UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 4th May 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/Polity
Caste Enumeration in India’s Next Census: Objectives, Implications, and Challenges
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Union Cabinet has made a significant decision to include questions on caste in India’s next Census, marking the first time in nearly a century that such data will be collected beyond the Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs).
- This move is politically timed, coinciding with the Bihar Assembly elections and increasing demands for updated caste data.
- The last comprehensive caste data was collected in the 1931 Census, after which the practice was discontinued.
- Recent state-level surveys have reignited discussions about representation and reservation policies.
Additional Details
- Historical Context: Caste data collection began in the 1881 Census and continued until 1931. The 1941 Census collected data, but it was never published due to the Second World War. Post-Independence, only SC and ST populations were counted.
- Objectives of the Census:
- Informed Policy-Making: Updated caste data will enhance the allocation of welfare benefits and development programs.
- Reservation Reassessment: The Census will provide a basis for evaluating and potentially revising reservation quotas.
- Social Justice: It aims to highlight marginalized communities within the OBC, SC, and ST categories.
- Evidence-Based Governance: Reliable data will support academic research and informed political interventions.
- Political Significance: The decision follows a series of state surveys that indicated a higher proportion of backward classes, influencing political dynamics and demands for greater representation.
- Implementation Challenges:
- Caste Classification: Developing a comprehensive national caste code will be complex due to regional variations.
- Overlap and Disputes: Variations in state OBC lists may create inconsistencies and conflicts.
- Political Sensitivities: Inclusion or exclusion of specific castes could lead to significant political controversy.
- Delayed Timeline: The Census schedule remains uncertain due to previous delays from the COVID-19 pandemic.
The inclusion of caste in the national Census is poised to enhance data-driven governance and inform equitable policymaking. While it promises to clarify the demographic landscape of caste groups in India, careful execution will be essential to avoid social fragmentation and political fallout.
GS3/Environment
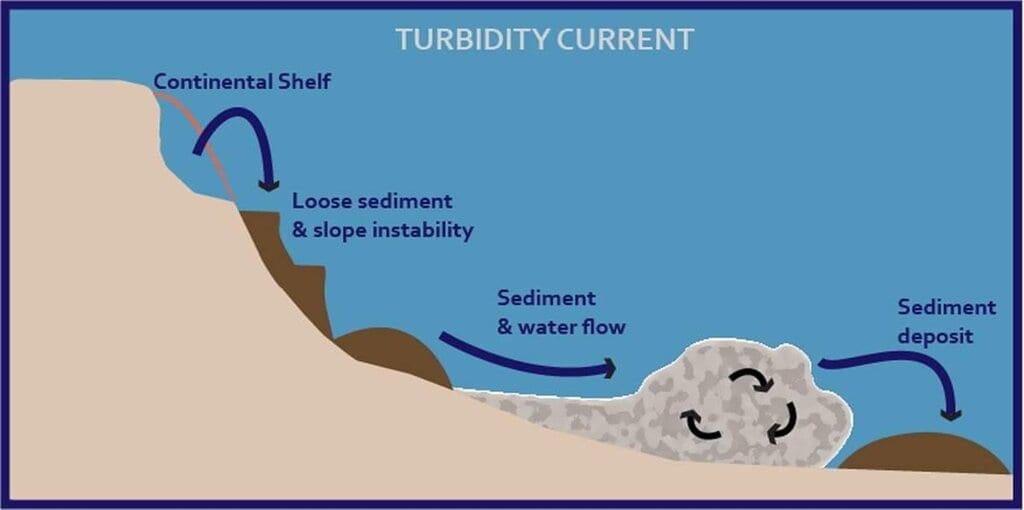
Turbidity Currents in Submarine Canyons
 Why in News?
Why in News?
A recent study published in ACS Environmental Science & Technology has provided the first direct evidence of turbidity currents transporting microplastics into the deep sea through submarine canyons, including regions not influenced by river inputs, such as the Whittard Canyon off the coast of Ireland.
- Turbidity currents are rapid, downslope flows of water that carry sediments, increasing the water's density.
- These currents can be triggered by geological disturbances like earthquakes and landslides.
- Submarine canyons are steep-sided underwater valleys that are primarily shaped by erosional forces.
- Globally, there are approximately 9,477 known submarine canyons, which cover nearly 11% of continental slope areas.
Additional Details
- Turbidity Currents: These flows behave similarly to underwater avalanches and can erode the seafloor, leading to the formation and enlargement of underwater features. They also deposit sediments in graded layers, with coarser particles settling first followed by finer ones.
