UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 2nd June 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/International Relations
International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)
Source: BBC
 Why in News?
Why in News?As of May 17, 2025, Iran possesses 408.6 kg of enriched uranium, nearing weapons-grade levels at 60%, an increase from 274.8 kg in February 2024, according to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
- The IAEA promotes the peaceful use of nuclear energy and prevents its use for weapon development.
- It was established in 1957 following President Dwight Eisenhower’s “Atoms for Peace” initiative.
- The agency has 178 member countries and is headquartered in Vienna, Austria.
- India, a founding member, has 14 out of its 22 nuclear reactors monitored by the IAEA.
Additional Details
- IAEA’s Mission: The IAEA works to ensure that nuclear energy is used safely and securely, including setting safety standards for nuclear facilities.
- Global Responsibilities: The IAEA monitors compliance with the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) to prevent the misuse of nuclear materials, conducts inspections, and provides training and support during nuclear emergencies.
- Recognition: In 2005, the IAEA was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for its efforts to curb the spread of nuclear weapons.
- India and IAEA: Under the Indo-U.S. Civil Nuclear Agreement of 2014, India agreed to implement IAEA safeguards, promoting transparency in its nuclear program.
- IAEA Safeguards in India: Some nuclear reactors are under IAEA safeguards because they use imported uranium, while others do not due to reliance on domestic supplies.
The IAEA plays a crucial role in ensuring nuclear safety and non-proliferation globally, addressing critical concerns related to nuclear energy and weapons development.
GS3/Economy
Growing Pains: On Economic Performance, Viksit Bharat
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
India's economic data for 2024-25 presents a mixed scenario: while the economy grew by 7.4% in the last quarter—better than expected—the overall annual growth fell to 6.5%, marking the lowest growth in four years since the pandemic.
- Strong growth in construction and agriculture sectors.
- Steady performance from the services sector.
- Inflation of GDP figures due to higher net tax collections.
- Annual growth of 6.5% is insufficient for 'Viksit Bharat 2047'.
Additional Details
- Robust Growth in Construction and Agriculture: The construction sector achieved double-digit growth, while strong agricultural performance enhanced rural incomes and demand. For example, infrastructure expansion and favorable harvests played significant roles.
- Strong Performance of Services Sector: The services sector showed consistent growth, especially in IT, finance, and hospitality, contributing significantly to GDP. Thus, the recovery post-pandemic has been notable.
- Statistical Boost from Higher Net Taxes: A 12.7% increase in net tax collections inflated GDP figures. Without this boost, real growth would have been around 6.8%.
- Inadequate Annual Growth: Despite being the highest globally, 6.5% growth is below the required 8% for India's development target by 2047. This rate fails to meet domestic demands for job creation and income uplift.
- Limitations of Stable Growth: While a 6.5% growth rate indicates stability with low inflation, it also suggests a plateau in economic acceleration. Experts indicate that significant growth spurts may not be imminent.
- Impact of Net Taxes on GDP Growth: A surge in net taxes can create an artificial boost in GDP figures, potentially obscuring sluggish performance in core sectors, such as manufacturing.
- Challenges of Stable Growth: Stable growth may not generate the necessary momentum for India's transition to a developed economy. With rising aspirations, a growth rate of 6.5% may not suffice to create adequate employment opportunities.
- Way Forward: To enhance productivity, India must focus on boosting investments in infrastructure, manufacturing, and digitalization, while simplifying regulations. Additionally, reviving rural consumption and supporting MSMEs is crucial for inclusive growth.
In conclusion, while the recent economic growth figures indicate some positive trends, they also highlight significant challenges that India must address to realize its vision of 'Viksit Bharat 2047'. Emphasizing structural reforms and enhancing domestic demand will be essential for sustainable economic development.
