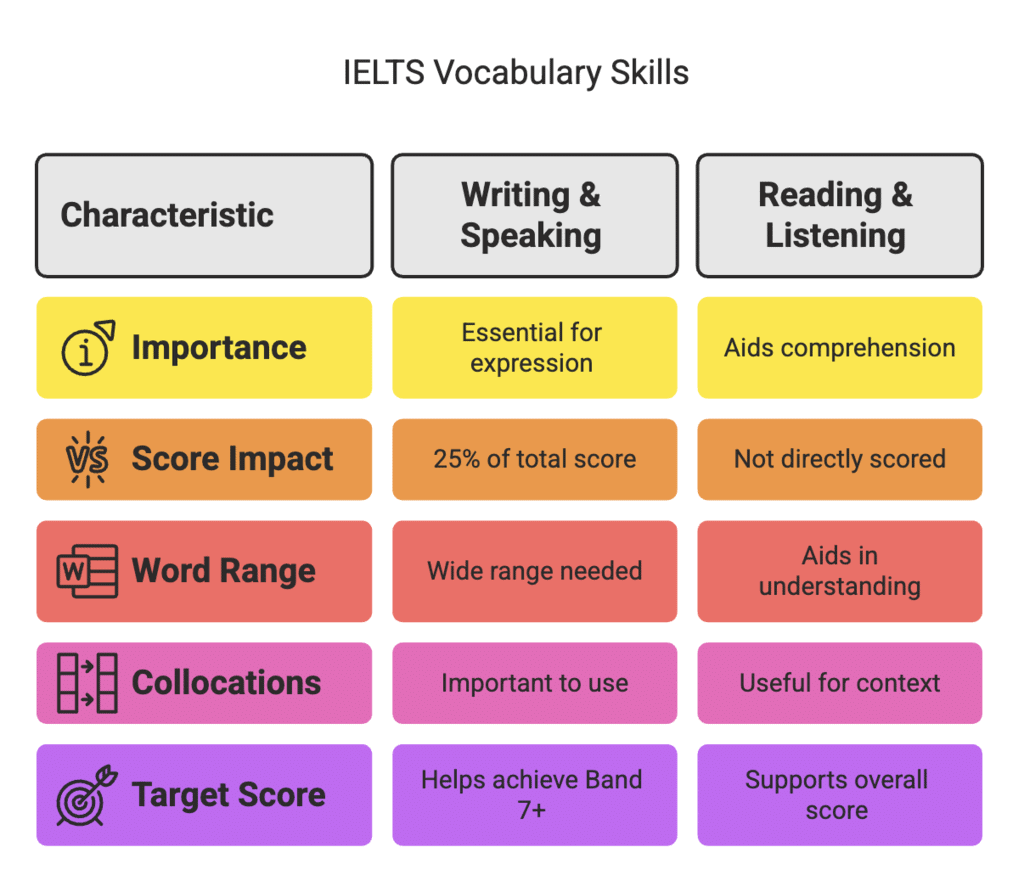
The IELTS test assesses your vocabulary, which contributes 25% to your scores in the Writing and Speaking sections. Using a broad range of accurate, appropriate words—especially collocations—can help you achieve Band 7 or above. A strong vocabulary also supports better understanding in the Reading and Listening sections. Regular practice with new words improves both comprehension and communication.
Strategies for Building IELTS Vocabulary | Vocabulary for IELTS PDF Download
1. Read Authentic English Materials
Reading diverse, high-quality texts exposes you to the academic and everyday vocabulary used in the IELTS Reading and Listening sections.
What to Do: Read articles from reputable sources like BBC News, The Guardian, or National Geographic, focusing on common IELTS topics (e.g., environment, education, technology).
How to Learn: Highlight unfamiliar words, note their context, and check meanings using a dictionary (e.g., Cambridge or Oxford). Create a vocabulary journal to record words, their definitions, and example sentences.
IELTS Benefit: Improves recognition of topic-specific vocabulary (e.g., “sustainability,” “innovation”) for Reading comprehension and Writing Task 2 essays.
Example: While reading an article on climate change, note the word “mitigate” (to reduce). Record: “Mitigate (v): to make less severe. Example: Governments must mitigate carbon emissions to combat climate change.”
2. Use Flashcards to Memorise
Flashcards help you memorise vocabulary essential for fluent speaking and writing.
