Revision Notes: Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
A. Purification Techniques
Crystallization
Principle: Crystallization is based on the principle that solubility of a compound in a solvent decreases as the solution cools, causing the solute to form crystals. Impurities generally remain dissolved in the solvent.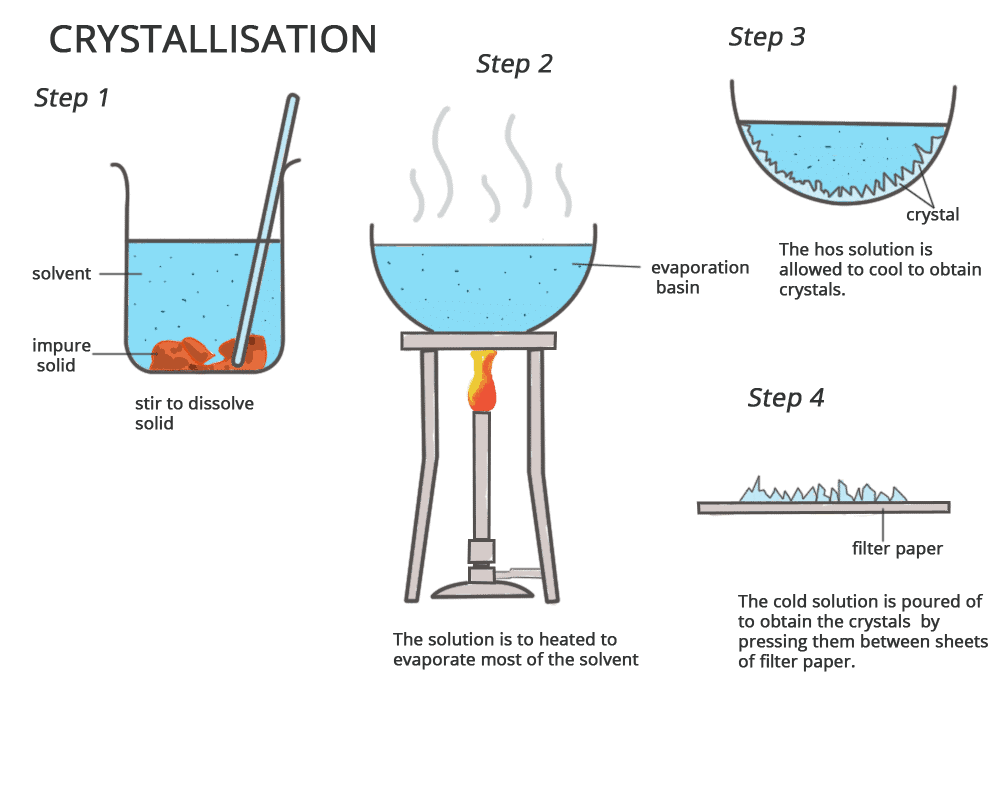
Procedure:
- Selection of solvent: Choose a solvent in which the compound has high solubility at high temperature and low solubility at low temperature.
- Dissolution: Dissolve the impure solid compound in the hot solvent.
- Filtration: Filter out any insoluble impurities from the solution.
- Cooling: Allow the solution to cool slowly, during which pure crystals of the compound will form.
- Separation: Filter the crystals and wash them with a small amount of cold solvent to remove soluble impurities.
- Drying: Dry the crystals in a desiccator or under reduced pressure.
Applications: Used for purifying solid compounds such as salts, organic compounds (like sugar), and antibiotics.
Sublimation
Principle: Sublimation occurs when a solid changes directly into a vapor and then back to a solid without passing through the liquid phase. This happens when the vapor pressure of a substance is sufficiently high at a given temperature.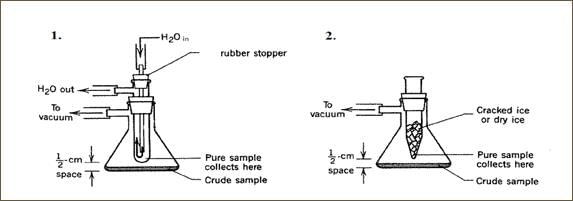 Sublimation Diagram
Sublimation Diagram
Procedure:
- Heat the impure substance in a sublimation apparatus.
