Revision Notes: Methods of Teaching | Teaching Aptitude for Teaching Exam - B.Ed Entrance PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Instructor/Teacher Centred Methods |

|
| Learner-Centred Methods |

|
| Few Other Teaching Technique |

|
| Offline (Traditional) Teaching Methods |

|
| Online (Digital) Teaching Methods |

|
Introduction
Teaching and learning are the two sides of a coin. The most accepted criterion for measuring good teaching is the amount of student learning that occurs. There are consistently high correlations between students’ ratings of the “amount learned” in the course and their overall ratings of the teacher and the course.
There are different types of teaching methods:
- Teacher-centered methods,
- Learner-centered methods,
Instructor/Teacher Centred Methods
- Here the teacher casts himself/herself in the role of being a master of the subject matter. The teacher is looked upon by the learners as an expert or an authority. Learners, on the other hand, are presumed to be passive and copious recipients of knowledge from the teacher.
- Examples of such methods are expository or lecture methods – which require little or no involvement of learners in the teaching process. It is also for this lack of involvement of the learners in what they are taught, that such methods are called “closed-ended”.
- In this approach, the teacher is the primary source of knowledge, and students are passive recipients. The teacher controls the learning process, content delivery, and assessment.
Key Teacher-Centered Methods:
a) Lecture Method
Traditional method where the teacher delivers knowledge through verbal instruction.
Effective for large classrooms and theoretical subjects.
b) Demonstration Method
The teacher explains concepts using models, experiments, or practical demonstrations.
Common in science and technical subjects.
c) Storytelling & Case Studies
Used in social sciences, humanities, and business studies to explain concepts through real-life stories.
d) Expository Teaching
Structured presentation where information is systematically delivered, ensuring clarity and comprehension.
Advantages:
Covers a large amount of content in a short time.
Provides structured and organized learning.
Efficient for large groups.
Challenges:
Passive learning with limited student engagement.
Less focus on critical thinking and problem-solving.
One-way communication may lead to reduced retention.
Learner-Centred Methods
- In learner-centered methods, the teacher/instructor is both a teacher and a learner at the same time. In the words of Lawrence Stenhouse, the teacher plays a dual role as a learner as well “so that in his classroom extends rather than constricts his intellectual horizons”.
- The teacher also learns new things every day which he/she didn’t know in the process of teaching. The teacher “becomes a resource rather than an authority”. Examples of learner-centered methods are the discussion method, the discovery or inquiry-based approach, and Hill’s model of learning through discussion (LTD).
This approach shifts the focus from the teacher to the student, encouraging active participation, problem-solving, and self-learning.
Key Learner-Centered Methods:
a) Discussion Method
Encourages interaction, debate, and critical thinking.
Promotes active student participation.
b) Problem-Based Learning (PBL)
Students work on real-world problems, developing analytical and research skills.
Common in medical, law, and management education.
c) Flipped Classroom
Students learn theoretical content at home through videos and readings, while classroom time is used for discussions and practical applications.
d) Group Activities & Peer Learning
Encourages teamwork and collaborative problem-solving.
Promotes deeper understanding through peer interactions.
e) Experiential Learning
Learning through hands-on experiences, including internships, lab work, and case studies.
Advantages:
Enhances critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving.
Encourages independent learning and responsibility.
Provides practical and application-based knowledge.
Challenges:
Requires more time and resources.
Teachers need to be facilitators rather than just knowledge providers.
Assessment can be complex and subjective.
The Lecture Method
- A formal or semi-formal discourse in which the instructor presents a series of events, facts, or principles, explores a problem or explains relationships. It creates new ideas.
- It is good for a large class. The teacher is experienced and has mastery of the subject, explains all points, and can answer all questions raised by students. Students can ask if they need any clarification.