GS2/International Relations
UN Official Blames Gaza Hunger Crisis on Human Actions
Source: BBC
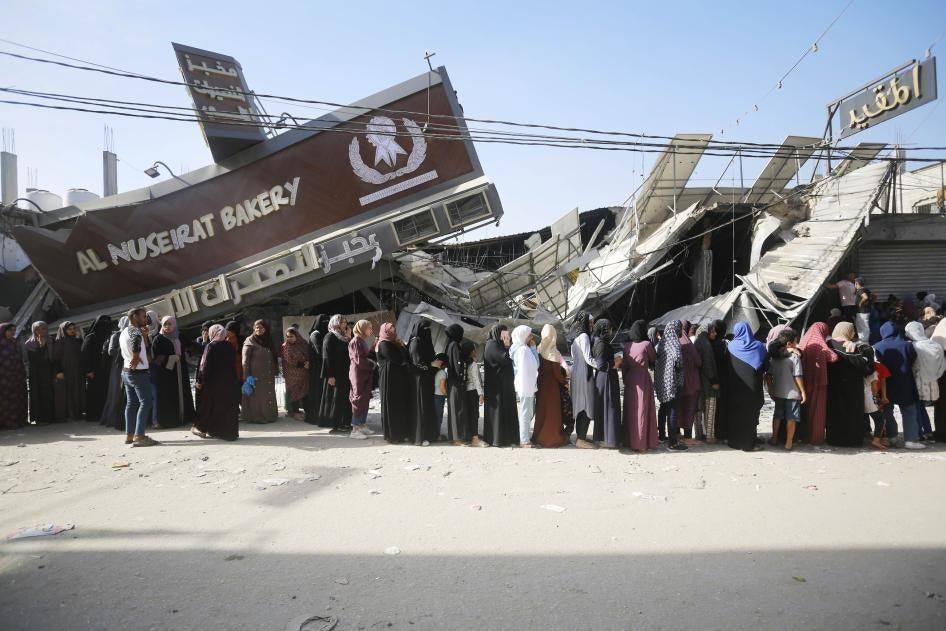 Why in News?
Why in News?Recently, approximately 50 individuals were shot and injured in Rafah as thousands of Palestinians gathered at a Gaza Humanitarian Foundation (GHF) aid distribution site amid severe food shortages. Gaza has been under a total blockade for nearly three months, exacerbating the humanitarian crisis. The UN Relief and Works Agency for Palestinian Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA) has distanced itself from GHF, following the resignation of the NGO's head, Jake Wood, on May 25, citing violations of humanitarian principles.
- Famine is looming over Gaza, attributed to human actions.
- Humanitarian aid in Gaza remains critically low.
- Legal restrictions on UNRWA disrupt essential services.
- UNRWA continues to play a vital role in Gaza's humanitarian efforts.
- India may have a significant role in addressing the Gaza crisis.
Additional Details
- Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC): This initiative, launched on May 12, provides a framework for assessing food insecurity and malnutrition. It involves collaboration among governments, UN agencies, NGOs, civil society, and other stakeholders.
- Impact of Ceasefire and Blockade: Following a ceasefire from January 19 to March 18, aid was temporarily increased. However, after the ceasefire ended and the blockade resumed, aid deliveries halted for nearly 11 weeks, resulting in acute food insecurity.
- Violation of International Law: The denial of food aid is a breach of international humanitarian law, specifically Article 54 of Additional Protocol I to the Geneva Conventions, which forbids starvation as a method of warfare.
- Rejection of GHF's Aid Model: UN and aid agencies have refused to collaborate with GHF due to its collection-point model, which violates key humanitarian principles, including impartiality and independence.
- Risks of Forced Displacement: Restricting aid to specific locations can lead to further displacement of Gazans, many of whom are already frequently relocated to so-called "safe zones" that are not safe.
- Impact in East Jerusalem: Recent Israeli laws have severely disrupted UNRWA operations in East Jerusalem, leading to the curtailment of international staff visas and the closure of schools, affecting around 800 students.
- Operational Breakdown in West Bank and Gaza: A new law has barred direct contact between UNRWA and Israeli officials, dismantling essential coordination systems. Despite this, UNRWA remains operational in Gaza, where it is the largest humanitarian agency.
- Key Services Provided:
- Logistics & Aid Distribution: Manages a wide network for aid distribution.
- Mobile Healthcare: Provides medical services through mobile healthcare points.
- Education & Psychosocial Support: Initiatives like ‘Back to Learning’ support over 20,000 children.
- Sanitation: Although UNRWA does not manage the camps, it provides sanitation services.
- Accountability & Neutrality Measures: UNRWA maintains strict neutrality and addresses allegations through internal disciplinary actions. In 2023, all accused staff were suspended pending investigations.
