Unit Test (Solutions): Crop Production and Management | Science Class 8 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each
Q1: Which of the following is a Rabi crop? (1 Mark)
(i) Paddy
(ii) Maize
(iii) Gram
(iv) Cotton
Ans: (iii)
Gram is a Rabi crop, which is sown in winter and harvested in the spring.
Q2: The process of loosening and turning the soil is called ___________. (1 Mark)
(i) Sowing
(ii) Irrigation
(iii) Harvesting
(iv) Ploughing
Ans: (iv)
Ploughing is the process of loosening and turning the soil before sowing seeds.
Q3: Which of the following is used to add nutrients to the soil? (1 Mark)
(i) Weedicides
(ii) Fertilizers
(iii) Pesticides
(iv) Herbicides
Ans: (ii)
Fertilizers are chemicals added to the soil to supply nutrients essential for plant growth.
Q4: ___________ is the technique where seeds are sown at appropriate depths and distances using machinery. (1 Mark)
(i) Broadcasting
(ii) Seed Drill
(iii) Hand Sowing
(iv) Ploughing
Ans: (ii)
Seed Drill is a modern technique where seeds are sown uniformly at correct depths and distances. Seed DrillQ5: Irrigation is important because it helps in ___________. (1 Mark)
Seed DrillQ5: Irrigation is important because it helps in ___________. (1 Mark)
(i) Providing moisture to the soil
(ii) Protecting crops from frost
(iii) Increasing the soil temperature
(iv) All of the above
Ans: (i)
Irrigation is essential for providing water to crops, ensuring proper growth and development.
Q6: What is crop rotation and why is it beneficial? (2 Marks)
Ans: Crop rotation is the practice of growing different types of crops in the same area across different seasons. It is beneficial because it helps maintain soil fertility and reduces soil erosion by replenishing the soil with different nutrients required by various crops. Crop Rotation
Crop Rotation
Q7: Explain the role of manure in agriculture. (2 Marks)
Ans: Manure is organic material derived from animal waste and decomposed plants. It enriches the soil by adding essential nutrients, improving soil texture, and increasing water retention capacity, leading to healthier crop growth.
Q8: What are weeds, and why is their removal important in crop fields? (2 Marks)
Ans: Weeds are undesirable plants that grow alongside crops and compete for water, nutrients, space, and light. Their removal is crucial because they can hinder crop growth, reduce yield, and even cause difficulties during harvesting. Weeds can also harbour pests and diseases, further affecting crop health.
Q9: What are the main steps involved in the preparation of soil before sowing? (3 Marks)
Ans: The main steps involved in the preparation of soil before sowing include:
1. Ploughing: Loosening and turning the soil to increase aeration and nutrient availability.
2. Levelling: Making the soil surface even to ensure uniform water distribution and prevent soil erosion.
3. Manuring: Adding organic matter or fertilizers to enrich the soil with nutrients needed for healthy crop growth
Q10: Describe the process of harvesting and threshing. (3 Marks)
Ans: Harvesting is the process of cutting mature crops from the fields. Traditionally done with a sickle, it is now often performed using machines like harvesters. Timing is crucial to ensure the crop is fully mature but not overripe, which helps maintain quality and yield.
Threshing follows harvesting and involves separating the grains from the stalks and chaff. This can be done manually by beating the crop or using animals, but modern farming often uses threshing machines or combines.
A combine is a machine that performs both harvesting and threshing simultaneously, efficiently separating grains from the husk and stalk, making the crop ready for further processing or storage.
Q11: Differentiate between manure and fertilizers in terms of their composition and effects on the soil. (3 Marks)
Ans: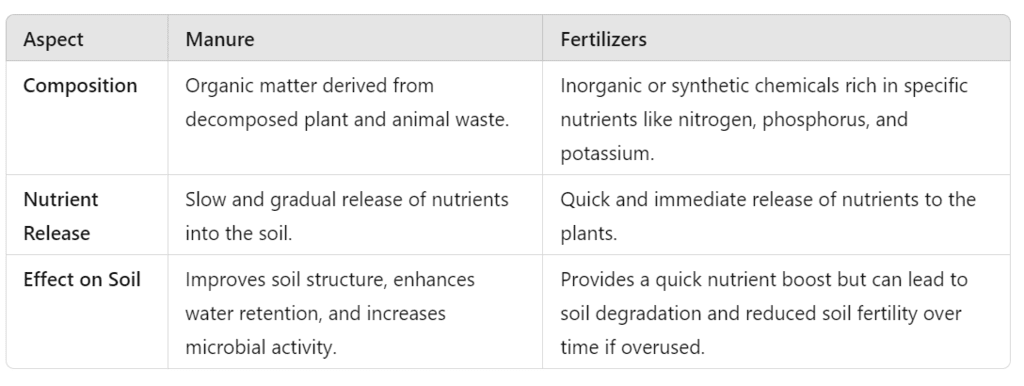
Q12: Explain the methods used for protecting crops from pests and diseases. Why is pest control important in agriculture? (5 Marks)
Ans: Crops can be protected from pests and diseases using several methods:
1. Chemical Control: Involves the use of pesticides to kill or repel pests. However, it should be used judiciously to avoid harmful effects on the environment and human health.
2. Biological Control: Utilizes natural predators or parasites to control pest populations, such as using ladybugs to control aphids.
3. Cultural Practices: Includes methods like crop rotation, intercropping, and maintaining field hygiene to prevent pest and disease outbreaks.
4. Mechanical Control: Involves physical methods such as traps or barriers to protect crops.
Pest control is important because pests can significantly reduce crop yields, affect the quality of the produce, and even lead to total crop failure, which impacts food supply and farmers' livelihoods.
Q13: Describe the modern methods of irrigation and their advantages over traditional methods. (5 Marks)
Ans: Modern methods of irrigation include:
1. Drip Irrigation: Delivers water directly to the roots of plants using a network of pipes and emitters. This method is highly efficient, reduces water wastage, and is ideal for water-scarce regions.
 Drip Irrigation2. Sprinkler Irrigation: Sprays water over the crops in a manner similar to rainfall, ensuring even distribution. It is suitable for uneven land and reduces soil erosion.
Drip Irrigation2. Sprinkler Irrigation: Sprays water over the crops in a manner similar to rainfall, ensuring even distribution. It is suitable for uneven land and reduces soil erosion.
 Sprinkler Irrigation
Sprinkler Irrigation
Advantages over Traditional Methods:
- Efficiency: Modern methods use water more efficiently, reducing wastage compared to traditional methods like surface irrigation.
- Water Conservation: They save water by delivering it directly to the roots or as fine droplets, minimizing evaporation and runoff.
- Improved Crop Yield: With better water management, crops receive the right amount of water, leading to healthier plants and higher yields.
- Labour Saving: Modern systems often require less manual labour compared to traditional methods, which can be labour-intensive.
|
136 videos|530 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Crop Production and Management - Science Class 8
| 1. What are the main types of crops grown in agriculture? |  |
| 2. How do farmers manage soil health for better crop production? |  |
| 3. What are the different methods of irrigation in crop management? |  |
| 4. Why is crop rotation important in agriculture? |  |
| 5. What role does technology play in modern crop production? |  |

