- Submarine Canyons: These canyons are found on continental slopes and rises, extending from the continental shelf to the deep ocean. Their steep walls are often vertical and susceptible to collapse, adding sediment to turbidity flows.
- Types of submarine canyons include bank and shoal formations, which are influenced by erosional and depositional processes. For example, Dogger Bank in the North Sea is a notable flat-topped elevation.
- Coral reefs, which are built from calcareous skeletons of corals and algae, are also significant as they create biodiversity hotspots in regions like the Pacific Ocean.
This study highlights the role of turbidity currents not just in sediment transport but also in the concerning issue of microplastic pollution in the deep sea, emphasizing the need for further research in these underexplored areas.
GS3/Economy
Evaluation of Innovation in Public-Funded R&D Organisations in India
 Why in News?
Why in News?
A detailed report titled 'Evaluation of Innovation Excellence Indicators of Public Funded R&D Organizations' was released by the Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser, CII, and the Centre for Technology, Innovation, and Economic Research. The report aims to assess the innovation outcomes and national contributions of public-funded R&D institutions in India.
- 244 public-funded R&D organisations were evaluated.
- Significant exclusions were made for sensitive scientific institutions and academic universities.
- The study aims to align R&D with national missions and sustainable development goals.
Additional Details
- Scope of the Study: The study covered 244 public-funded R&D organisations from various ministries, excluding sensitive areas like defence and atomic energy.
- Objective of the Study: To determine if public-funded labs focus more on academic science or industry-driven innovations and to contribute to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Methodology: An online questionnaire with 62 parameters was used, with self-selection of lab types based on their research focus.
- Key Findings: Limited engagement with startups and industry, with only 25% providing incubation support to startups and a notable decline in permanent staff.
- Recommendations: Labs need to realign their mandates towards the 'Viksit Bharat' vision, prioritize critical technologies, and strengthen collaborations.
The report concludes that strengthening public-funded R&D institutions through focused innovation and collaboration is vital for achieving India's vision of 'Viksit Bharat'. With strategic reforms and inclusive participation, these institutions can significantly contribute to sustainable development, technological self-reliance, and global scientific leadership.
GS1/Indian Society
Lairai Devi Temple Incident
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, a tragic incident occurred during the annual Lairai Jatra procession at Shree Lairai Devi temple in Shirgaon village, North Goa. At least six people lost their lives, and over 70 others sustained injuries due to a stampede that took place in the early hours of Saturday.
- Incident at the annual Lairai Jatra procession leading to casualties.
- The temple is a significant cultural and religious site for the local community.
Additional Details
- Lairai Devi Temple: A revered spiritual site in Shirgaon, Bicholim, North Goa, dedicated to Goddess Lairai, an incarnation of Goddess Parvati.
- Architectural Significance: The temple showcases traditional Goan architecture, featuring intricate carvings and vibrant interiors, enhancing its sacred appeal.
- Religious Harmony: The temple symbolizes unity, with both Hindus and Catholics regarding Lairai Devi and the Virgin Mary of Mapusa as sisters.
- Lairai Devi Jatra: An annual festival known for its dramatic fire-walking ritual (Agnidivya), which attracts tens of thousands of devotees.
- The festival includes processions, devotional dances, and drumming, culminating in a fire-walking ritual where devotees chant the goddess's name.
This unfortunate event highlights the need for better crowd management during large religious gatherings to ensure the safety of participants and preserve the sanctity of such cultural events.
GS3/Environment
Campi Flegrei: A Volcanic System of Concern
Why in News?
Recent observations by scientists have indicated cyclical episodes of unrest at Campi Flegrei, particularly noted during the periods of 1982–1984 and 2011–2024. These events are characterized by land uplift, increased seismic activity, and rumbling sounds resulting from underground fluid pressure.
- Campi Flegrei, also known as the Phlegraean Fields, is an active volcanic region located near Naples, Italy.
- Unlike traditional volcanoes, Campi Flegrei is a volcanic system within a large caldera.
- The caldera spans approximately 12–15 km in diameter and was formed due to a massive eruption around 39,000 years ago.
- This ancient eruption is believed to have significantly impacted the climate, potentially contributing to the decline of Neanderthals.
