UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 27th May 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Environment
Heat-Resilience Despite the Monsoon
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The national conference titled India 2047: Building a Climate-Resilient Future has underscored the pressing reality that climate change is not a future concern but a current and escalating health crisis. This event brought together various stakeholders, including garment workers, climate modellers, paediatricians, and architects, emphasizing the need for interdisciplinary collaboration to effectively address the impacts of extreme heat on public health.
- India's health system must transition from a reactive approach to a proactive and preventive model.
- Extreme heat significantly strains public health, leading to dehydration, heatstroke, and chronic illnesses.
- Community health workers can play a pivotal role in heat safety education and intervention.
- Effective heat-related health management requires integration of clinical protocols and interdisciplinary action.
Additional Details
- Primary Care as the First Line of Defence: Strengthening the primary health care system is essential for addressing heat-related health issues. Community health workers, such as ASHAs (Accredited Social Health Activists), can provide early warnings and educate communities about heat safety.
- Integration of Meteorological Systems: Collaborating meteorological data with local health networks can enhance community responses during heat alerts, such as distributing hydration kits and offering education on staying safe during extreme temperatures.
- Updating Clinical Protocols: There is a critical need for standardized clinical protocols to effectively identify and manage heat-related illnesses. Initiatives like summer readiness drills in hospitals can prepare healthcare providers for heat crises.
- Equity in Climate Resilience: The most vulnerable populations, including outdoor workers and low-income families, face the greatest risks. Addressing social vulnerabilities is crucial for effective heat resilience strategies.
The window for actionable responses to climate extremes is narrowing. As India faces increasing temperatures, it is imperative to embed heat resilience into public health frameworks. This requires a decisive shift towards proactive healthcare, cross-sector collaboration, and equitable solutions that prioritize the safety of those at greatest risk.
GS3/Defence & Security
Arms Deals: India Moves Away from Russia; Pakistan from the U.S.
Source: New York Times
Why in News?
Recently, India’s Operation Sindoor has highlighted the changing dynamics in the defence procurement strategies of India and Pakistan.
- India's defence imports are increasingly diversified, reducing reliance on Russia.
- Pakistan's military procurement is heavily aligned with China due to regional dynamics.
Additional Details
- India’s Defence Import Trends: Russia's share in Indian defence imports has dropped from 96.5% in the 1990s to 75% in the 2020s. Currently, India imports over 9% from France, 5.5% from the UK, nearly 5% from Israel, and 3% from the US. Notably, over 55% of India's air-power weapons are sourced from Western nations.
- Reasons for India's Shift:
- Strategic Diversification: To prevent overdependence on a single supplier, India is building defence partnerships with countries like France (e.g., Rafale jets) and the U.S. (e.g., Apache helicopters, Predator drones).
- Technological Advancement: Western nations provide more advanced and reliable weapon systems, as seen with the Israeli-origin SkyStriker drone.
- Geopolitical Concerns: Sanctions on Russia post-Ukraine war have led to concerns regarding timely deliveries, including delays in the S-400 missile system due to global sanctions.
- Weaponry Used in Operation Sindoor:
- India: Utilized Israeli and Russian weapons, including Pechora and OSA-AK missiles for air defense and precision strikes.
- Pakistan: Employed Chinese-made PL-15 missiles and Turkish UAVs, indicating its military dependence on China.
- China's Role in Pakistan's Arms Supply:
- Strategic Partnership: China and Pakistan share a strong geopolitical alliance, bolstered by initiatives like the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC).
- Decline of U.S. Cooperation: Pakistan's defense relationship with the U.S. has weakened significantly, with U.S. arms imports dropping from 67% in the 2000s to 0.85% in the 2020s.
- Cost-Effective Equipment: China provides affordable military technology tailored to Pakistan's needs, including systems like the JF-17 fighter jet and HQ-9 air defense systems.
- Global Arms Export Market Leaders:
- United States: Dominates with over 65% of global arms exports, supplying advanced systems like the F-35 and Patriot missile systems.
- Russia: Its influence has diminished, now accounting for around 20% of global exports, with former major buyers reducing their reliance.
- China: Holds less than 2% of global exports but plays a crucial role regionally, particularly with Pakistan.
- India’s Arms Exports:
- India is a minor player in global arms exports, contributing less than 1% of total exports, focusing primarily on light arms and defence equipment.