- What to Do: Practice using different flashcards.
- How to Learn: Review flashcards daily, testing yourself on meanings and usage. Group words by IELTS themes (e.g., health, society) for relevance.
- IELTS Benefit: Enhances quick recall of precise words during Speaking (e.g., “well-being” instead of “health”) and Writing (e.g., “detrimental” instead of “bad”).
- Example: Flashcard for “exacerbate” – Front: exacerbate. Back: (v) /ɪɡˈzæsərbeɪt/, to make worse. Example: Pollution can exacerbate health issues.
3. Group Words by Topic/Theme
Organising vocabulary by IELTS topics helps you prepare for Writing Task 2, Speaking Part 3, and Reading/Listening tasks.
- What to Do: Create lists of words and phrases for common IELTS topics like environment, education, health, technology, and society. Include synonyms, collocations, and related terms.
- How to Learn: Study one topic per week, writing sentences or short paragraphs using the words. Practice using them in speaking responses or writing essays.
- IELTS Benefit: Enables you to use topic-specific vocabulary accurately (e.g., “renewable energy” for environment essays), boosting lexical resource scores.
- Example: For “education”: Words: curriculum, pedagogy, literacy. Collocation: “lifelong learning.” Sentence: “A modern curriculum promotes lifelong learning and critical thinking.”
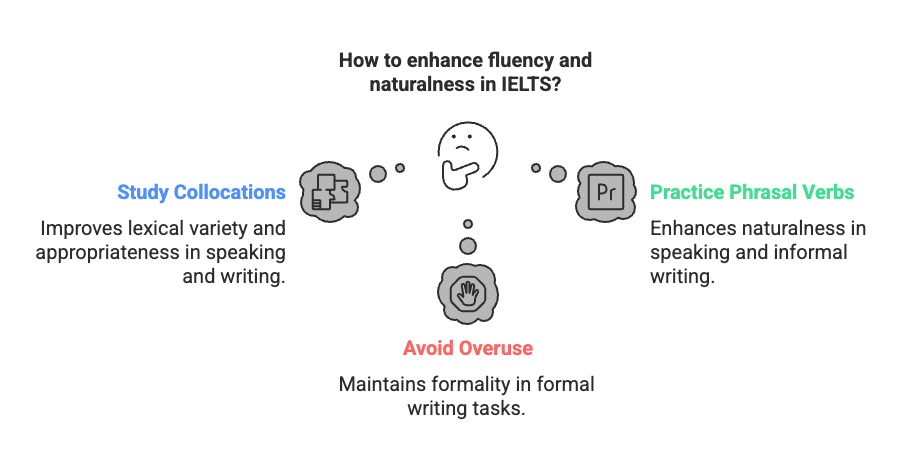
4. Learn Collocations and Phrasal Verbs
Collocations (words that naturally go together) and phrasal verbs enhance fluency and naturalness, key for Band 7+ in Speaking and Writing.
- What to Do: Study common collocations (e.g., “make a decision,” “address an issue”) and phrasal verbs (e.g., “cut down on,” “bring about”) from IELTS preparation books or online resources.
- How to Learn: Practice using collocations in Writing Task 2 essays and phrasal verbs in Speaking or General Training Writing Task 1 letters. Avoid overusing phrasal verbs in the formal Writing Task 2.
- IELTS Benefit: Improves lexical variety and appropriateness, e.g., using “tackle a problem” instead of “solve a problem” in Speaking.
- Example: Collocation: “sustainable development.” Sentence: “Governments should prioritise sustainable development to protect natural resources.”
5. Practice Paraphrasing
Paraphrasing means expressing ideas using different words and sentence structures, a critical skill for Writing Task 1 and Speaking.
- What to Do: Rephrase IELTS sentences using synonyms and different grammar structures. Practice restating Speaking Part 1 questions in your answers.
- How to Learn: Use a thesaurus to find synonyms, but ensure they fit the context (e.g., “significant” vs. “important”). Practice with sample tasks, e.g., rephrasing “The chart shows a rise in sales” as “The graph indicates an increase in revenue.”
- IELTS Benefit: Enhances Writing Task 1 (data description) and Speaking (avoiding repetition), improving lexical resource and coherence.
- Example: Original: “Technology has improved education.” Paraphrase: “Advancements in technology have enhanced learning opportunities.”