- India's Role: Countries like India can advocate for upholding international law and supporting decisions from the International Court of Justice (ICJ) and the UN General Assembly regarding Gaza.
The situation in Gaza remains dire, with humanitarian needs escalating and the ongoing conflict leading to violations of international law. Multilateralism is crucial in addressing these challenges to ensure global order and protect human rights.
GS2/Governance
The University Under Attack: Universities Undermined
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
Universities are currently facing significant challenges that threaten their core principles of autonomy, creativity, and dissent. This issue has been escalating in India for decades and has recently intensified in the United States since the beginning of 2025. Factors such as changing societal expectations, political interference, and financial constraints are transforming the roles of higher education institutions.
- Increased political encroachment and financial coercion are threatening academic freedom.
- Bureaucratisation in academia undermines democratic functioning and promotes conformity.
- Financial models of higher education impact institutional autonomy significantly.
Additional Details
- Political Encroachment: The actions of the Trump administration, especially regarding financial threats to institutions like Harvard, illustrate how political agendas can influence educational policies.
- Bureaucratisation: Leadership in universities often prioritizes alignment with political ideologies over intellectual merit, stifling debate and dissent.
- Funding Issues: Public funding, which is critical for research and education, has been weaponized in both India and the U.S., leading to increased political control over institutions.
The primary function of universities is to foster socially relevant knowledge, which requires the freedom to question and innovate. However, the autonomy necessary for this mission is currently under threat from various external pressures, potentially resulting in intellectual stagnation and conservatism. To maintain their transformative potential, universities must defend their autonomy as a public necessity.
GS3/Defence & Security
NDA Opens Route for Women to Lead Armed Forces
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?Seventeen women cadets graduated from the 148th NDA batch, marking a historic milestone that opens pathways for women to potentially ascend to top leadership positions within the Indian armed forces.
- The inclusion of women in the NDA signifies a transformative shift in the Indian military.
- Women can now pursue foundational leadership training and career paths previously reserved for men.
- There remains a need for cultural and structural reforms within the armed forces.
Additional Details
- Historical Background: Women's entry into the Indian military commenced with the British-era Military Nursing Service in 1888, followed by the Indian Army Medical Corps granting commissions to women doctors in 1958.
- Opening Non-Medical Roles (1992–2008): The Women Special Entry Scheme (WSES) introduced in 1992 allowed women to join select non-combat branches as Short Service Commission (SSC) officers. By 2008, women in the Judge Advocate General and Army Education Corps became eligible for Permanent Commission (PC).
- Expanding Opportunities (2019–2020): In 2019, women were permitted PC in eight additional non-combat streams. A landmark Supreme Court verdict in 2020 affirmed women's rights to PC and command roles, challenging gender discrimination.
- Breaking Barriers (2021–2024): Following a Supreme Court directive, the NDA opened its doors to women, leading to the graduation of the first female cadets in 2022, symbolizing a new chapter in gender inclusion.
- Gender-Neutral Training Approach: The NDA has adopted a gender-neutral training model, allowing male and female cadets to undergo the same regimen, fostering equality.
- Integration into Squadrons: Women cadets are fully integrated into the NDA’s squadrons, promoting camaraderie and discipline, and reflecting true equality.
- Path to Becoming Service Chiefs: Women NDA graduates can now serve for 35–40 years, essential for rising to the rank of service chief, and are prepared for combat command roles in various military branches.
- Need for Cultural and Structural Reforms: Senior military leaders stress the necessity for cultural shifts and systemic reforms regarding combat roles, maternity policies, and promotion criteria.
The opening of the NDA to women cadets marks a significant step towards gender equality in the Indian military, providing women the opportunity to pursue a career path that includes leadership and command roles. However, for true equality to be realized, ongoing reforms are necessary to address remaining challenges within the armed forces.