Additional Details
- Geographic Characteristics: One-third of Campi Flegrei is submerged beneath the Tyrrhenian Sea, situated between the Italian mainland and the island of Sardinia. It is recognized as the largest active volcanic caldera in Europe, surpassing the much-studied Mount Vesuvius.
- The last significant eruption occurred in 1538, which led to the formation of Monte Nuovo after a period of approximately 3,000 years without eruptions.
- As a supervolcano, any large-scale eruption from Campi Flegrei could have global repercussions, including severe climate disruptions.
In conclusion, the ongoing monitoring of Campi Flegrei is crucial due to its potential for significant volcanic activity that could affect both local and global environments.
GS3/Health
Rise in Vaccine-Preventable Diseases
Why in News?
Diseases that can be prevented through vaccination, such as measles, meningitis, and yellow fever, are experiencing a resurgence due to millions of children missing vaccinations. This situation has been exacerbated by funding cuts and disruptions in immunization efforts globally.
- WHO, UNICEF, and Gavi highlight the impact of misinformation, population growth, and humanitarian crises on vaccination progress.
- In 2023, 14.5 million children missed routine vaccinations, marking a troubling increase from previous years.
- Global leaders are urged to prioritize and enhance vaccination programs.
Additional Details
- Global Vaccination Crisis: A WHO review across 108 low- and lower-middle-income countries found that nearly half are experiencing moderate to severe disruptions in vaccinations due to reduced funding.
- Impact on Disease Surveillance: More than half of the surveyed countries reported disruptions in disease surveillance, raising the risk of outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases.
- Resurgence of Diseases: Countries with strong healthcare systems, such as the U.S., have reported significant increases in measles cases, contradicting previous elimination status.
- Funding Concerns: Health leaders emphasize the ongoing need for investment in vaccination initiatives like the 'Big Catch-Up' to address gaps created during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Economic Impact: WHO states that immunization is a highly cost-effective health investment, yielding a return of $54 for every $1 spent.
- Progress in India: India has made significant strides in vaccination, achieving milestones like being declared polio-free in 2014 and reducing maternal and neonatal tetanus rates by 2015.
- Despite these achievements, 23.9% of Indian children still miss full immunization, highlighting the need for continued effort.
The ongoing rise in vaccine-preventable diseases underscores the critical need for renewed commitment to vaccination efforts globally. WHO, UNICEF, and Gavi are calling for sustained investment in vaccines and adherence to the Immunisation Agenda 2030, with a key pledging summit scheduled for June 2025 to secure funding aimed at protecting children worldwide.
GS3/Science and Technology
Altermagnets, Spintronics & Valleytronics
Why in News?
A research team from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has made a significant breakthrough by reporting the first experimental observation of a two-dimensional layered altermagnet that operates at room temperature.
- Altermagnets are a new class of antiferromagnetic materials.
- They exhibit momentum-dependent spin splitting without the need for spin–orbit coupling (SOC).
- This mechanism is driven by exchange interactions between magnetically connected sublattices.
- Altermagnetism combines the advantages of antiferromagnets with spintronics for enhanced performance.
Additional Details
- Altermagnets: These materials feature a phenomenon called C-paired spin-valley locking (SVL), which allows for unique spin dynamics that are beneficial for various applications.
- They provide long spin lifetimes and magnetic stability, making them suitable for spintronic applications.
- Spintronics: This field, short for spin transport electronics, utilizes both the intrinsic spin and charge of electrons for data storage, processing, and transfer.
- Key advantages of spintronics include faster processing speeds, higher integration densities, and reduced energy consumption.
- Examples of spintronic devices are spin transistors, spin diodes, spin filters, spin RAM, and spin logic gates.
- Valleytronics: This emerging field leverages valley degrees of freedom (minima in energy bands) for data manipulation, offering potential for faster and denser data processing.
This recent discovery not only enhances our understanding of altermagnets but also opens new avenues for the development of advanced electronic devices in both the spintronics and valleytronics domains.
GS3/Science and Technology
Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) Develops Genome-Edited Rice Varieties
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) has made significant strides in agricultural biotechnology by successfully developing two genome-edited rice varieties, which are expected to enhance food security and agricultural productivity in India.
- ICAR has developed two new genome-edited rice varieties: DRR Dhan 100 Kamala and one based on MTU1010.
- The new varieties offer increased yields and earlier harvest times, contributing to improved food security.
Additional Details
- Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR): An autonomous organization under the Department of Agricultural Research and Education (DARE), ICAR plays a critical role in coordinating and managing agricultural research and education across India.
