wider, but arm length doesn’t change the angle.

Measuring an Angle with a Protractor
A protractor is a semicircular tool with two scales (inner and outer) marked from 0° to 180°.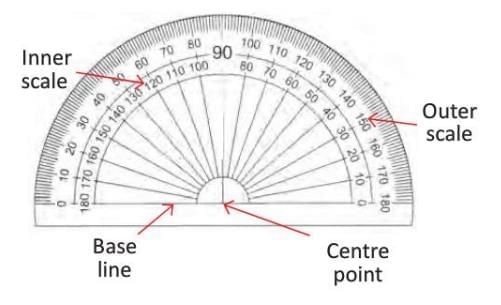
- Inner scale: 0° to 180° anticlockwise.
- Outer scale: 0° to 180° clockwise.
- Example: A protractor’s inner scale starts at 0° on the right and goes to 180° anticlockwise.
Steps to Measure an Angle:
- Place the protractor’s center on the angle’s vertex.
- Align the baseline with one arm of the angle.
- Check which scale starts at 0° where the baseline arm lies (inner if right, outer if left).
- Read the degree mark where the other arm points on that scale.
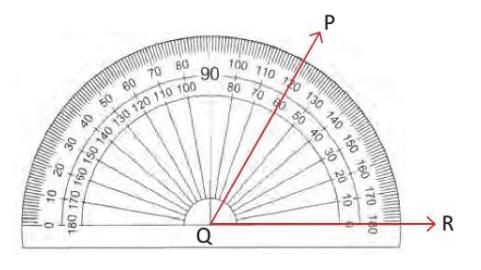
- Example: For ∠PQR, place the protractor’s center at Q, align baseline QR to 0° on the inner scale (since QR is to the right), and read 60° where QP points, so ∠PQR = 60° (acute).
Constructing Angles with a Protractor
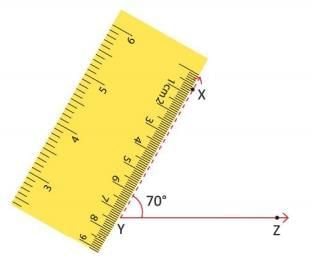
Steps to Construct an Angle (e.g., 70°):
- Draw a ray YZ using a ruler.

- Place the protractor’s center at vertex Y, aligning the baseline with ray YZ.
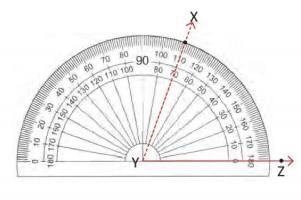
- Find 70° on the inner scale and mark it as point X.
- Remove the protractor and join points X and Y to form ∠XYZ = 70°.
Symmetry in 2D Shapes
Symmetry means a shape can be divided into two identical halves that match perfectly.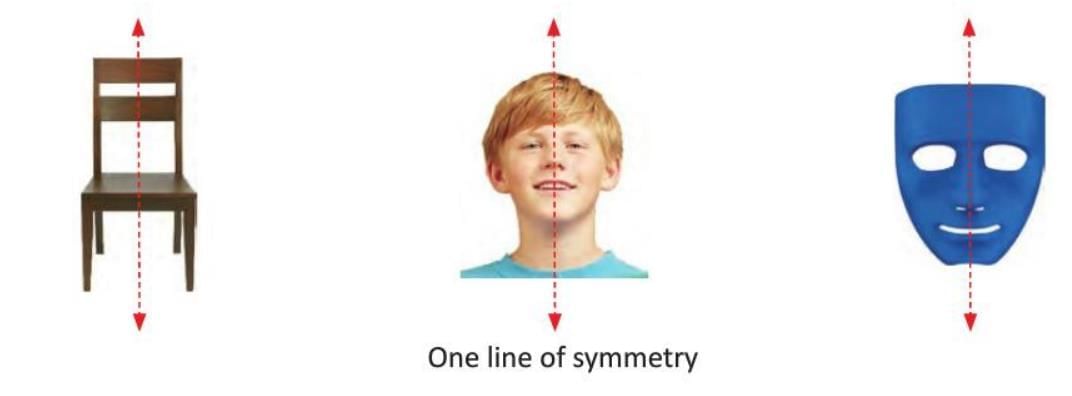
- The dividing line is called the line of symmetry (or mirror line), which can be horizontal, vertical, or in any direction.
