Revision Notes: Triangles and Quadrilaterals | Mathematics Class 6 ICSE PDF Download
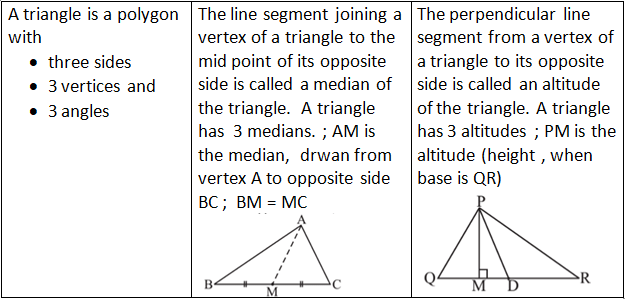
Triangles
Classification based on sides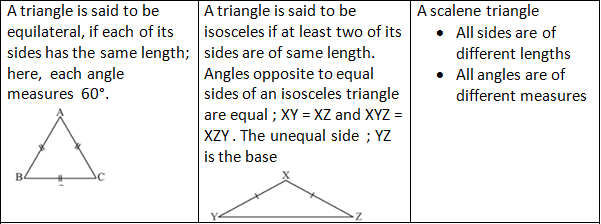
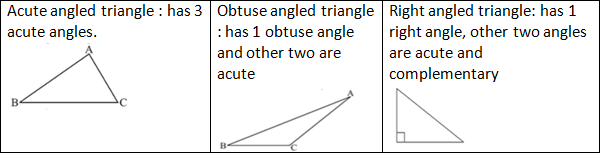
Classification based on angles
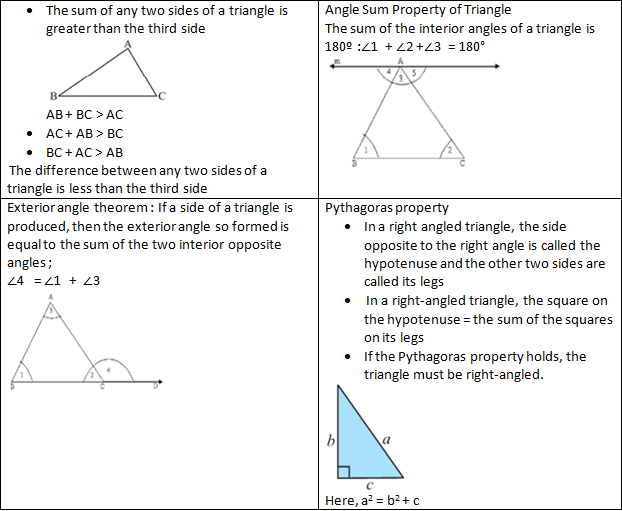
Properties of Triangles
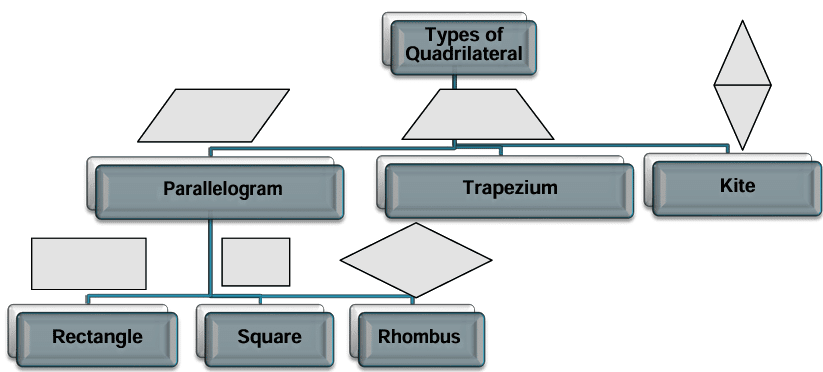
Quadrilaterals
A quadrilateral is a plane figure bounded by four straight lines.
Properties of Quadrilaterals
- The sum of the four interior angles of a quadrilateral = 360 degrees
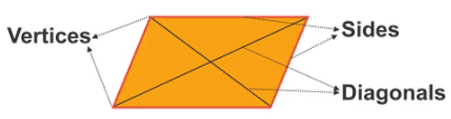
- Its two diagonals intersect.
- The line joining the midpoints of any two adjacent sides is parallel to the corresponding diagonal
- Lines joining the midpoints of the sides of a quadrilateral in an order form a Parallelogram.