6. Watch and Listen to English Media
Exposure to spoken English through media builds vocabulary for listening and speaking, improving pronunciation and context understanding.
- What to Do: Watch TED Talks, documentaries, or podcasts on IELTS topics (e.g., environment, health). Listen to BBC Radio or IELTS Listening practice tests.
- How to Learn: Note new words, paying attention to their pronunciation and meaning. Mimic native speakers’ phrasing in your Speaking practice.
- IELTS Benefit: Improves listening comprehension and speaking fluency by familiarising you with academic and conversational vocabulary (e.g., “groundbreaking,” “on the contrary”).
- Example: From a TED Talk on innovation, note “disruptive technology.” Sentence: “Disruptive technology has transformed modern industries.”
7. Use Vocabulary in Real Situations
Applying vocabulary in real tasks ensures you understand and use words correctly, aligning with IELTS’s emphasis on appropriate usage.
- What to Do: Write short essays for Writing Task 2 or practice Speaking Part 2 responses using new vocabulary. Record yourself speaking to check accuracy.
- How to Learn: Focus on one new word or phrase per response, ensuring it fits the context. Get feedback from a teacher or use online tools to verify usage.
- IELTS Benefit: Reinforces accurate and context-appropriate word use, crucial for Writing Task 2 arguments and Speaking responses.
- Example: Use “alleviate” in a Writing Task 2 essay: “Investing in healthcare can alleviate poverty by improving workforce productivity.”
8. Avoid Common Vocabulary Mistakes
Understanding words to avoid and correcting overuse improves lexical precision, a key Band 7+ criterion.
- What to Do: Study lists of overused words (e.g., “very,” “good”) and their alternatives (e.g., “considerably,” “beneficial”). Practice replacing them in sample essays or responses.
- How to Learn: Review your Writing and Speaking practice for repetitive or vague words. Use precise alternatives in revisions.
- IELTS Benefit: Reduces errors in word choice, enhancing Writing and Speaking scores by demonstrating a wider vocabulary range.
- Example: Replace “very important” with “crucial.” Sentence: “Education is crucial for personal development.”
9. Review and Test Regularly
Regular review and self-testing consolidate vocabulary, ensuring retention for test day.
- What to Do: Schedule weekly reviews of your vocabulary journal or flashcards. Take practice IELTS Reading, Listening, or Writing tasks to test word usage.
- How to Learn: Create mini-quizzes (e.g., match words to definitions) or write sentences with 5 new words each week. Track progress by noting improved usage in practice tests.
- IELTS Benefit: Strengthens long-term retention, enabling confident use of vocabulary across all sections, particularly under time pressure.
- Example: Quiz: Match “ameliorate” to “improve.” Sentence: “Policies to ameliorate living standards are essential.”
10. Seek Feedback and Refine
Feedback from teachers or peers helps identify vocabulary misuse and areas for improvement.
- What to Do: Share your Writing essays or recorded speaking responses with a teacher, tutor, or study partner. Ask for specific feedback on vocabulary range and accuracy.
- How to Learn: Note feedback on incorrect or awkward word choices and practice corrected versions. Use online platforms (e.g., IELTS forums) for additional input.
- IELTS Benefit: Ensures vocabulary is used appropriately, aligning with IELTS criteria for lexical resource and boosting overall band scores.
- Example: Feedback: “Big” is too basic in “big problem.” Revision: “Significant challenge.” Sentence: “Unemployment is a significant challenge in urban areas.”
By following these strategies, you can build a strong, varied, and accurate vocabulary tailored to IELTS requirements. Focus on consistent practice, thematic learning, and context-appropriate usage to maximise your lexical resource score and achieve your target band.
|
15 videos|6 docs
|
FAQs on Strategies for Building IELTS Vocabulary - Vocabulary for IELTS
| 1. How can I effectively use flashcards for vocabulary retention in IELTS preparation? |  |
| 2. What types of English media should I watch or listen to for improving my vocabulary? |  |
| 3. Why is practicing collocations and phrasal verbs important for the IELTS exam? |  |
| 4. How often should I review and test my vocabulary knowledge when preparing for IELTS? |  |
| 5. What strategies can I use to avoid common vocabulary mistakes in IELTS writing? |  |






