GS2/International Relations
Places in News: Zangezur Corridor
Source: India.com
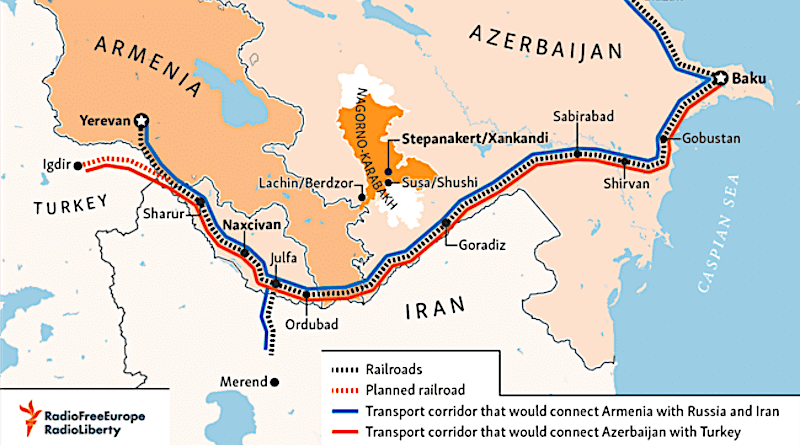 Why in News?
Why in News?The recent developments following Operation Sindoor have brought India's strategic concerns regarding the proposed Zangezur Corridor in Armenia, which is backed by Azerbaijan and Turkiye, into focus.
- The Zangezur Corridor is a proposed land route through Armenia's Syunik Province, connecting Azerbaijan to its Nakhchivan region.
- Azerbaijan and Turkiye support the project for a direct link without Armenian border checks.
- The corridor is approximately 43-44 km long and holds significant geopolitical value due to its proximity to the Iran-Armenia border.
Additional Details
- Background: The corridor's proposal follows Azerbaijan's victory in the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh conflict, which has led to claims of full control over any transport routes through Armenian territory.
- Turkiye’s Interest: Turkiye aims to incorporate this corridor into its Middle Corridor project to establish land connections with Central Asia and Europe.
- Opposition: Iran and Armenia oppose the corridor due to fears it could isolate Armenia, weaken Iranian access, and threaten Armenia's territorial integrity.
How it Concerns India?
- Strategic Ties: India is a crucial defense partner for Armenia, advocating for regional stability in the South Caucasus.
- Trade Ambitions: India is pursuing the development of Chabahar Port in Iran and is working on a transport route via Iran-Armenia-Georgia to Europe, aiming to bypass Pakistan and the Suez Canal.
- Concerns: If the Zangezur Corridor operates without Armenian oversight, it could disrupt India’s land trade routes to Europe, reduce Iran’s regional access, and weaken India’s strategic influence.
- Larger Geo-Politics: The increasing influence of Turkiye and Azerbaijan is a concern for India, particularly as Turkiye opposes the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor (IMEC).
India’s Stand
- India supports Armenia's sovereignty and opposes unilateral moves, aiming to protect its trade routes and maintain a strategic balance in the region.
- India seeks to counter regional encirclement through diplomatic and strategic means.
In summary, the Zangezur Corridor poses significant geopolitical implications, especially for India, which must navigate its strategic interests while supporting Armenia's sovereignty in the face of external pressures.
[UPSC 2023]
Consider the following pairs:
- Regions often mentioned in news : Reason for being in news
- 1. North Kivu and Ituri : War between Armenia and Azerbaijan
- 2. Nagorno-Karabakh : Insurgency in Mozambique
- 3. Kherson and Zaporizhzhia : Dispute between Israel and Lebanon
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
Options: (a) Only one (b) Only two (c) All three (d) None
GS3/Environment
Nalsarovar Bird Sanctuary
Source: TOI
Why in News?
Recently, a rare Arctic seabird, the Sabine’s Gull, was spotted at Gujarat’s Nalsarovar Wildlife Sanctuary. This marks its first recorded sighting in India since 2013, when it was observed in Kerala.
- Nalsarovar Bird Sanctuary is approximately 64 km west of Ahmedabad.
- The sanctuary spans an area of 120.82 sq km and contains shallow waters and muddy lagoons interspersed with 360 islets.
- Established as a bird sanctuary in 1969, it is recognized for its ecological significance.
Additional Details
- Historical Background: The history of Nalsarovar dates back to the 15th century when the lake was formed due to the construction of a check dam across the Sabarmati River. Initially, it served as a source of irrigation and drinking water.
- The lake gained ecological importance over the years, becoming a habitat for numerous bird species, leading to its protection by the British colonial administration in the early 20th century.
- In 2012, the sanctuary was designated under the Ramsar Convention, highlighting its significance as a wetland habitat.
