Notes: Methods of Teaching | Teaching Aptitude for Teaching Exam - B.Ed Entrance PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Methods of Teaching |

|
| Teacher-Centred Teaching Methods |

|
| Mixed Group Teaching Methods |

|
| Gagne’s Teaching – Learning Process |

|
| Offline vs Online Methods |

|
Methods of Teaching
After specifying the instructional objectives, the next step is to choose an appropriate instructional method to achieve them. Teachers have various methods at their disposal, which can be categorized into three approaches:
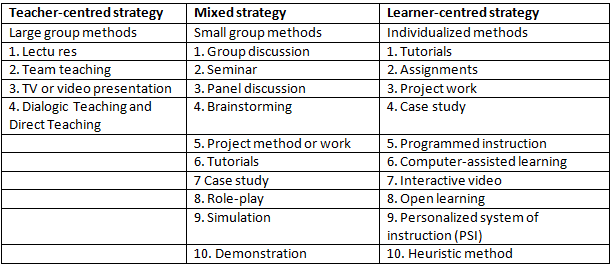
Teacher-Centred Methods: These methods focus on the teacher as the primary source of knowledge and authority in the learning process. The teacher directs the learning activities, and students are expected to follow instructions and absorb information.
Learner-Centred Methods: In contrast, learner-centred methods prioritize the needs, interests, and active participation of students in the learning process. Students take a more active role in shaping their learning experiences, and the teacher acts as a facilitator or guide.
Mixed Approach: This approach combines elements of both teacher-centred and learner-centred methods. It recognizes the importance of teacher guidance while also allowing for student input and active participation.
Teacher-Centred Teaching Methods
Lecture Method
- The lecture method is a traditional and widely used teaching approach where the teacher explains facts, principles, or relationships to help students understand.
- In this method, the teacher is active, and students are passive listeners, making it a one-way communication process.
- While it can be made interactive by allowing questions, discussions are not typically part of this method.
- Lectures are continuous in nature, with students listening, writing, and noting down information for later reflection.
Basic Features.
(i) Formal and narrative in nature.
(ii) Presents a series of events or facts.
(iii) Explores a problem.
Advantages.
(i) Economical as one teacher can reach a large number of students.
(ii) Saves time and easily covers the syllabus.
(iii) Simplifies the teacher's task.
(iv) Useful for imparting factual information and highlighting important points.
(v) Reduces interruptions and distractions.
Limitations.
(i) Provides limited opportunities for student activity.
(ii) Does not encourage problem-solving by learners.
(iii) Offers minimal chances to check learning progress.
(iv) Ignores individual student interests, abilities, and intelligence.
(v) Does not accommodate different learning paces.
Suggestions for Improvement.
(i) Avoid reading lecture notes verbatim.
(ii) Maintain eye contact with students to keep their attention.
(iii) Plan lessons well with clear structure and important data.
(iv) Use simple language and repeat main points in different ways.
(v) Incorporate audio-visual aids for better communication.
(vi) Use illustrations and examples effectively.
(vii) Allow short breaks for thought-provoking questions.
(viii) Reserve time at the end for clarifications and questions.
Important Methods of Instruction
Team Teaching Method
Team teaching is an innovative approach where two or more teachers collaborate in planning, executing, and evaluating learning experiences for a group of students.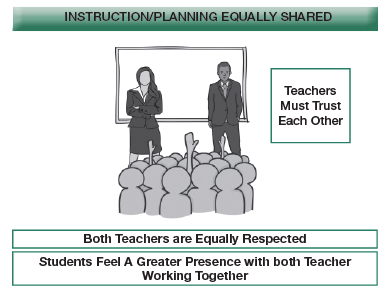
Advantages.
(i) Sharing the expertise of the best faculty among more students.
(ii) Optimal use of various teaching techniques and devices.
(iii) Enhancement of overall teaching quality.
Limitations.
(i) Difficulty in finding teachers with specialized competencies.
(ii) Requirement of more teachers for this method.
(iii) Not suitable for teaching all subjects.
(iv) Need for significant time in planning and scheduling.
TV or Video Presentation
- Television or video presentation enhances the traditional radio or audio presentation by visually bringing expert personalities and demonstrations into the classroom.
- It is particularly beneficial for subjects like geography and astronomy.
Advantages.
(i) Brings important personalities and experts into the classroom.
(ii) Particularly useful for adult learners.
(iii) Illustrated lectures can be supplemented with slides, models, and specimens.
(iv) Accessible for learners in remote areas.
(v) Useful for subjects requiring visual demonstrations.
Limitations.
(i) Limited potential for two-way communication.
(ii) Challenges in adjusting complicated schedules for telecasts.
Dialogic Teaching and Direct Teaching
- Dialogic teaching, developed by Robin Alexander in the early 2000s, leverages the power of conversation to stimulate and extend students' thinking, thereby advancing their learning and understanding.
- Direct teaching involves straightforward and explicit methods to teach specific skills, often used in language instruction where native language use is unnecessary.
Mixed Group Teaching Methods
Most of the methods of instructional delivery for the learning of smaller groups numbering between 3 and 12 trainees lean towards trainee-centred approach. Some of these methods are group discussion, seminar, project work, tutorials, role playing, etc.
Group Discussion (GD)