- Under initiatives like ‘Make in India’ and the Defence Export Policy 2020, India aims to boost domestic production and export systems such as the Akash missile and BrahMos.
- Way Forward:
- Accelerate Indigenous Defence Manufacturing: Enhance R&D investment and involve the private sector to develop advanced technologies.
- Forge Strategic Export Alliances: Target defense exports through partnerships and diplomacy, focusing on regions like Southeast Asia and Africa.
India's evolving defence procurement strategy reflects a significant shift towards diversification and modernization, while Pakistan's reliance on China underscores the changing geopolitical landscape in South Asia.
GS2/Governance
National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS) and the National Apprenticeship Training Scheme
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
The 38th Meeting of the Central Apprenticeship Council (CAC), led by the Minister of State (Independent Charge) of the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), has proposed a significant 36% increase in stipends for participants under the National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS) and the National Apprenticeship Training Scheme (NATS).
- The NAPS was initiated on August 19, 2016, to support apprenticeship programs across India.
- The scheme aims to enhance the employability of candidates through practical training.
- Registration under NAPS is mandatory for candidates and establishments to access benefits.
Additional Details
- Objectives of NAPS:
- To develop skilled manpower for industries through on-the-job experiential training.
- To incentivize establishments to enroll apprentices by providing partial stipend support.
- To offer up-skilling opportunities for candidates who have completed short-term skill training.
- To promote apprenticeship enrollment in small enterprises (MSMEs) and in underserved regions, such as aspirational districts and the North-East.
- The scheme offers financial incentives to establishments that engage apprentices under the Apprentices Act, 1961.
- Candidates completing the training receive a NAPS certificate, which enhances their employability.
The National Apprenticeship Training Scheme, another key initiative, provides practical, hands-on training opportunities for Graduate, Diploma, and Vocational certificate holders. These apprenticeships typically last between 6 months to 1 year, during which apprentices receive a stipend, with 50% reimbursed to employers by the government. Upon completion, they receive a Certificate of Proficiency, recognized as valid employment experience across India.
While the scheme promotes skill development, it does not guarantee employment after training. This initiative is crucial in bridging the gap between education and employment, ensuring that the workforce aligns with industry demands.
GS3/Environment
Mumbai’s Monsoon Arrives Early Amid Unusual May Weather
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
Mumbai has encountered an unexpectedly early and intense monsoon, arriving two weeks prior to the typical schedule. This early onset has caused significant disruptions in daily life, including waterlogging, traffic congestion, and delays in train services. According to records from the India Meteorological Department (IMD) dating back to 1950, this marks the earliest recorded onset of the monsoon in the city, surpassing the previous record of May 29, with the usual date being June 11.
- The monsoon in Mumbai commenced on May 27, 2023, significantly earlier than usual.
- Factors contributing to this early onset include the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) and favorable atmospheric conditions.
Additional Details
- Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO): This is a large-scale atmospheric circulation pattern characterized by alternating phases of enhanced and suppressed rainfall, influencing weather patterns globally.
- The MJO consists of two primary phases:
- Enhanced Rainfall Phase: Characterized by increased cloud formation and rainfall due to rising air.
- Suppressed Rainfall Phase: Features descending air that leads to dry conditions and reduced rainfall.
- The MJO travels across the Indian and Pacific Oceans, affecting weather patterns by altering wind and atmospheric conditions.
- The recent rapid progression of the monsoon from Kerala to Mumbai within just 24 hours is attributed to an active MJO and strong cross-equatorial flow.
This unusual early onset of the monsoon has significant implications for the region, including changes in agricultural patterns and potential impacts on tropical cyclone activity. The IMD attributes this event to a combination of strong atmospheric conditions and the active phase of the MJO, which has created an environment conducive to enhanced rainfall across India.
GS3/Science and Technology
State of the World’s Animal Health Report, 2025 by WOAH
Source: DTE
Why in News?
The World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH) has published its inaugural State of the World’s Animal Health report, highlighting significant challenges faced globally, particularly in India regarding animal diseases.
- India is at high risk from transboundary animal diseases, with 47% of global outbreaks from 2005 to 2023 being zoonotic, affecting both animals and humans.
- The spread of African Swine Fever (ASF) reached Sri Lanka in 2024, posing a threat to India's northeastern pig-rearing regions.