- Flora: The sanctuary hosts 48 species of algae and 72 species of flowering plants, with common aquatic plants including Cyperus sp., Scirpus sp., and Typha angustata.
- Fauna: Home to about 250 bird species, including flamingoes, pelicans, and cranes, as well as various mammals such as wild ass and jungle cats.
The sighting of the Sabine's Gull is a reminder of the sanctuary's rich biodiversity and its importance as a conservation area. Nalsarovar remains a vital habitat for both resident and migratory bird species, attracting bird watchers and nature enthusiasts alike.
GS2/Governance
What is Krishi Nivesh Portal?
Source: Financial Express
Why in News?
The Krishi Nivesh Portal is an important initiative by the government aimed at enhancing investments within the agriculture sector by integrating various schemes from different ministries and state governments into a single digital platform.
- The portal is developed by the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare.
- It provides easy access to information for farmers, investors, and various stakeholders in the agriculture sector.
- It serves as a comprehensive platform for availing benefits from diverse government schemes.
- The portal currently features 17 flagship schemes related to agriculture.
Additional Details
- One-Stop Solution: The Krishi Nivesh Portal acts as a centralized interface for tracking investment opportunities, monitoring application statuses, and accessing information about various government schemes, thereby streamlining the investment process.
- User-Friendly Interface: The portal includes features such as real-time assistance via a chatbot and interactive dashboards to facilitate data-driven decision-making.
- The portal currently integrates initiatives from seven ministries, including agriculture, food processing, and rural development.
- Investment Benefits: Investors can access subsidized benefits meant for farmers through multiple government departments, enhancing agribusiness opportunities and improving farmers' income.
In summary, the Krishi Nivesh Portal is a significant step towards modernizing the agricultural investment landscape in India, making processes more transparent and efficient while supporting farmers and investors alike.
GS2/Governance
Balancing National Pride and Indigenous Rights - The Khangchendzonga Controversy
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?The recent ascent of Mt. Khangchendzonga by a team from the National Institute of Mountaineering and Adventure Sports (NIMAS) has sparked significant protests from civil society and the Chief Minister of Sikkim, Prem Singh Tamang. This controversy arises because the mountain is considered sacred by the indigenous Sikkimese people, and climbing it is prohibited from the Indian side by the Sikkim government.
- The NIMAS team's climb from the Nepal side has caused widespread unrest among local communities.
- Mount Khangchendzonga holds immense spiritual significance for the Sikkimese, being viewed as a deity.
- Indigenous rights and environmental sustainability are often at odds with national pride and development projects.
Additional Details
- Spiritual and Cultural Significance: For many indigenous groups, mountains are sacred spaces. For the Sikkimese, Khangchendzonga is not merely a peak but a revered deity.
- Environmental Importance: Mountains are crucial ecosystems that are highly sensitive to climate change and serve as key water sources.
- Indigenous Stewardship: Indigenous knowledge systems foster sustainable coexistence with the environment, aiding in climate resilience.
- Tension Between Development and Indigenous Rights: Development projects often ignore indigenous beliefs, prioritizing scientific and strategic goals. For example, the India-based Neutrino Observatory has restricted access to sacred sites for local communities.
- Evolving Legal Framework: International instruments like UNDRIP and ILO Convention 169 emphasize the importance of consulting indigenous peoples prior to any development on their lands.
- NIMAS Controversy: The climbing expedition was part of a nationalistic initiative, raising ethical concerns about bypassing local sentiments in favor of national pride.
The incident surrounding Mt. Khangchendzonga highlights the pressing need to balance national interests with the rights and spiritual beliefs of indigenous communities. Achieving this harmony is essential for fostering inclusive governance that respects indigenous wisdom while pursuing development initiatives.
GS3/Environment
How the Technology Industry is Trying to Meet its Climate Goals
Source: The Hindu
 Why in the News?
Why in the News?A groundbreaking study by Microsoft and WSP Global, published in Nature, demonstrates significant advancements in making data centres more environmentally friendly.
- Data centres are specialized facilities that store, process, and manage data.
- Cold plates and immersion cooling technologies are critical in reducing environmental impact.
- Life cycle assessments help evaluate the full environmental impact of cooling technologies.
