Methods of Research (Detailed) - Research Aptitude Notes
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Action Research |

|
| Quantitative Research Method |

|
| Qualitative Research Method |

|
Introduction
Research methods refer to the various strategies, processes, or techniques utilized in the collection of data or evidence for analysis with the aim of uncovering new information or deepening the understanding of a particular subject.
There are several types of research methods, each employing different tools for data collection. These include:
- Historical Research Method
- Descriptive Research Method
- Experimental Method of Research
- Action Research
- Quantitative Research Method
- Qualitative Research Method
In continuance to methods of research:
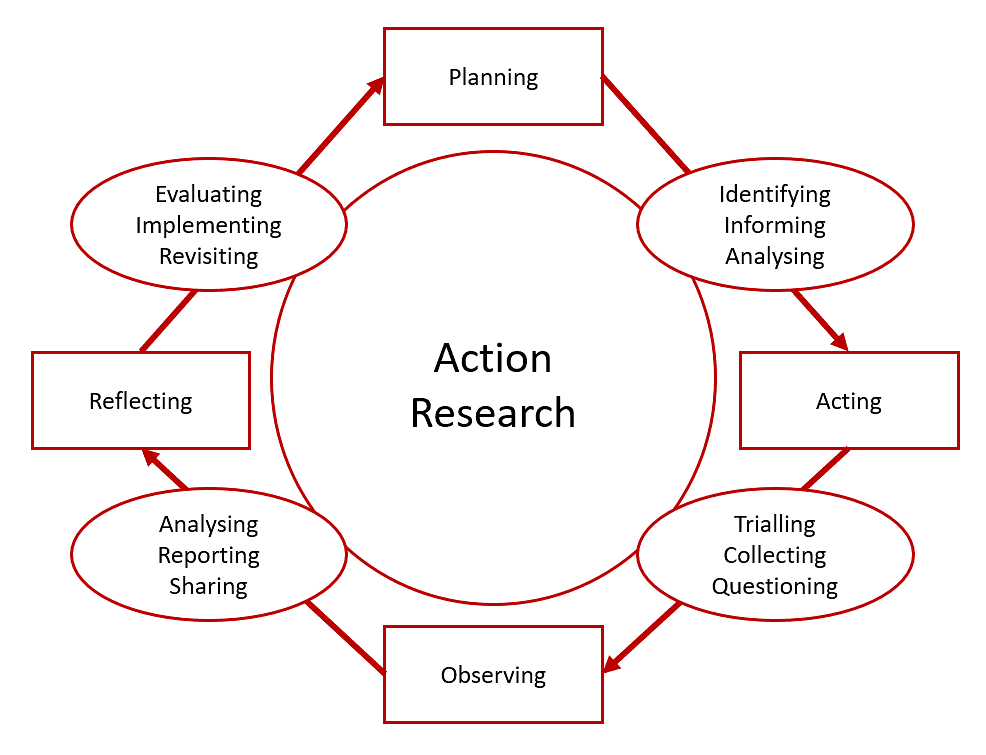
Action Research
Action research involves a systematic and thorough examination of one’s own educational practices using various research techniques. While Kurt Lewin popularized the term "action research" in 1940, the underlying principles had been explored in different educational contexts prior to this time.
- It encompasses various evaluative, investigative, and analytic research methods aimed at diagnosing problems or weaknesses and devising practical solutions promptly.
- This type of research is typically conducted to address immediate issues and is considered a form of applied research.
Objectives of Action Research:
- Identifying problematic areas and enhancing working conditions within educational institutions.
- Fostering a scientific attitude among teachers, students, principals, and administrators to study, understand, and resolve current academic issues.
- Unleashing the potential of school functionaries to improve overall school functioning.
Features of Action Research
- Typically arises from specific situational needs, with solutions tailored accordingly.
- Action is taken in response to real-world problems that occur in practical situations.
- Focuses on urgent problems that need immediate attention.