- Learn through listening. The teacher explains all the points.
- Students give their input. The teacher discusses the whole topic in the class in easy language students can easily understand the topic.
- It is good for a large class. The teacher provides all knowledge related to the topic.
- Time-saving as a teacher is supposed to finish the lecture on time.
- Students give their views at the end of the lecture.
- Students can ask the question if they have any problem understanding the lecture.
- Students attentively listen to a lecture and take notes as the teacher ask questions at the end of the lecture.
- Students know and understand basic concepts.
- The teacher knows all the students so he/she can use suitable strategies for the class to make them understand.
Uses
- To orient students.
- To introduce a subject.
- To give directions on procedures.
- To present basic material.
- To introduce a demonstration, discussion, or performance.
- To illustrate the application of rules, principles, or concepts.
- To review, clarify, emphasize or summarise.
 Advantages
Advantages
- Saves time.
- Permits flexibility.
- Requires less rigid space requirement.
- Permits adaptability.
- Permits versatility.
- Permits better center over contact and sequence.
Disadvantages
- Involves one-way communication.
- Poses problems in skill teaching.
- Encourages student passiveness.
- Poses difficulty in gauging student reaction.
- Require highly skilled instructors.
The Discussion Method
A method in which group discussion techniques are used to reach instructional objectives.
- Students listen to other’s opinions & express their opinion.
- Discuss with teachers the points that were missed during the discussion.
- Students learn on their own & find out key points.
- Students exchange their ideas.
- Students get point of view of all and not only those who always speak.
- After discussion when students give their presentation, the teacher corrects their mistakes.
- Students can make their own notes.
- The learning is more effective.
- They don’t have to rely on rote learning.
- Develops creativity among students.
- It evokes thinking among students.
- Students have time for the preparation of the topic.
- Students should have material and knowledge before the discussion.
 Uses
Uses
- To develop imaginative solutions to problems.
- To stimulate thinking and interest and to secure student participation.
- To emphasize main teaching points.
- To supplement lectures, reading & laboratory exercises.
- To determine how well the student understands concepts and principle
Advantages
- Increase students interest
- Increases student’s acceptance and commitments.
- Utilizes student knowledge and experience.
- Results in more permanent learning because of the high degree of student participation.
Disadvantages
- Require highly skilled instructor.
- Requires preparation by the student.
- Limits content.
- Consumes time.
- Restricts the size of groups.
The Programmed Instruction Method
A method of self-instruction
- To provide remedial instruction.
- To provide make-up instruction for late arrivals, absentees, or translents.
- To maintain previously learned skills that are not performed frequently enough.
- To provide retraining on equipment and procedures which have become obsolete.
- To upgrade production.
- To accelerate capable students.
- To provide enough common background among students.
- To provide the review and practice of knowledge and skills.
Uses/Advantages
- Reduce failure rate.
- Improves end-of-course proficiency.
- Saves time.
- Provides for self-instruction.
 Disadvantages
Disadvantages
- Require local or commercial preparation.
- Requires lengthy programmer training.
- Increases expenses.
- Requires considerable lead time.
The Study Assignment Method
A method in which the instructor assigns reading to books, periodicals, project,s or research papers or exercises for the practice.
- To orient students to a topic prior to classroom or Laboratory work.
- It enhances the ability of research on any topic as the student’s search topic from different books, websites, etc.
- Active learning
- To set the stage for a lecture-demonstration or discussion.
- To provide for or capitalize on individual differences in ability, background, or experience through differentiated assignments.
- To provide for the review of material covered in class or to give practice.
- To provide enrichment material.
Uses/Advantages
- Increase coverage of material.
- Reduce classroom time.
- Permits individual attention.

