What is Static Friction | Civil Engineering Optional for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Static Friction |

|
| What is Static Friction? |

|
| Laws of Static Friction |

|
| Laws of Limiting Friction |

|
Static Friction
- Fluid Friction: The resistance experienced by layers of fluid in motion relative to each other.
- Lubricated Friction: The resistance occurring between two solid surfaces separated by a layer of lubricant.
- Skin Friction: The resistance experienced by an object moving through a fluid, related to the surface texture of the object.
- Internal Friction: The resistance to motion within a deformable body due to internal forces.
- Dry Friction: The resistance between two solid surfaces in contact without any lubrication.
- Kinetic Friction: The resistance experienced by two surfaces in relative motion.
- Static Friction: The resistance that prevents relative motion between two surfaces in contact, keeping an object at rest until an applied force exceeds this frictional force.
Static friction is the force that keeps an object at rest and prevents it from moving. It acts to balance the applied force up to a certain limit, known as the limiting friction, beyond which motion begins and kinetic friction takes over.
What is Static Friction?
Static friction is a force that keeps an object at rest. It can be defined as the friction experienced when trying to move a stationary object on a surface, without actually causing any relative motion between the object and the surface.
In more detail, static friction is the force that exactly balances the applied force, maintaining the object in a stationary state. This force is self-regulating, meaning that it will always be equal and opposite to the applied force, preventing motion.
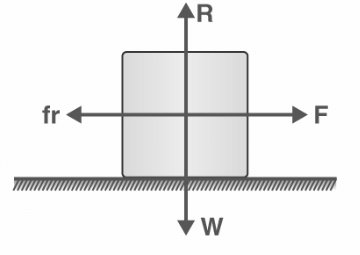
For example, if an external force F is applied to a stationary object with weight W, the reaction force R due to the weight and the frictional force fr will act in the opposite direction. When no motion occurs, the external force F and the frictional force fr are equal and opposite, so −fr.
Static Friction Examples
Some real-life examples of static friction are given in the points below.- Papers on a tabletop
- A towel hanging on a rack
- A bookmark in a book
- A car parked on a hill
Laws of Static Friction
- Independence from Area of Contact: The maximum force of static friction does not depend on the contact area between the surfaces.
- Proportional to Normal Force: The maximum force of static friction is proportional to the normal force. As the normal force increases, the maximum external force the object can withstand without moving also increases.
Limiting Friction
Limiting friction is the maximum value of static friction that occurs just before an object begins to slide over another surface. When an external force exceeds the limiting friction, the object starts to move.
Once motion begins, static friction is no longer applicable, and kinetic friction comes into play.
Laws of Limiting Friction
- Opposition to Motion: The direction of the limiting frictional force is always opposite to the direction of motion.
- Tangential Action: Limiting friction acts tangentially to the two interacting surfaces.
- Proportionality to Normal Reaction: The magnitude of limiting friction is proportional to the normal reaction force between the two surfaces.
- Dependence on Material and Surface Characteristics: Limiting friction depends on the material and nature of the interacting surfaces and their smoothness.
- Independence from Shape and Area: For any two given surfaces, as long as the normal reaction is the same, the magnitude of limiting friction is independent of the shape or area of the surfaces in contact.
|
352 videos|468 docs|2 tests
|
FAQs on What is Static Friction - Civil Engineering Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is static friction? |  |
| 2. What are the laws of static friction? |  |
| 3. What are the laws of limiting friction? |  |
| 4. How is static friction different from kinetic friction? |  |
| 5. How can the coefficient of static friction be determined experimentally? |  |














