Class 7 Social Science Chapter 1 HOTS Questions - Geographical Diversity of India
Q1: How do the geographical features of India, such as the Himalayas and the Thar Desert, shape the culture and way of life in the country?
Ans:
- The Himalayas protect India from cold winds, shape climate patterns, and provide water for agriculture.
- They also influence cultural practices, such as pilgrimage routes like the Char Dham Yatra.
- The Thar Desert, on the other hand, has shaped the lifestyle of its inhabitants by leading to unique adaptations such as rainwater harvesting and reliance on camels for transport.
- These geographical features influence food, clothing, festivals, and farming practices, creating distinct cultural identities in different regions.
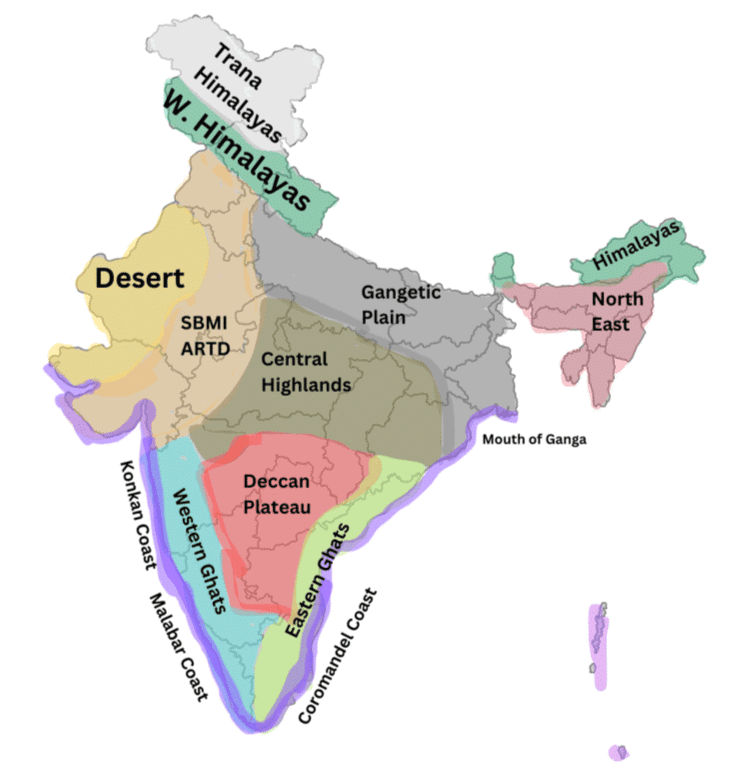
Q2: Compare the Gangetic Plains and the Thar Desert in terms of agriculture, climate, and population density.
Ans:
- The Gangetic Plains are fertile, supported by rivers like the Ganga, and ideal for farming crops like rice and wheat.
- They have a temperate climate and support a high population density due to their fertile soil.
- In contrast, the Thar Desert has an arid climate with very little rainfall, making agriculture challenging.
- People in the Thar have adapted to its harsh conditions through rainwater harvesting and camel transport.
- The population density is lower here due to the limited resources available for farming and water supply.
Q3: If you were to design a sustainable tourism plan for Ladakh, how would you balance tourism with environmental conservation?
Ans:
- To design a sustainable tourism plan for Ladakh, I would promote eco-friendly practices, such as using local materials for construction and reducing the use of plastic.
- I would ensure that tourists are educated about Ladakh’s fragile environment and the importance of preserving it.
- Strict regulations would be enforced to limit waste, conserve water, and protect wildlife.
- Additionally, promoting responsible tourism like hiking, cultural exchanges, and monastery visits would help reduce the ecological footprint while benefiting the local community.
Q4: Imagine the Aravalli Hills are at risk due to mining activities. What steps would you take to protect this important natural barrier while considering economic factors?
Ans:
- I would first educate the local population and government about the ecological importance of the Aravalli Hills, such as preventing the Thar Desert from spreading and preserving biodiversity.
- I would propose alternative economic activities like eco-tourism, sustainable mining, and promoting the extraction of minerals with minimal environmental impact.
- Collaborating with environmental NGOs, I would push for stricter environmental regulations on mining and the restoration of mined areas to ensure long-term ecological health while also providing jobs for the local population.
.
Q5: Do you think the Peninsular Plateau's unique geography has contributed to India’s economic growth? Justify your answer.
Ans:
- Yes, the Peninsular Plateau’s unique geography has contributed significantly to India’s economic growth.
- The plateau is rich in minerals like coal, iron, and bauxite, which are crucial for industries.
- Rivers like the Godavari and Krishna provide water for irrigation, supporting agriculture.
- The plateau’s proximity to the Western and Eastern Ghats also provides hydropower potential, fueling industrial growth.
- Furthermore, the plateau's location between two seas has made it an ideal region for ports, contributing to trade and commerce.
Q6: What do you think might happen if the Himalayas stopped growing? How would this affect the rivers that originate from them?
Ans:
- If the Himalayas stopped growing, it could have long-term consequences for the rivers that originate from them, such as the Ganga and Brahmaputra.
- The continuous growth of the Himalayas feeds the rivers with water from melting snow, maintaining their flow throughout the year.
- Without this growth, the rivers might lose their source of fresh water, potentially leading to decreased water availability for agriculture, industry, and daily life.
- This could also affect the fertility of the plains and lead to challenges in water management and agriculture.
Q7: Design a model to protect the Sundarbans mangrove ecosystem while promoting sustainable development. What key features would you include in the model?
Ans:
- The model would integrate sustainable tourism, eco-friendly fishing practices, and strict regulations against deforestation.
- I would encourage eco-tourism, where tourists are educated about the importance of mangroves, and involve local communities in conservation efforts.
- The model would promote alternative livelihoods, such as sustainable farming or handicrafts, to reduce dependence on the forest.
- Additionally, I would implement a monitoring system to track the health of the ecosystem and enforce laws against illegal activities like poaching or over-exploitation of resources.
|
23 videos|274 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Social Science Chapter 1 HOTS Questions - Geographical Diversity of India
| 1. What are the major geographical features of India? |  |
| 2. How does geographical diversity affect the climate of India? |  |
| 3. What role do rivers play in the geographical diversity of India? |  |
| 4. How does India's geographical diversity impact its biodiversity? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the Western Ghats in India's geography? |  |

