Disadvantages
- Require careful planning and follow-up.
- Poses an evaluation problem.
- Produce non-standard results.
The Tutorial Method
- To reach highly complicated skills operations or operations involving danger or expensive equipment.
- To provide individualized remedial assistance
Uses/Advantages
- Permits adaptive instruction.
- Stimulates active participation.
- Promotes safety.
Disadvantages
- Requires a highly competent instructor.
- Demands time and money.
The Seminar Method
A tutorial arrangement involving the instructor and groups, rather than instructor and individual.
- To provide general guidance for a group working on an advanced study or research project.
- To exchange information on techniques and approaches being explored by members of a study or research group.
- To develop new and imaginative solutions to problems under study by the group.
Uses/Advantages
- Provides motivation and report.
- Stimulates active participation.
- Permits adaptive instruction.

Disadvantages
- Requires a highly competent instructor.
- Poses evaluation problems.
- Is more costly than most other methods.
The Demonstration Method
A method of instruction where the instructor by actually performing an operation or doing a job shows the students what to do, how to do it, and through explanations brings out why, where, and when it is done.
- To teach manipulative operations or procedures.
- To teach troubleshooting.
- To illustrate principles.
- To teach operation or functioning of equipment.
- To teach teamwork.
- To set standards of workmanship.
- To teach safety procedures.
Uses/Advantages
- Minimize damage and waste
- Saves time
- Can be presented to large groups.
- Enable learning evaluation.

Disadvantages
- Require careful preparation and rehearsal.
- Requires special classroom arrangements.
- Requires tools and equipment.
- Requires more instructors.
Few Other Teaching Technique
Brainstorming
- More interesting
- More informative
- Gain knowledge
- Learning is effective
- More participation of students
- Students give their opinion
- Active learning
- Creative thinking is encouraged.
- Students think beyond their knowledge.
- Everyone gets the chance to express their thoughts.
- Simple topics can be learned from different angles.
Roleplay
- Interesting method
- Creative thinking is encouraged.
- Students think beyond their knowledge.
- Students enjoy the situation
- Active learning
- Easy to learn
Case study
- Active learning
- Creative thinking is encouraged.
- Students think beyond their knowledge.