- A shape can have one, multiple, or infinite lines of symmetry.
- Example: A square has four lines of symmetry, dividing it into identical halves when folded along each line.
Types of Symmetry
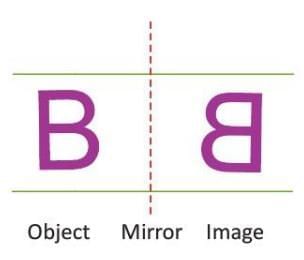
Reflection Symmetry
One half of a shape is a mirror image of the other when flipped across a line.
- Also called mirror symmetry.
- Example: The letter B has reflection symmetry, where its left half mirrors the right half across a vertical line.
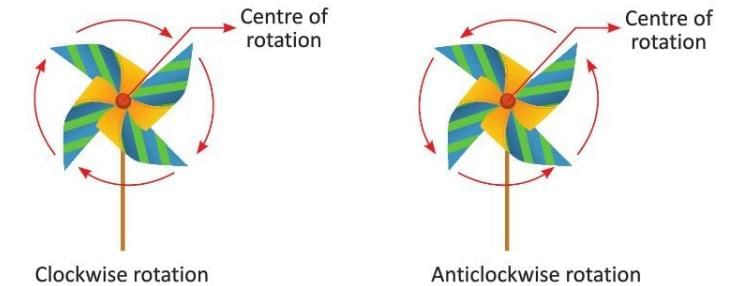
Rotational Symmetry
- Rotation can be clockwise or anticlockwise.
- Example: A pinwheel looks the same after rotating around its center, showing rotational symmetry.
Quarter Turn
- A 90° rotation.
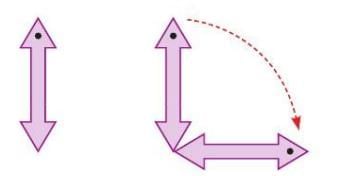
- A shape with rotational symmetry looks the same after a 90° turn.
- Example: A square looks the same after a quarter turn (90°) around its center.
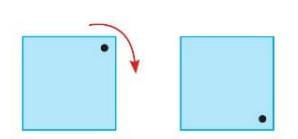
Half Turn
- A 180° rotation.
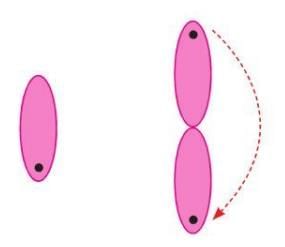
- A shape looks the same after a 180° turn.
- Example: Letter 'S' looks the same after a half turn (180°) around its center.
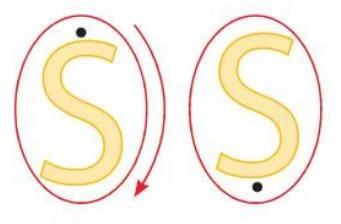
Full Turn
- A 360° rotation.
- A shape looks the same after a full 360° turn.
- Example: Letter 'L' looks the same after a full turn (360°) around its center.
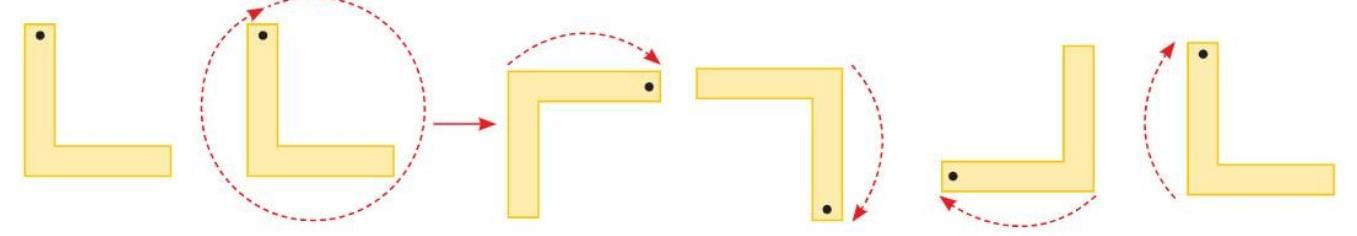
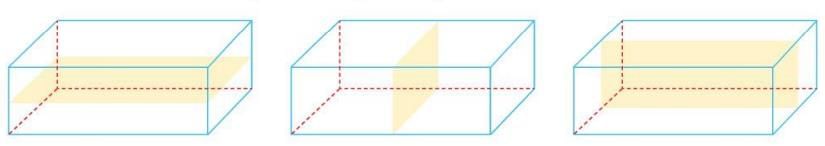
Symmetry in 3D Shapes or Solids
A 3D shape has symmetry if a plane divides it into two identical halves (mirror images).