- Outbreaks of Avian Influenza (HPAI) in 2024 affected non-poultry species more than poultry, raising concerns due to India's dense poultry population.
- Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) remains endemic in India, with new serotypes SAT 3 and SAT 1 emerging, complicating vaccine adaptation.
- Diseases such as Lumpy Skin Disease and Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR) are spreading to new regions, increasing the risk of reintroduction in India.
- WOAH emphasizes the need for global action on vaccine equity, surveillance, and biosecurity to safeguard livelihoods, trade, and food security.
Additional Details
- World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH): Established in 1924 and headquartered in Paris, France, WOAH operates independently from the United Nations and has 183 member countries.
- Mandate: It serves as the global authority on animal health, focusing on controlling animal epidemics and enhancing animal welfare.
- Key Functions:
- Manages the World Animal Health Information System (WAHIS) for tracking disease outbreaks.
- Establishes international health standards for animal trade.
- Promotes science-based animal welfare policies and transparent disease reporting.
- Provides technical support to countries, particularly developing nations.
- Global Cooperation: Collaborates with over 70 global partners, including the FAO.
- India’s Role: As a member and active participant, India engages through the World Assembly of Delegates.
In summary, the report underscores the critical need for enhanced awareness and action regarding animal health, particularly for nations like India that are significantly impacted by zoonotic diseases and other animal health crises.
Quiz Question:
Which one of the following diseases of milching animals are infectious?
- 1. Foot and Mouth disease
- 2. Anthrax
- 3. Black Quarter
- 4. Cowpox
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
- (a) 1, 2 and 3
- (b) 2, 3 and 4
- (c) 1 and 4
- (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4*
GS3/Science and Technology
Discovery of New Cambrian Sea Creature Mosura fentoni
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
Scientists have recently identified a new marine organism from the Cambrian period, named Mosura fentoni. This significant discovery occurred in Canada’s Burgess Shale, which is renowned as one of the most critical fossil sites globally.
- The discovery was made in the Burgess Shale, a key site for Cambrian fossils.
- Mosura fentoni belongs to the group known as radiodonts, which are extinct marine predators.
- This creature measures between 1.5 to 6 cm and has a complex body structure comprising 26 segments.
- Its anatomical features include specialized zones for swimming and breathing.
- The find provides insights into the early evolution of arthropods.
Additional Details
- Discovery Site: The creature was found in Burgess Shale, an important Cambrian fossil location.
- Biological Group: It is classified as a radiodont, relating to insects, crabs, and spiders.
- Size and Structure:Although small, the organism has a long, segmented body divided into three main zones:
- Neck: Supports the head.
- Mesotrunk: Contains six paddle-shaped flaps for swimming, resembling mini propellers.
- Posterotrunk: Comprises up to 16 segments with thin gills and small flaps.
- Breathing Adaptation: The gills likely functioned as a breathing zone, similar to the tails of horseshoe crabs, enhancing oxygen collection.
- Evolutionary Importance: This discovery sheds light on the early evolution of arthropods, showcasing advanced swimming and breathing systems.
- Evolutionary Position: M. fentoni is positioned near the base of the hurdiid family in the radiodont family tree.
- Segment Specialization: Its body exhibits early examples of segment division for specific functions, a characteristic of modern arthropods.
- Key Insight: The discovery implies that complex body plans in arthropods may have originated much earlier than previously believed.
Overall, the discovery of Mosura fentoni not only adds a new chapter to our understanding of Cambrian marine life but also highlights the evolutionary developments of arthropods during this period.
GS3/Environment
GEDA Invites Tenders for Solar Waste Recycling in Gujarat
Source: DTE
 Why in News?
Why in News?
As India approaches a renewable energy capacity of 500 GW by 2030, the issue of solar waste is becoming increasingly critical. In response, the Gujarat Energy Development Agency (GEDA) has initiated a recycling framework designed to establish standards and promote sustainable waste management in conjunction with solar energy growth.
- Gujarat aims to create standardized protocols for solar waste management.
- The initiative will focus on research-driven frameworks for material recovery.
- Specialized recycling approaches will be developed for various photovoltaic technologies.
- Worker safety and safe dismantling practices are key components of the initiative.