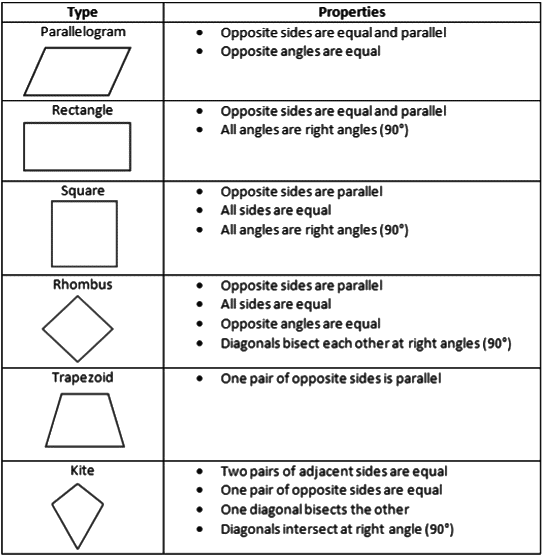
Properties of a Parallelogram
- Opposite angles are equal.
- Diagonals bisect each other.
- The angles on the same side are supplementary
- Each diagonal bisects the parallelogram into two congruent triangles
- The angle bisectors of the opposite vertices are parallel
- The angle between the angular bisectors of the same side is a right angle
Properties of a Trapezium
- Diagonals intersect each other
- The line joining the midpoints of non-parallel sides is parallel to the parallel side, and its length is half of the sum of the parallel sides.
- An isosceles trapezium has non-parallel sides equal, and it can be inscribed in a circle.
Properties of a Rectangle
(i) Diagonals are equal and bisect each other.(ii) The lines joining the midpoints of the sides in an order form a rhombus.
(iii) The line joining the midpoints of opposite sides of a rectangle is parallel to either of the sides
(iv) A rectangle can be inscribed in a circle.
Properties of a Kite
A kite is a quadrilateral which has two pairs of adjacent sides equal.
Properties of a Square
(i) Diagonals are equal and bisect at right angles.
(ii) Diagonals bisect the opposite angles.
(iii) Each diagonal divides the square into two congruent isosceles right-angled triangles.
(iv) It can be inscribed in a circle
(v) A circle can be inscribed in a square touching all its sides.
Properties of a Rhombus
(i) All sides are equal
(ii) Opposite angles are equal.
(iii) Diagonals bisect each other perpendicularly.
(iv) Diagonals are bisectors of the angles at the corresponding vertices.
- Theorem: If a pair of opposite sides of a quadrilateral are equal and parallel, it is a parallelogram
- Theorem: In a parallelogram, opposite sides are equal, opposite angles are equal, and each diagonal bisects the parallelogram
- Theorem: The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
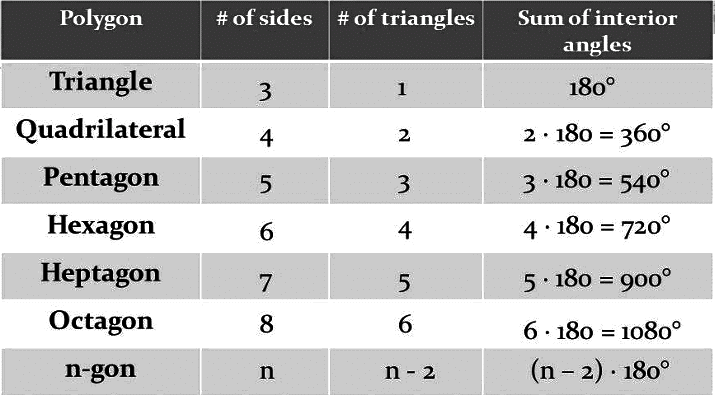
Polygons
A polygon is a closed figure formed by line segments, such that:
- Two line segments intersect only at their endpoints.
|
44 videos|229 docs|24 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Triangles and Quadrilaterals - Mathematics Class 6 ICSE
| $1. What are the different types of triangles based on their sides? |  |
| $2. What are the different types of triangles based on their angles? |  |
| $3. How do you calculate the perimeter of a triangle? |  |
| $4. What is the sum of the angles in a triangle? |  |
| $5. How can you determine if three sides can form a triangle? |  |