- The substance sublimates into a vapor.
- The vapor condenses on a cooler surface to form crystals of the purified substance.
Applications: Used to purify volatile solids like iodine, camphor, and naphthalene.
Distillation
Principle: Distillation is based on the differences in the boiling points of components in a mixture. When a liquid mixture is heated, the component with the lowest boiling point vaporizes first, followed by condensation into a liquid.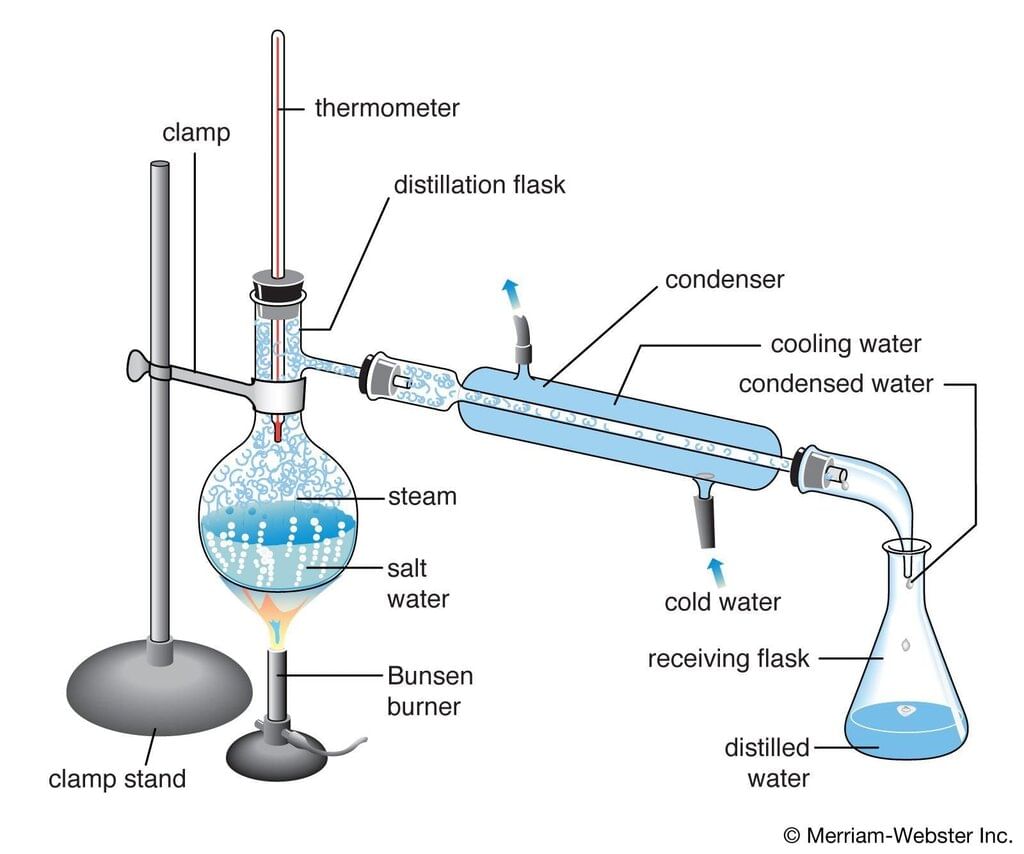 Distillation Process
Distillation Process
Types of Distillation:
- Simple Distillation: Used when the boiling points of components are significantly different.
- Fractional Distillation: Used for mixtures where components have closer boiling points.
- Vacuum Distillation: Used when components decompose at high temperatures; reduces the boiling point by applying a vacuum.
Procedure:
- Heat the liquid mixture in a distillation apparatus.
- The component with the lowest boiling point vaporizes.
- The vapor is condensed and collected in a separate container.
Applications: Separation of volatile liquids (e.g., separating water and ethanol), purification of solvents, essential oils, and crude oil.