Additional Details
- Standardised Protocols: GEDA's goal is to develop robust, eco-friendly, and enforceable protocols for managing solar and electronic waste.
- Research-Driven Framework: The tender invites organizations to conduct feasibility studies and experiments to recover valuable materials such as silicon, silver, copper, aluminum, and rare metals.
- Focus on PV Technologies: The recycling initiative will encompass various technologies, including crystalline silicon, CdTe, CIGS, and TOPCon cells, each requiring specialized recycling methods.
- Dismantling and Worker Safety: Guidelines will be established to ensure safe dismantling, regulatory compliance, and protection for workers involved in the recycling process.
Gujarat is well-positioned for this initiative due to its prominence as a solar manufacturing hub, housing the highest number of solar module manufacturers in India. The state is also home to numerous large-scale solar projects, generating significant quantities of end-of-life solar panels that necessitate eco-friendly disposal methods. Furthermore, the support from government policies and initiatives fosters a robust recycling infrastructure, reflecting Gujarat's commitment to clean energy sustainability.
Solar Waste Crisis in India
The solar waste crisis in India is serious, with projections indicating that solar waste will escalate from 100 kilotons in FY2023 to 340 kilotons by 2030. The volume of waste is expected to increase thirty-twofold between 2030 and 2050, particularly as panels installed during India’s solar boom (2010–2020) approach the end of their 20–25 year lifespan. Compounding the issue is the lack of a national solar waste policy, making Gujarat’s proactive measures even more vital.
Challenges in E-waste Recycling
- Informal Sector Dominance: A significant portion of e-waste recycling is conducted by informal workers using unsafe methods, posing health risks and environmental hazards.
- Lack of Infrastructure: There is an insufficient number of formal recycling facilities and technology gaps that hinder efficient e-waste processing.
- Weak Enforcement and Awareness: Poor regulatory enforcement and low public awareness impede effective e-waste collection and recycling.
Government Initiatives
- Implementation of E-Waste Management Rules: The government has enacted rules to ensure proper handling of electronic waste, including mandatory Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) for manufacturers.
- Promoting Formal Recycling Infrastructure: Efforts are underway to establish certified recycling units and authorized e-waste recycling centers that utilize environmentally sound processes.
- Awareness and Capacity Building: Campaigns and training programs are being conducted to educate stakeholders about e-waste hazards and management practices.
Way Forward
- Strengthen Policy Enforcement and Infrastructure: There is a need for strict implementation of e-waste and solar waste management regulations, alongside investments in formal recycling infrastructure.
- Promote Stakeholder Collaboration and Awareness: Enhancing collaboration between government agencies, industry, and informal workers is essential for fostering sustainable recycling practices.
The GEDA initiative addresses both solar waste and electronic waste recycling, highlighting the urgent need for a robust, eco-friendly recycling framework to manage hazardous materials effectively.
GS2/International Relations
Key Facts about East China Sea
Source: The Guardian
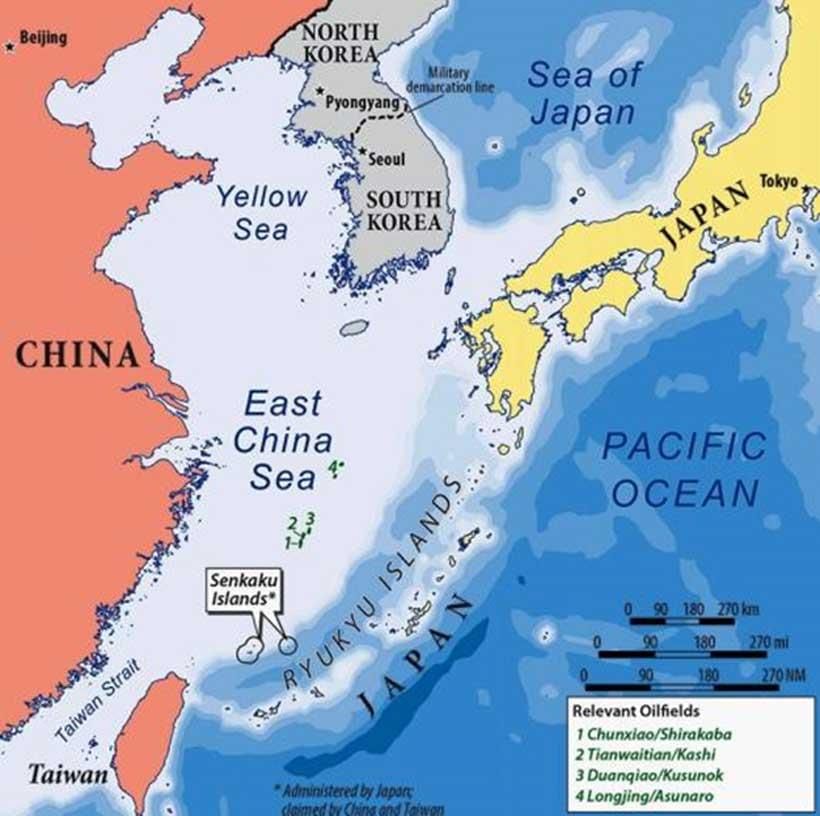 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, China’s Liaoning aircraft carrier made its first entry into the East China Sea near Japan’s Senkaku Islands, conducting aggressive military drills in close proximity to Japanese territory. This development raises concerns regarding regional security and international relations.
