Commerce Exam > Commerce Notes > Accountancy Class 12 > Mind Map: Accounting for Partnerships Basic Concepts
Mind Map: Accounting for Partnerships Basic Concepts | Accountancy Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
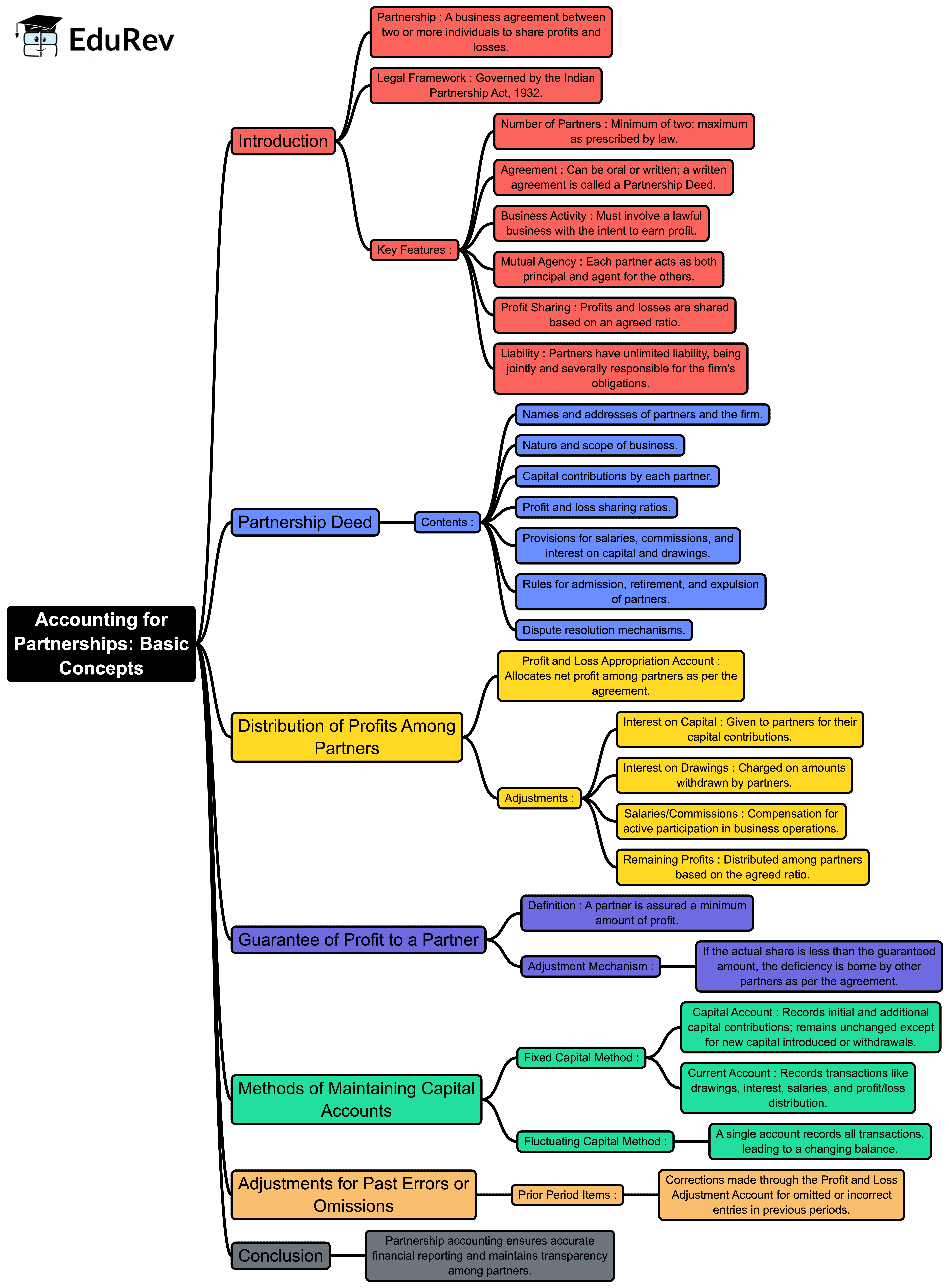
The document Mind Map: Accounting for Partnerships Basic Concepts | Accountancy Class 12 - Commerce is a part of the Commerce Course Accountancy Class 12.
All you need of Commerce at this link: Commerce
|
42 videos|255 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Accounting for Partnerships Basic Concepts - Accountancy Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What are the key characteristics of a partnership in accounting? |  |
Ans. A partnership in accounting is characterized by two or more individuals who agree to share the profits and losses of a business. Key features include mutual agency, shared profits, unlimited liability for partners, and a partnership agreement that outlines the terms of the partnership, including the roles and responsibilities of each partner.
| 2. How is profit sharing determined in a partnership? |  |
Ans. Profit sharing in a partnership is typically determined by the partnership agreement, which outlines the ratio in which profits and losses will be shared among partners. This ratio can be equal or based on the capital contributions or other agreed-upon factors. If no agreement exists, profits and losses are usually shared equally.
| 3. What is the significance of a partnership agreement in accounting? |  |
Ans. A partnership agreement is crucial in accounting as it outlines the terms and conditions of the partnership, including profit-sharing ratios, management responsibilities, and procedures for admitting new partners or dissolving the partnership. It helps prevent disputes and provides a clear framework for the partners' relationship.
| 4. How are the assets and liabilities of a partnership reported in financial statements? |  |
Ans. In financial statements, the assets and liabilities of a partnership are reported on a balance sheet similar to a sole proprietorship. The total assets are listed alongside the total liabilities, and the difference represents the partners' equity, which is divided among the partners based on their profit-sharing agreement.
| 5. What are the tax implications for partnerships compared to corporations? |  |
Ans. Partnerships are generally pass-through entities for tax purposes, meaning that income is reported on the individual partners' tax returns, thereby avoiding double taxation. In contrast, corporations are taxed at the corporate level, and dividends paid to shareholders are taxed again at the individual level. This makes partnerships often more tax-efficient than corporations.
Related Searches

