- Historical Background: Established on July 16, 1929, ICAR was formerly known as the Imperial Council of Agricultural Research. It is headquartered in New Delhi and oversees 113 institutes and 74 agricultural universities.
- Impact of Research: From 1950-51 to 2021-22, ICAR’s research efforts have significantly increased agricultural production, with foodgrains up by 6.21 times and fruits and vegetables by 11.53 times.
- New Varieties: The first variety, DRR Dhan 100 Kamala, derived from Samba Mahsuri, can be harvested 15-20 days earlier and yields about 25% more than its predecessor, producing an additional eight tonnes per hectare.
The advancements made by ICAR in genome-editing technology represent a crucial step toward enhancing agricultural productivity and ensuring food security in India, showcasing the importance of research and innovation in agriculture.
GS3/Economy
Insider Trading
Why in News?
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has raised allegations against a director of multiple group companies for sharing price-sensitive information, which constitutes a breach of regulations designed to prevent insider trading.
- Definition of Insider Trading: Involves buying or selling publicly traded stocks based on nonpublic, material information.
- Material Information: Any undisclosed information that could significantly influence an investor's decision regarding a security.
- Insider Definition: According to SEBI, an insider is someone with access to price-sensitive information about a company's shares or securities.
- Regulatory Framework: In India, insider trading is governed by the SEBI under the Insider Trading Regulations of 2015.
Additional Details
- SEBI's Role: SEBI prohibits firms from buying their own shares from the secondary market to safeguard investor interests and promote fair trading.
- Enforcement Actions: SEBI can impose fines and restrict individuals or entities from participating in capital market trading upon violation of regulations.
In summary, the allegations against the director highlight the importance of adhering to regulations set by SEBI to maintain fair trading practices and protect investors in the financial markets.
GS3/Defence & Security
Abdali Missile Successfully Launched by Pakistan
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Pakistan recently announced that it has successfully conducted a training launch of the Abdali Weapon System, marking a significant milestone in its defense capabilities.
- The Abdali (Hatf-II) is a short-range ballistic missile developed by Pakistan's Space and Upper Atmosphere Research Commission (SUPARCO).
- The missile is designed for tactical battlefield use and can carry both conventional and nuclear warheads.
- Its maximum range has been claimed to be 450 kilometers, which is an increase from the previously reported range of 180-200 kilometers.
Additional Details
- Navigation System: The Abdali missile features an advanced inertial navigation system that provides a Circular Error Probable (CEP) of 100-150 meters, indicating its high accuracy in targeting.
- Launch System: It is launched from a road-mobile Transporter-Erector-Launcher (TEL), which enhances its rapid deployment and mobility on the battlefield.
- Payload Capacity: The missile can carry a single payload weighing between 250-500 kg, which can include high explosives, submunitions, or conventional warheads.
- The missile's solid-fuel engine enables quick reaction times and ease of storage, further improving its utility in combat situations.
- The Abdali missile has been in operational service with Pakistan's Army Strategic Forces Command since 2005.
This successful test of the Abdali missile underscores Pakistan's commitment to maintaining and enhancing its defense capabilities in a rapidly evolving geopolitical landscape.
GS2/International Relations
India-Angola Diplomatic Relations
Why in News?
Recently, the President of India welcomed the President of Angola at Rashtrapati Bhavan during his inaugural State visit to India. This visit marked the 40th anniversary of diplomatic relations between India and Angola.
- Angola is situated on the southwestern coast of Africa, boasting a strategic coastline along the Atlantic Ocean.
- The capital city, Luanda, serves as a significant hub for maritime activities and oil exports.
- Angola shares borders with several countries, including the Republic of the Congo, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Zambia, and Namibia.
Additional Details
- Major Rivers: The Cuango River and Cuanza River are crucial for hydropower generation and inland water transport.
- Highest Peak: Mount Moco is the tallest mountain in Angola, located in the Huambo province.
This meeting underscores India's commitment to fostering a mutually beneficial and sustainable partnership with African nations, as emphasized by President Droupadi Murmu.
|
49 videos|5376 docs|1137 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 4th May 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the objectives of caste enumeration in India's next census? |  |
| 2. What are the implications of including caste data in the census? |  |
| 3. What challenges might arise during the caste enumeration process? |  |
| 4. How can the government ensure the accuracy of caste data collected in the census? |  |
| 5. What has been the historical context of caste enumeration in India? |  |
