- Mainly concentrates on social contexts such as educational institutions.
- Involves small-scale interventions rather than large-scale studies.
- Employs both quantitative and qualitative research methods for investigation.
Steps followed in Action Research:
1. Identification of a Problem: The initial step involves recognizing and pinpointing a specific issue or challenge within a given context. This problem serves as the focal point for the research process.
2. Defining, Analyzing, and Explaining the Problem: Once identified, the problem must be clearly defined, thoroughly analyzed, and comprehensively explained. This stage involves delving into the nuances of the issue to gain a deeper understanding.
3. Listing and Stating the Probable Causes: After understanding the problem, it is crucial to list and articulate the potential factors or reasons contributing to its existence. This process helps in identifying the root causes.
4. Development of Propositions/Formulation of Hypotheses: Based on the analysis of causes, researchers develop propositions or hypotheses that serve as tentative explanations to be tested during the research.
5. Planning, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation of Action Research: This stage involves creating a detailed plan of action, executing the plan, and evaluating the outcomes. It is where the proposed solutions are put into practice.
6. Drawing Conclusions and Making Decisions: Following the implementation phase, researchers draw conclusions based on the findings. These conclusions inform decisions regarding the effectiveness of the interventions and potential next steps.
7. Sharing of Results: The final step involves sharing the results of the action research with relevant stakeholders. This sharing of insights and outcomes is crucial for promoting learning and driving further improvements.
Example: Imagine a school where the teachers notice a significant drop in student engagement during mathematics classes. Through action research, the teachers can systematically analyze their teaching methods, identify the issues, and implement new strategies to enhance student learning and participation.
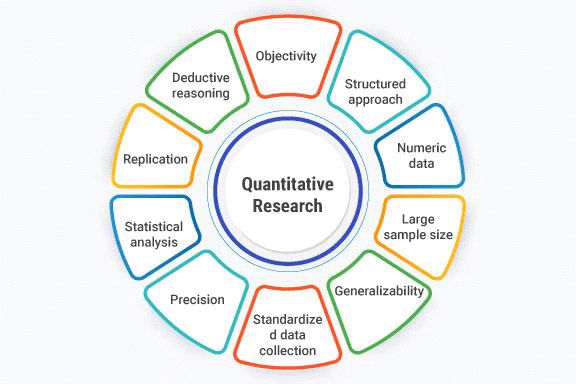
Quantitative Research Method
Quantitative research is a structured way of collecting and analyzing data obtained from different sources. This method involves the use of computational, statistical, and mathematical tools to derive results.
- Data Collection Tools: Surveys and Experiments.
- Experiments in Quantitative Research: Provide specific results regarding cause and effect relationships
- Reliability of Results: Results obtained from quantitative research are extremely reliable.
- Impartiality and Fairness: No scope for personal comments or biasing of results.
Characteristics of Quantitative Research
- Deductive Approach: Quantitative research follows a deductive or 'top-down' approach, where researchers formulate and test hypotheses.
- Logical-Positive Paradigm: It is based in the logical-positive paradigm, although different philosophical perspectives may influence various methods.
- Subject Independence: Researchers treat their subjects as independent entities without inherent meaning.
- Regularity and Predictability: The behaviour of subjects is considered regular and predictable.
- Research Objectives: Common objectives include describing, explaining, and predicting social phenomena.
- Controlled Settings: The research aims to study behaviour in controlled environments to ensure objective and consistent observations.
- Data Collection Methods: Data is collected using structured methods such as closed-ended questionnaires, tests, attitude scales, and rating scales for precise measurement.
- Probability Sampling: The main sampling method is probability sampling, which selects a representative sample from a larger population.
- Deductive Focus: Quantitative research is deductive in nature, concentrating on testing existing theories and analysing quantitative data using advanced statistical techniques.