- The East China Sea is an arm of the Western Pacific Ocean located in East Asia.
- It is bordered by the Yellow Sea to the north, the South China Sea and Taiwan to the south, Japan's Ryukyu and Kyushu islands to the east, and the Chinese mainland to the west.
- It connects with the Japan Sea via the Tsushima Strait and with the South China Sea via the Taiwan Strait.
- Countries bordering the East China Sea include South Korea, Japan, the Republic of China (Taiwan), and the People's Republic of China.
Additional Details
- Geographical Area: The East China Sea covers approximately 290,000 square miles (750,000 sq.km) and is largely shallow, with nearly three-fourths of its area being less than 650 feet (200 meters) deep.
- Major Rivers: The Yellow River (Huanghe) and the Yangtze River (Changjiang) flow into the East China Sea, contributing fresh water and suspended particles.
- Weather Patterns: The weather in the East China Sea region is predominantly influenced by monsoon winds.
- The sea contains several significant islands, including the Ryukyu Islands (part of Japan) and the Diaoyu Islands (known as the Senkaku Islands in Japan), which are a source of territorial dispute.
- Numerous submerged reefs are present in the northern region, such as Yajiao Rock, Hupijiao Rock, and Socotra Rock.
- In 2023, approximately 35% of global petroleum and petroleum product shipments passed through the East China Sea.
This strategic maritime area plays a crucial role in geopolitics, especially given its resource richness and the ongoing territorial disputes among neighboring countries.
GS2/Governance
Panchayat Advancement Index (PAI) Version 2.0
Source: PIB
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Ministry of Panchayati Raj recently held a two-day national write-shop in New Delhi to discuss the implementation of the Panchayat Advancement Index (PAI) Version 2.0 for the financial year 2023-24.
- The PAI is a multi-domain and multi-sectoral index designed to evaluate the overall development and performance of Panchayats.
- It aims to measure progress towards localized Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and support the achievement of the SDG 2030 Agenda.
- The index utilizes various socio-economic indicators to assess the well-being of local communities.
Additional Details
- Purpose of PAI: It helps identify development gaps within Panchayats by evaluating scores across various local SDG themes, facilitating evidence-based planning at the grassroots level.
- Data Compilation: The index is based on 435 unique local indicators (331 mandatory & 104 optional), encompassing 566 unique data points across 9 themes aligned with the National Indicator Framework (NIF) of the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- The PAI reflects India's commitment to participatory and bottom-up development aimed at meeting the SDG 2030 Agenda.
- Panchayats are categorized based on their PAI scores:
- Achiever: 90+
- Front Runner: 75 to below 90
- Performer: 60 to below 75
- Aspirant: 40 to below 60
- Beginners: below 40
- Version Transition: PAI Version 1.0 served as the baseline covering 2.16 lakh Gram Panchayats across 29 States/UTs, while Version 2.0 enhances functionality and usability with refined indicators.
In summary, the Panchayat Advancement Index serves as a crucial tool for assessing and improving the performance of local governance structures in India, fostering sustainable development at the grassroots level.
