Worksheet: Paths to Modernisation | History Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: Japan's physical landscape is characterized by over 50% of mountainous terrain and its location in an active earthquake zone. There is no major ______________ system.
Q2: The Meiji government imposed a new administrative structure by altering old village and domain boundaries to integrate the nation, effectively abolishing ______________.
Q3: The ______________ movement was launched in China in 1958 to galvanize the country to industrialize rapidly.
Q4: The Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution led to a period of turmoil in China, weakening the Communist Party and severely disrupting the economy and educational system. This period emphasized ______________ over professional knowledge.
Q5: Deng Xiaoping introduced a socialist market economy in China in 1978 and declared the goal of the Four Modernizations in the areas of science, industry, agriculture, and defense. The Fifth Modernization advocated for ______________.
Q6: Taiwan was a Japanese colony until the end of World War II. The ______________ Declaration in 1943 and the ______________ Proclamation in 1949 restored sovereignty to China over Taiwan.
Q7: The Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution in China was initiated in 1966 and led by ______________.
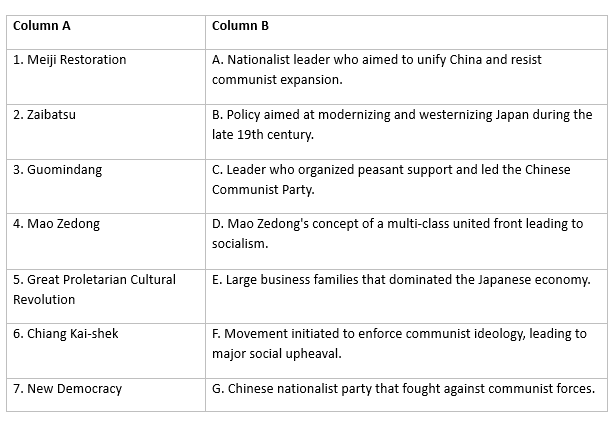
Match the Column
Q1: Match the elements from the left column with the correct descriptions in the right column.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: The Meiji Restoration is considered one of the most significant events in Japanese history.
Reason: It marked the beginning of Japan's transformation into a modern, industrialized nation.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the Reason is true.
Q2: Assertion: The Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution in China had a lasting impact on the country.
Reason: It emphasized the importance of professional knowledge and expertise.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the Reason is true.
Q3: Assertion: Taiwan transformed into a democracy after the death of Chiang Kai-shek.
Reason: Chiang Kai-shek's repressive government forbade political opposition.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the Reason is true.
Q4: Assertion: The Japanese government's Meiji Reforms included constitutional changes.
Reason: The Meiji Constitution established a Diet and declared the emperor as the commander of the forces.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the Reason is true.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the significance of the Meiji Restoration in Japan in one sentence.
Q2: What were the Four Modernizations introduced in China in 1978?
Q3: Briefly describe the key features of the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution in China.
Q4: Who was Sun Yat-sen, and what were his Three Principles?
Q5: What are Zaibatsu in the context of Japan's history?
Q6: How did Taiwan transform into a democracy?
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the key factors that contributed to Japan's successful modernization process during the Meiji period.
Q2: Discuss the main differences between the paths to modernization taken by Japan and China in the 19th and 20th centuries.
Q3: Describe the major objectives and outcomes of the Great Leap Forward movement in China.
Q4: Compare and contrast the roles of Sun Yat-sen and Chiang Kai-shek in the Guomindang and China's political landscape.
Q5: Explain how Deng Xiaoping's economic reforms transformed China's economy and what the Five Modernizations referred to.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Compare and contrast the Meiji Restoration in Japan and the establishment of the People's Republic of China regarding their political, economic, and social transformations. Highlight the key differences and similarities between these two historical events.
Q2: Analyze the role and impact of the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution in China, including its consequences for the Chinese society, economy, and political landscape. Discuss the reasons behind its initiation and its lasting effects on China.
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
27 videos|151 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Paths to Modernisation - History Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What are the key themes discussed in the article "Paths to Modernisation"? |  |
| 2. How does the article explain the concept of modernisation? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of modernisation presented in the article? |  |
| 4. How does the article address the challenges faced during the process of modernisation? |  |
| 5. What role does education play in the process of modernisation according to the article? |  |