Differential Extraction
Principle: Differential extraction separates components of a mixture based on their differential solubility in immiscible solvents.
Procedure:
- Add an immiscible solvent to the mixture.
- Shake the mixture and allow the layers to separate.
- Separate the desired component from one of the layers.
Applications: Used for separating organic compounds from aqueous solutions, such as in the extraction of alkaloids, acids, and phenols.
Chromatography
Principle: Chromatography separates the components of a mixture based on the differential distribution between a stationary phase and a mobile phase.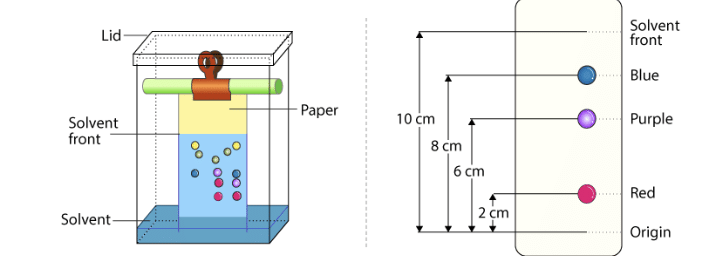
Types of Chromatography:
- Paper Chromatography: Uses paper as the stationary phase.
- Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC): Uses a thin layer of adsorbent material as the stationary phase.
- Column Chromatography: Uses a column packed with adsorbent material.
- Gas Chromatography (GC): Uses a gas as the mobile phase for separating volatile compounds.
- High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC): Uses a liquid mobile phase to separate compounds based on their polarity and interactions with the stationary phase.
Applications: Separation of complex mixtures (e.g., amino acids, proteins, pesticides), and analysis of organic compounds in environmental and pharmaceutical samples.
B. Qualitative Analysis
Detection of Nitrogen
Test: Lassaigne's test for Nitrogen
Procedure:
- Heat the organic compound with sodium metal in a fusion tube.
- Add water to the fusion product and filter the solution.
- Add ferric chloride (FeCl3) to the filtrate.
- If a prussian blue color appears, nitrogen is present.
Reaction:
NaCN + FeCl3 → Fe(CN)63− (Prussian blue formation)
Detection of Sulphur
Test: Lassaigne's test for Sulphur
Procedure:
- Heat the organic compound with sodium metal in a fusion tube.
- Add water to the fusion product and filter the solution.
- Add lead acetate solution (Pb(CH3COO)2) to the filtrate.
- If a black precipitate of PbS forms, sulphur is present.

Reaction:
Na2S + Pb(CH3COO)2 → PbS (black precipitate) + 2NaCH3COO
Detection of Phosphorus
Test: Lassaigne's test for Phosphorus
Procedure:
- Heat the organic compound with sodium metal in a fusion tube.
- Add water to the fusion product and filter the solution.
- Add ammonium molybdate (NH4)6Mo7O24 to the filtrate.
- If a yellow precipitate forms, phosphorus is present.
Reaction:
Na2HPO4 + (NH4)6Mo7O24 → MoO3.P2O5 (yellow precipitate)
Detection of Halogens
Test: Lassaigne's test for Halogens
Procedure:
- Heat the organic compound with sodium metal in a fusion tube.
- Add water to the fusion product and filter the solution.
- Add silver nitrate solution (AgNO3) to the filtrate.
- A white precipitate (AgCl) indicates chlorine, yellow precipitate (AgBr) indicates bromine, and yellowish-white precipitate (AgI) indicates iodine.
Reactions:
NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl (white precipitate)NaBr + AgNO3 → AgBr (yellow precipitate)NaI + AgNO3 → AgI (yellowish-white precipitate)
|
75 videos|339 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are the common purification techniques used for organic compounds? |  |
| 2. How can qualitative analysis help in characterizing organic compounds? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of melting point and boiling point in the purification of organic compounds? |  |
| 4. What role does chromatography play in the separation of organic compounds? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges faced during the purification of organic compounds? |  |
