GS3/Defence & Security
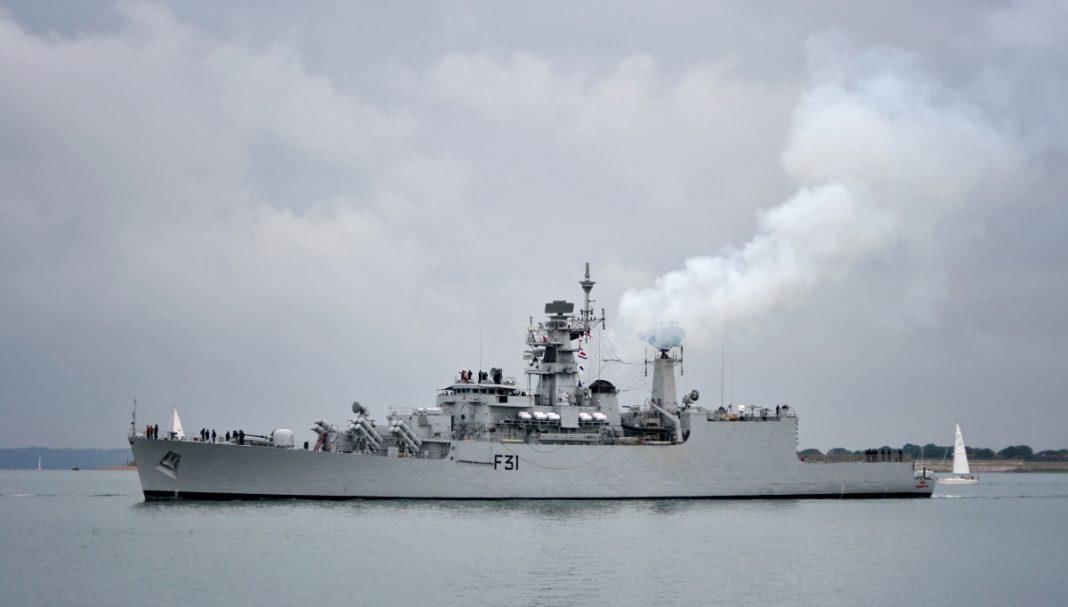
INS Brahmaputra: Current Status and Features
Source: Economic Times
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Indian Navy's guided missile frigate, INS Brahmaputra, which sustained significant damage in a dockyard accident last year, is expected to regain seaworthiness by the end of 2025 and achieve full combat readiness by mid-2026, according to senior officials.
- INS Brahmaputra is the first indigenously built Brahmaputra-class guided missile frigate.
- Commissioned into the Indian Navy on April 14, 2000, it serves multiple roles.
- The frigate is currently undergoing repairs and is projected to return to active service soon.
Additional Details
- Construction: Built by Kolkata-based Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers Limited (GRSE).
- Roles:The frigate is tasked with various missions, including:
- Coastal and offshore patrolling
- Monitoring sea routes
- Conducting maritime diplomacy
- Counter-terrorism and anti-piracy operations
- Specifications:
- Displacement: 5,300 tonnes
- Length: 125 meters
- Width: 14.4 meters
- Speed: Over 27 knots (approximately 50 km/h)
- Armament:Equipped with:
- Medium- and close-range guns
- Anti-aircraft weapons
- Surface-to-surface and surface-to-air missiles
- Torpedo launchers
- The frigate is also equipped with advanced sensors for comprehensive maritime warfare and can operate Sea King and Chetak helicopters.
- Total crew: 40 officers and 330 sailors.
With these enhancements and updates, INS Brahmaputra is poised to strengthen the Indian Navy's capabilities in maritime security and operations.
GS1/Geography
Early Monsoon Onset in India This Year
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
The India Meteorological Department (IMD) announced the onset of the monsoon over Kerala on May 24, marking its arrival eight days earlier than the usual date of June 1. This event signals the commencement of the southwest monsoon, which spans from June to September and is crucial as it contributes over 70% of India's annual rainfall, playing a vital role in the country's agriculture and economy. The last early onset was recorded in 2009, on May 23.
- The monsoon onset was declared on May 24, 2023.
- This marks an early arrival compared to the normal schedule.
- Over 70% of India’s annual rainfall comes from the southwest monsoon.
Additional Details
- Monsoon Onset Declaration:The IMD follows specific criteria to declare the onset of the southwest monsoon after May 10. Key criteria include:
- Rainfall: At least 60% of 14 meteorological stations in southern India must report a minimum of 2.5 mm of rainfall for two consecutive days, including stations like Thiruvananthapuram and Kochi.
