India, That Is Bharat NCERT Solutions | Social Studies for Class 6 PDF Download
The Big Questions (Page 75)
Q1: How do we define India?
Ans: India is a vast and diverse country in South Asia, the seventh-largest in the world. It is bordered by Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, and Myanmar, and is surrounded by the Indian Ocean, Arabian Sea, and Bay of Bengal. Known for its rich culture, history, and geographical diversity, India is often called a land of “unity in diversity” for its many languages, traditions, and beliefs that coexist harmoniously.
Q2: What were the ancient names for India?
Ans: Ancient names for India include:
Sapta Sindhava: From the Rig Veda, meaning "land of the seven rivers."
Bhāratavarṣa: Used in the Mahabharata, meaning "the country of the Bharatas."
Jambudvīpa: Meaning "the island of the fruit of the jamun tree."
Hind or Hindu: Names used by the Persians, derived from "Sindhu" (Indus River).
Indoi or Indike: Names used by the Greeks.
Yintu or Yindu: Names used by the ancient Chinese, derived from "Sindhu."
Tianzhu: Another Chinese term for India, reflecting respect for India as the land of the Buddha.
Hindustān: A term first used in a Persian inscription about 1,800 years ago.
Think About It (Page 77)
Q: Consider the physical map of the Indian Subcontinent at the start of the chapter. What are its natural boundaries that you can make out?
Ans: From the physical map of the Indian Subcontinent, the following natural boundaries can be identified:
- North: The towering Himalayan mountain range forms a natural barrier, protecting the northern boundary.
- South: The Indian Ocean surrounds the southern tip of the subcontinent.
- West: The Thar Desert and the Arabian Sea serve as natural boundaries to the west.
- East: The Bay of Bengal and dense forests of the northeastern region form the eastern boundary.
Let's Explore (Page 78)
Q: Do you recognise the names of any regions given in the map (Fig. 5.4) on page 79? List the ones that you have heard of.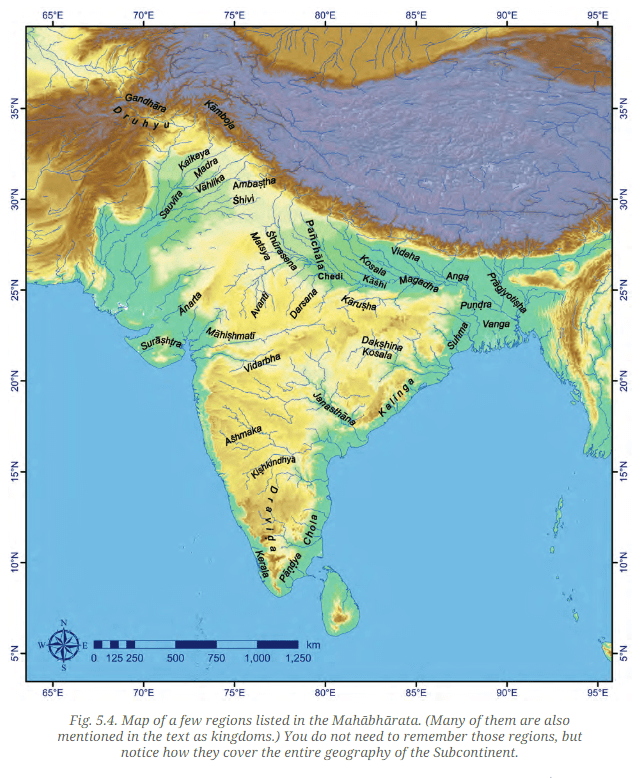 Ans: Looking at the map, here are some recognisable regions from the names provided:
Ans: Looking at the map, here are some recognisable regions from the names provided:
- Kalinga – Known for the famous Kalinga War fought by Emperor Ashoka.
- Magadha – A well-known ancient region, home to powerful dynasties and the Mauryan Empire.
- Kosala – A historical kingdom, linked with the epic Ramayana.
- Vanga – A region that corresponds to modern Bengal.
- Dakshina Kosala – Another region linked to southern India’s cultural history.
- Saurashtra – Known today as part of Gujarat.
- Anga – One of the ancient kingdoms mentioned in the Mahabharata.
- Surashtra – Another familiar region, correlating to parts of present-day Gujarat.
Think About it (Page 80)
Q: Have you identified the 'snowy mountains'? Do you think this brief description of Bhärata is correct?Ans: Yes, the ‘snowy mountains’ mentioned refer to the Himalayas, which are located in the northern part of India. These mountains are known for their snow-covered peaks and serve as a natural boundary for the subcontinent. The brief description of Bhārata seems correct as it highlights the geographical diversity of India, including the snowy Himalayas, vast plains, deserts, and surrounding seas. This reflects the rich and varied landscapes that shape the country’s identity.
Let's Explore (Page 81)
Q: In this reproduction of the first page of the original Constitution of India in Fig. 5.5 (page 82), can you make out the phrase 'India, that is Bharat'?
 Ans: Yes, the phrase 'India, that is Bharat' appears in the first article of the original Constitution of India. It is mentioned in Article 1, which states: "India, that is Bharat, shall be a Union of States."This phrase highlights the dual name of the country, recognising both 'India' and 'Bharat' as official names in the Constitution.
Ans: Yes, the phrase 'India, that is Bharat' appears in the first article of the original Constitution of India. It is mentioned in Article 1, which states: "India, that is Bharat, shall be a Union of States."This phrase highlights the dual name of the country, recognising both 'India' and 'Bharat' as official names in the Constitution.