Offline (Traditional) Teaching Methods
Offline teaching refers to face-to-face learning in physical classrooms, focusing on direct teacher-student interaction.
Key Methods:
Lecture-Based Learning (Chalk & Talk, Whiteboard, Smart Classes)
Classroom Discussions & Debates
Laboratory & Practical Work (Experiments, Demonstrations)
Field Trips & Outdoor Learning (Excursions, Industrial Visits)
Workshops & Seminars (Guest Lectures, Hands-on Training)
Advantages:
Direct interaction and better student engagement
Immediate feedback from teachers
Structured learning with discipline
Social and emotional development through peer interaction
Challenges:
Limited flexibility (fixed time and location)
High cost (travel, infrastructure)
Limited access to study materials (depends on textbooks and libraries)
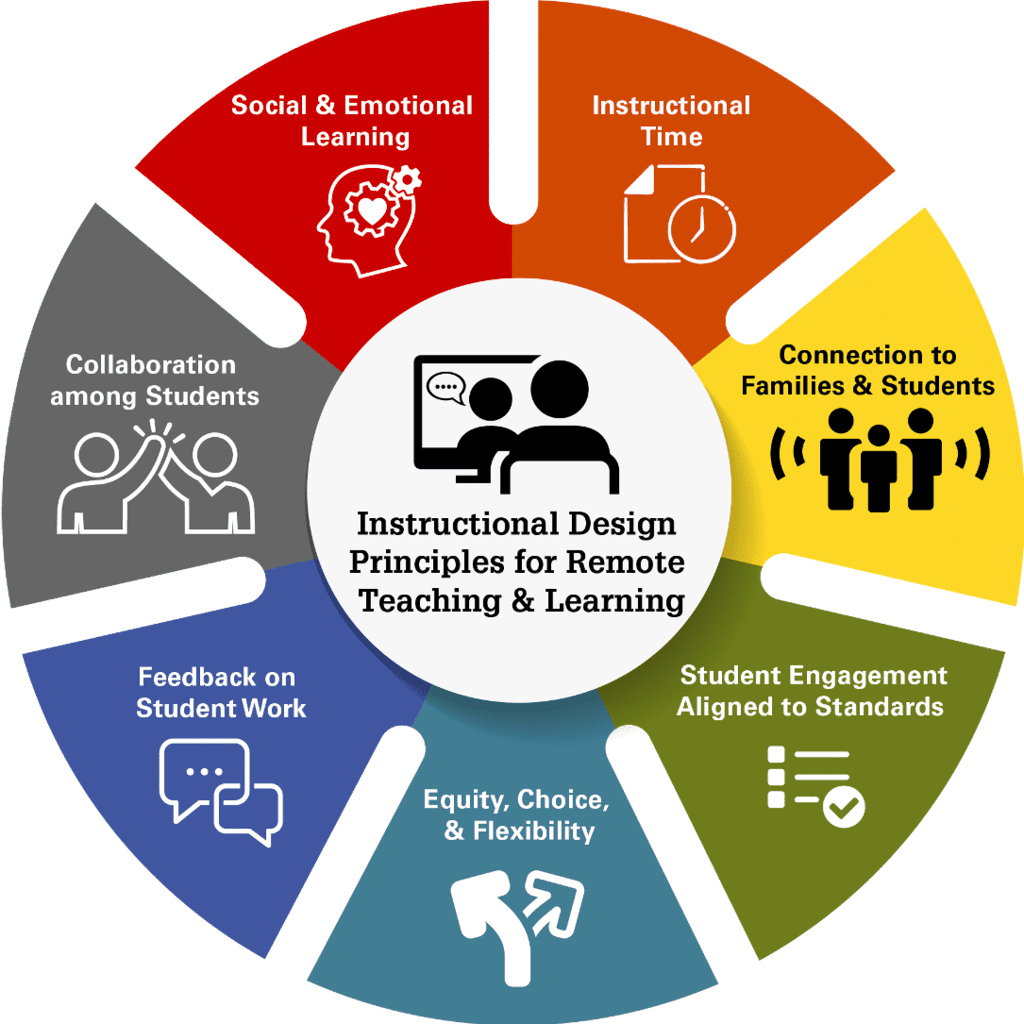
Online (Digital) Teaching Methods
Online education uses technology-based platforms for remote learning, offering greater flexibility and accessibility.
Key Online Platforms & Tools:
a) SWAYAM (Study Webs of Active Learning for Young Aspiring Minds)
Launched by the Government of India to provide free online courses from top universities (IITs, NPTEL, IGNOU, etc.).
Covers UG, PG, and school-level subjects.
Certification available at a nominal fee.
b) SWAYAM Prabha
32 DTH (Direct-to-Home) channels broadcasting educational content 24/7.
Best for students with limited internet access (TV-based learning).
Covers school, college, and competitive exam content.
c) MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses)
Online courses accessible to anyone worldwide.
Platforms: Coursera, edX, Udemy, NPTEL, Khan Academy.
Include video lectures, quizzes, assignments, and discussion forums.
d) Learning Management Systems (LMS)
Used by universities for online course delivery.
Examples: Moodle, Google Classroom, Blackboard.
Helps in content management, quizzes, assessments, and tracking student progress.
Advantages:
Flexible learning (anytime, anywhere)
Cost-effective (many courses are free or affordable)
Access to global faculty and updated content
Recorded lectures and self-paced learning
Challenges:
Lack of face-to-face interaction
Requires internet access and digital literacy
Less discipline and engagement compared to offline learning
|
29 videos|48 docs|11 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Methods of Teaching - Teaching Aptitude for Teaching Exam - B.Ed Entrance
| 1. What are the advantages of using the Lecture Method in teaching? |  |
| 2. How does the Discussion Method enhance student engagement? |  |
| 3. What is the role of the Programmed Instruction Method in personalized learning? |  |
| 4. In what ways does the Seminar Method differ from traditional teaching methods? |  |
| 5. What are some effective strategies for implementing the Demonstration Method in the classroom? |  |