Quantitative research is characterised by its emphasis on measuring and analysing data to draw conclusions. By employing a systematic and structured approach, researchers strive for objective insights into various phenomena. For instance, in a study examining the relationship between academic performance and socioeconomic status, quantitative researchers may utilise statistical methods to assess the strength and direction of this connection.
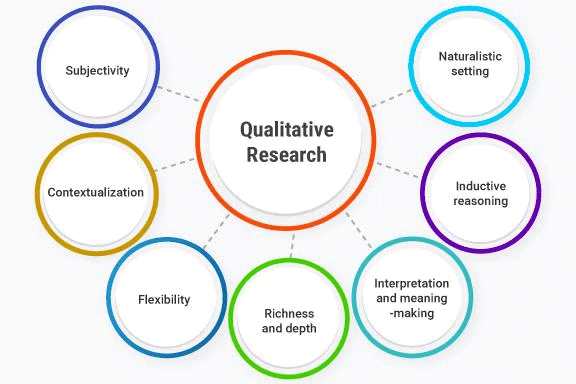
Qualitative Research Method
Qualitative research is a method of naturalistic inquiry that seeks in-depth understanding of social phenomena within their natural setting. It focuses on the 'why' rather than the 'what' of social phenomena and relies on the direct experiences of human beings as meaning-making agents in their everyday lives.
In the late 18th century, thinkers like Immanuel Kant, Wilhelm Dilthey, Edmund Husserl, and Maurice Merleau-Ponty proposed that life consists of experiences and that we are embedded in a web of intricate relationships. Their foundational ideas played a significant role in the development of naturalistic or qualitative research.
Importance of Qualitative Research
- Qualitative research is crucial for establishing causal relationships between independent and dependent variables.
- It aims to reveal general patterns of phenomena, providing insights into how different factors interact and influence each other.
- Replicability is another important aspect of qualitative research. Ensuring that research can be replicated adds to its credibility and validity.
- Qualitative research emphasizes objectivity in the collection, analysis, interpretation of data, and reporting of results. This objectivity is essential for producing reliable and unbiased findings.
- Furthermore, qualitative research often employs various methods that differ from the typical hypothetico-deductive approach used in natural sciences. While quantitative research focuses on numerical analysis, qualitative research covers a broader range of areas, delving into the nuances and complexities of human behaviour, social phenomena, and other intricate subjects.
Key Points:
- Qualitative research emphasizes understanding over numerical measurement.
- It investigates the 'why' of social phenomena.
- Researchers collect data through methods like interviews, observations, and open-ended surveys.
- Findings are often descriptive and context-specific.
- Qualitative research is crucial for exploring complex human behaviors and social interactions.
Methods of Qualitative Research
- In-depth Interview: This method involves personal interviews with one respondent at a time. Researchers can ask questions and follow-up questions to gather precise data on beliefs and motivations.
- Focus Group: A research method involving a limited number of respondents (6-12) focusing on specific research topics. It aims to uncover answers to questions of 'why,' 'what,' and 'how.'
- Ethnographic Research: This method studies sociocultural phenomena through close field observations, aiming to understand cultures, challenges, motivations, and settings as they naturally occur.
- Text or Content Analysis: Researchers analyze social life by decoding words and images from various forms of media. The goal is to identify and present important content characteristics in a simplified manner for better understanding.
- Phenomenology: A method that describes the structures of experiences as they appear to consciousness without relying on theories or assumptions from other disciplines. It focuses on individual experiences and perceptions.
Qualitative research methods offer various approaches to understanding human behaviour and societal phenomena. Each method has its unique advantages and applications, providing valuable insights into different aspects of research.
|
12 videos|40 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on Methods of Research (Detailed) - Research Aptitude Notes
| 1. What is the difference between action research and quantitative research methods? |  |
| 2. How do qualitative research methods differ from quantitative research methods? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of using different research methods in academic studies? |  |
| 4. How can researchers determine which research method is most appropriate for their study? |  |
| 5. Can a research study involve a combination of different research methods? |  |