- This plane is called a plane of symmetry.
- Example: A cube has 9 planes of symmetry, each dividing it into two identical halves.
Symmetry in Geometrical Shapes
- A cuboid has 3 planes of symmetry.
- A sphere and cone have infinite planes of symmetry.
- Example: A cuboid’s planes of symmetry divide it into two equal halves along its length, width, or height.
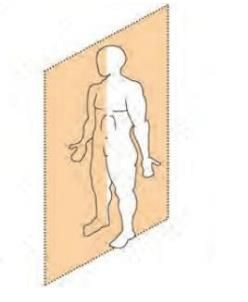
Symmetry in Human Body and Animals
- Called bilateral or mirror symmetry.
- A vertical plane divides the body into left and right mirror-image halves.
- Example: The human body shows bilateral symmetry, with left and right halves mirroring each other.
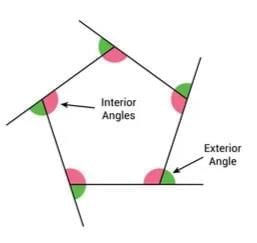
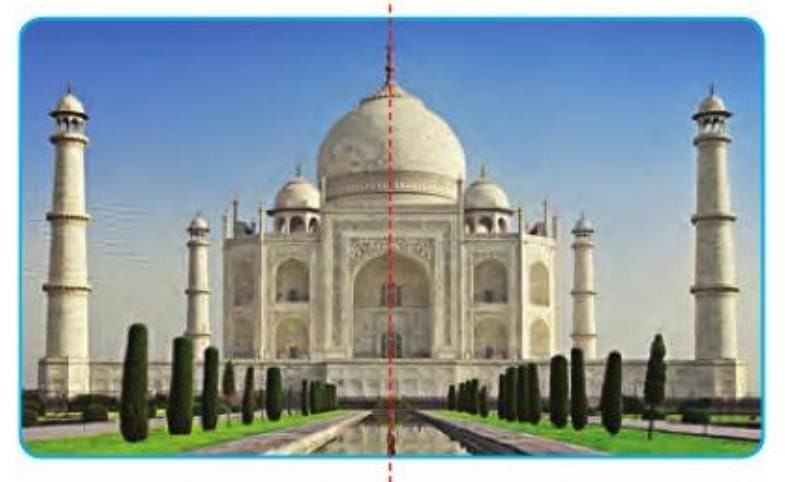
Symmetry in Buildings and Monuments
- Many structures have planes of symmetry.
- Example: A monument like the Taj Mahal has a plane of symmetry dividing it into mirror-image halves.

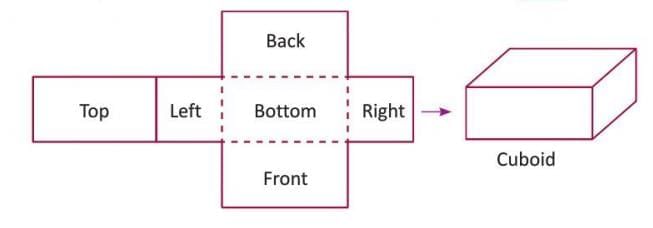
Nets
A net is a 2D shape that can be folded to form a 3D object.
- A solid can have multiple nets.
- Example: A net of a cuboid has 4 rectangles and 2 squares, which fold to form the cuboid.
|
31 videos|143 docs|25 tests
|
FAQs on Geometry Chapter Notes - Mathematics for Grade 5
| 1. What are the different types of angles and how are they classified? |  |
| 2. How can I measure an angle using a protractor? |  |
| 3. What is symmetry and what are the different types of symmetry in 2D shapes? |  |
| 4. How can I construct angles using a protractor? |  |
| 5. What is symmetry in 3D shapes and what are some examples? |  |



