Let's Explore (Page 83)
Q: Can you complete this table of the many names of India?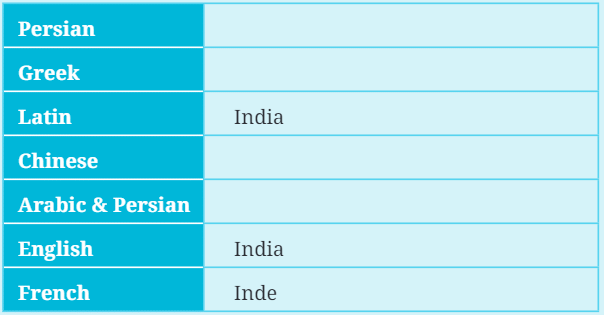 Ans:
Ans: 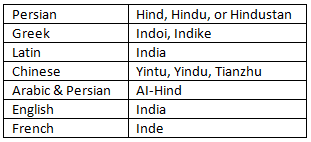
Questions, Activities and Projects (Page 84)
Q1: Discuss what could be the meaning of the quotation at the start of the chapter.
Ans: The quotation by Sri Aurobindo suggests that the principles forming the core of India’s spiritual and cultural unity were established in ancient times. These principles have been passed down through generations and have continued to shape the way of life for people across the country throughout history.
For example
The Vedas which are India’s oldest religious texts have given rise to several schools of thought. The Upanishads and the different schools of Indian philosophy discussed many issues regarding the nature of the ultimate reality. Buddhism and Jainism departed from the authority of the Vedas laying emphasis on different values and practices. But common to all belief systems which helped to Unite India spiritually was belief in the need to detach from material things and understand the nature of the ultimate reality.
Similarly, our culture has evolved due to the fusion of our various religious belief systems, which have contributed to our rich heritage of art, sculpture, music, painting, etc.
Q2: True or false?
- The Rig Veda describes the entire geography of India.
Ans: False. The Rig Veda mainly describes the northwest region of the subcontinent as 'Sapta Sindhava'. - The Vishnu Purana describes the entire Subcontinent.
Ans: True. The Vishnu Purana refers to the entire subcontinent as 'Bharata'. - In Ashoka’s time, ‘Jambudvipa’ included what is today India, parts of Afghanistan, Bangladesh and Pakistan.
Ans: True. Ashoka used 'Jambudvipa' to describe the entire region. - The Mahabharata lists many regions, including Kashmir, Kutch, and Kerala.
Ans: True. The Mahabharata mentions many regions, such as Kashmira, Kaccha, and Kerala. - The term ‘Hindustan’ first appeared in a Greek inscription more than 2,000 years ago.
Ans: False. The term 'Hindustan' first appeared in a Persian inscription about 1,800 years ago. - In ancient Persian, the word ‘Hindu’ refers to the Hindu religion.
Ans: False. In ancient Persian, 'Hindu' was a geographical term referring to the region around the Indus River. - ‘Bharata’ is a name given to India by foreign travellers.
Ans: False. 'Bharata' is a name given by the ancient inhabitants of India.
Q3: If you were born some 2,000 years ago and had the chance to name our country, what name or names might you have chosen, and why? Use your imagination!
Ans: If I were born 2,000 years ago and had the chance to name our country, I might have chosen:
- Aryavarta: Meaning "Land of the Noble Ones," reflecting the ancient Vedic texts that referred to the region where noble or righteous people lived.
- Saptasindhu: Meaning "Land of the Seven Rivers," highlighting the significance of the major rivers in sustaining life and culture.
- Himalaya-Varsha: Meaning "Land of the Himalayas," emphasising the majestic mountain range that defines the northern boundary.
- Dharmakshetra: Meaning "Field of Dharma" or "Land of Righteousness," showcasing the region’s rich spiritual and moral heritage.
- Vishvaguru: Meaning "Teacher of the World," underlining the ancient knowledge, wisdom, and cultural influence India had over other civilisations.
These names encapsulate the cultural, geographical, and spiritual essence of ancient India, emphasising its heritage, natural beauty, and role as a centre of learning.
Q4: Why did people travel to India from various parts of the world in ancient times? What could be their motivations in undertaking such long journeys? (Hint: There could be at least four or five motivations)
Ans: People travelled to India from various parts of the world in ancient times for several reasons:
- Trade: India was famous for its rich resources, including spices, silk, precious stones, and textiles. Merchants and traders travelled to acquire these goods and establish trade relations.
- Education and Knowledge: India was home to renowned learning centres like Nalanda and Takshashila, which attracted scholars from around the world seeking knowledge in subjects like philosophy, astronomy, medicine, and mathematics.
- Pilgrimage and Spirituality: Many travellers came to India to visit sacred sites and explore its rich spiritual traditions, as India was the birthplace of religions like Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism.
- Cultural Exchange: Artists, musicians, and writers travelled to India to experience its diverse and vibrant cultural heritage, including art, architecture, and literature.
- Conquests and Empires: Some travelled as part of military expeditions or to expand their empires, driven by the desire for power, land, and wealth.
|
48 videos|293 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on India, That Is Bharat NCERT Solutions - Social Studies for Class 6
| 1. What are the main themes discussed in "India, That Is Bharat"? |  |
| 2. How does the article describe the concept of 'Bharat'? |  |
| 3. What role does history play in shaping the identity of India according to the article? |  |
| 4. In what ways does the article address the challenges faced by modern India? |  |
| 5. How does the article suggest we reconcile traditional values with modernity? |  |






