- Renewable energy is essential for sustainable cooling solutions.
- Liquid-cooling methods outperform traditional air cooling in efficiency and resource usage.
Additional Details
- What are Data Centres: These facilities house numerous computer servers, network equipment, and storage systems, forming the backbone of the digital infrastructure that powers the internet and cloud computing.
- Environmental Benefits of Cold Plates and Immersion Cooling:
- Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions: These methods can reduce emissions by 15–21% compared to traditional air cooling. For instance, Microsoft's study indicated a significant drop in carbon emissions during peak operations.
- Reduced Energy Consumption: They consume 15–20% less energy as liquid coolants transfer heat more effectively than air.
- Significant Water Conservation: Water usage can decrease by 31–52%, which is especially beneficial in water-stressed regions.
- Life Cycle Assessment (LCA):
- LCA measures the full environmental impact from cradle to grave, considering energy use and water consumption throughout a product's lifecycle.
- It identifies sustainability trade-offs, which helps in comparing the true impact of different cooling methods.
- LCA supports informed decision-making, providing data-driven insights for the ICT sector to help cut emissions by 42% by 2030.
- Importance of Renewable Energy:
- Using renewable sources like solar and wind can cut carbon emissions by 85–90%, regardless of the cooling technology employed.
- Renewables significantly enhance the impact of green cooling technologies, potentially increasing water savings up to 50%.
- True sustainability requires that the electricity source is eco-friendly; renewables ensure this.
- Advantages of Liquid-Cooling Methods:
- Higher Cooling Efficiency: Liquid-cooling systems transfer heat more effectively, reducing overheating risks and improving hardware performance.
- Lower Resource Consumption: Liquid-cooling methods use less energy and up to 52% less water, making them more cost-effective in the long run.
Cooling innovations are vital for achieving ICT emission targets by 2030, with liquid cooling technologies capable of reducing emissions by 15–21%, supporting the goal of a 42% reduction in emissions from 2015 levels. Governments should promote policy incentives for green cooling technologies, and mandatory life cycle assessments can further guide the industry towards sustainable practices.
GS3/Environment
Valley of Flowers National Park
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Valley of Flowers in Uttarakhand has opened its doors to tourists starting June 1 for its annual four-month visiting period.
- Located in the Chamoli district of Uttarakhand, within the Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve.
- Spans an area of 87 square kilometers, with elevations ranging from 3,352 to 3,658 meters above sea level.
- Designated as a National Park in 1980 and recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1988.
Additional Details
- Natural Features: The park is renowned for its vibrant meadows, dense forests, picturesque waterfalls, and majestic snow-capped mountains.
- Mountain Range: Situated at the transition zone between the Zanskar and Great Himalaya ranges.
- River System: The Pushpawati River, originating from the Tipra Glacier, flows into the Alaknanda River.
- Ecosystem: This area is part of a UNESCO Man and Biosphere (MAB) Reserve, designated in 2004.
Flora and Fauna of the Valley
- Plant Diversity: The valley is home to over 520 to 650 species of flowers, including orchids, primulas, poppies, daisies, and the sacred brahmakamal.
- Flora by Altitude Zones:
- Sub-alpine (3,200–3,500 m): Dominated by trees such as maple, fir, birch, and rhododendron.
- Lower alpine (3,500–3,700 m): Characterized by shrubs like junipers, willows, and geraniums.
- Higher alpine (above 3,700 m): Features mosses, lichens, and the blue Himalayan poppy.
- Animal Life: The park supports rare species including the Asiatic black bear, snow leopard, musk deer, brown bear, red fox, and the Himalayan monal bird.
In summary, the Valley of Flowers National Park is a significant ecological and tourist destination, showcasing a diverse range of flora and fauna, and is recognized for its natural beauty and conservation efforts.
|
49 videos|5376 docs|1137 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 2nd June 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the role of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) in global nuclear governance? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the Krishi Nivesh Portal in India's agricultural sector? |  |
| 3. How does the Gaza hunger crisis relate to human actions according to UN officials? |  |
| 4. What are the implications of women leading the armed forces as per the recent NDA policy? |  |
| 5. Why is the Khangchendzonga controversy significant in the context of balancing national pride and indigenous rights? |  |





