- Wind Field: Dominance of westerly winds up to the 600 hPa pressure level, with wind speeds at 925 hPa ranging between 15-20 knots (27-37 km/h).
- Outgoing Longwave Radiation (OLR): Requires OLR values to be below 200 W/m², indicating favorable conditions for monsoon onset.
- This Year’s Onset: The monsoon onset occurred simultaneously over multiple regions, including Kerala, Lakshadweep, and parts of the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal. Factors such as a low-pressure area over the Arabian Sea and a trough across Vidarbha boosted moisture and contributed to the monsoon's early advance.
- Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO): This important ocean-atmosphere phenomenon originating in the Indian Ocean significantly influences the Indian monsoon. It consists of eastward-moving disturbances in clouds, winds, and pressure that can enhance monsoon rainfall during favorable phases.
- Mascarene High: A high-pressure area around the Mascarene Islands influences rainfall along India’s west coast due to its variable intensity during the monsoon season.
- Convection and Rainfall: Increased convective activity can lead to rainfall, evidenced by a recent convective system over Haryana affecting the Delhi region.
- Somali Jet: This low-level, cross-equatorial wind system enhances monsoon winds when strong, contributing to a more robust monsoon.
- Heat-Low and Moisture Inflow: A low-pressure zone develops over the Arabian Sea as the Sun shifts north, drawing moist air into the monsoon trough and intensifying rainfall.
- Monsoon Trough: This elongated low-pressure area stretches from the heat low in northwest India to the Bay of Bengal, with its oscillation bringing rainfall across the core monsoon zone from June to September.
The early onset of the southwest monsoon this year reflects a combination of favorable atmospheric and oceanic conditions, suggesting a potentially impactful monsoon season ahead.
GS3/Science and Technology
Scientists Verify Mendel’s Experiments on Inheritance
Source: Nature
Why in News?
Researchers have recently unraveled the genetic complexities behind Mendel's Experiments on Inheritance using cutting-edge DNA sequencing and genome analysis techniques.
- Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk, studied pea plants to understand trait inheritance.
- His foundational work laid the groundwork for modern genetics, highlighting the role of genes and alleles.
- Recent studies have revealed new genetic details that enhance our understanding of plant traits.
Additional Details
- Mendel's Background: Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk who conducted experiments with pea plants starting in 1856 to discover how traits like height or color are inherited.
- Years of Study: Over 8 years, Mendel tested more than 10,000 plants, publishing his findings in 1865, which were initially overlooked.
- Rediscovery: Mendel's significance was acknowledged in 1900 by other scientists.
- Traits Studied: Mendel focused on 7 traits in pea plants: seed shape, seed color, flower color, pod shape, pod color, flower position, and plant height.
- Findings: He discovered that certain traits, such as round seeds, are dominant over others like wrinkled seeds, establishing the concept of dominant and recessive traits.
- Recent Study (2024): Scientists analyzed the DNA of 697 pea plant varieties to identify the specific genes responsible for Mendel's 7 traits.
- Big Data Usage: The analysis processed 14 billion pages of data to reach its conclusions.
- Surprising Results: The pea plant family was found to be more genetically diverse than previously thought, with 8 distinct genetic groups resulting from crossbreeding.
- New Genetic Insights: Changes in pod color are linked to absent DNA segments, pod shape is influenced by two specific genes, and flower position varies with minor DNA alterations.
- Beyond Mendel: The research identified 72 additional traits associated with seeds, pods, leaves, and roots.
- Practical Applications: This research can assist farmers in cultivating superior crops, enhancing disease resistance, and adapting to climate change.
These advancements not only reaffirm Mendel's legacy but also pave the way for innovations in agricultural practices and genetic research.
|
44 videos|5359 docs|1133 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 27th May 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the key features of the National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS) in India? |  |
| 2. How does the Panchayat Advancement Index (PAI) help in assessing local governance? |  |
| 3. What are the implications of India moving away from Russia in arms deals? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the discovery of the new Cambrian sea creature Mosura fentoni? |  |
| 5. What impact does early monsoon arrival have on Mumbai's climate and agriculture? |  |





