- Group Discussion (GD) is a method of teaching that involves discussing a topic in a group setting, encouraging participation and interaction among students. It is considered a democratic approach to learning and has been used since ancient times by scholars.
- GD aims to develop a better understanding of a topic by analyzing facts, their relationships, and drawing conclusions. It stimulates critical thinking, presentation skills, and the ability to express ideas clearly.
- There are various forms of discussion, including classroom discussion, formal group discussion, symposium, panel, seminar, and conference.
Types of Discussion
- Classroom Discussion: An informal method where the teacher or a student leader guides the discussion on a selected topic within the class. The leader helps summarize and note down key points.
- Formal Group Discussion: Involves small group discussions followed by a larger group discussion. The teacher acts as a chairman, introduces the topic, and facilitates small group discussions. Afterward, groups present their findings to the larger group for discussion.
- Planned Group Discussion: The discussion has clear objectives and is guided by the trainer in a specific sequence.
- Partly Planned Group Discussion: The opening and concluding statements are known, but the discussion in between is loosely guided.
- Unplanned Group Discussion: The topic is presented without an opening statement, and the discussion is spontaneous.
Role of Teacher in Group Discussion
- The teacher plays a crucial role in guiding and facilitating group discussions.
- They act as a facilitator, helping students organize into groups, and providing support as needed.
- The teacher also acts as a resource person, offering assistance and guidance to groups during the discussion.
Advantages of Group Discussion
- Stimulates critical thinking and helps in the development of analytical skills.
- Pooling of knowledge and ideas from multiple participants promotes intelligent learning.
- Rationalization of facts leads to better understanding and learning.
- Encourages teamwork and collaboration among students.
- Helps in discovering and nurturing students' talents.
- Develops oral and non-verbal communication skills.
Limitations of Group Discussion
- Requires significant time, effort, and resources from both teachers and students.
- Risk of unnecessary arguments and discussions going off-track.
- Potential for emotional stress and unpleasant feelings among participants.
- Possibility of a few students dominating the discussion.
- Not suitable for all topics or subjects.
General Principles for Organizing Discussion
- Clearly define and communicate the objectives of the discussion to all participants.
- Participants should come prepared with a basic understanding of the topic.
- The leader should guide the discussion to keep it focused and on track.
- A recorder may be appointed to note down key points, which can be displayed on the blackboard.
- Encourage participation from all members, especially those who are shy.
- Consider all points of view fairly during the discussion.
- Conclude discussions with a summary, decision, or recommendation based on the points discussed.
Seminar
- Definition:. seminar is a form of group discussion where one or more trainees prepare a paper on a specific topic, issue, or problem. This paper is then presented to the entire group for discussion and analysis.
- Objective: The main goal of a seminar is to encourage in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular subject through collective discussion and input from all participants.
- Stages of a Seminar:
- Preparation: The trainee(s) prepare a paper on the assigned topic, conducting thorough research and analysis.
- Presentation: The prepared paper is presented to the group, outlining the key points and findings.
- Discussion: After the presentation, the group engages in a discussion, providing feedback, additional insights, and raising questions related to the topic.
- Series of Seminars: Trainees can organize a series of seminars around a major topic, where each seminar builds on the previous one, creating a linked discussion thread. This approach allows for a comprehensive exploration of complex subjects.
- Variations: Seminars can vary in size and scope, from small group discussions to larger, more formal settings. The key is to maintain a focus on collaborative learning and discussion.
Types of Seminars
- Mini Seminar: These are conducted at the classroom level, usually involving a small group of students or participants.
- Main Seminar: These seminars take place at the departmental or institutional level, involving a larger audience within the organization.
- National Seminar: This type of seminar is conducted at the national level, attracting participants from across the country.
- International Seminar: These seminars are held at the international level, involving participants and speakers from around the world.
Advantages of Group Discussion Method
- Development of Presentation Skills: Participants gain independence, leading to improved presentation skills.
- In-Depth Research: Trainees have the opportunity to prepare and contribute thoroughly to a specific topic.
- Practical Leadership Experience: Provides trainees with practical group leadership experience and the chance to use analytical skills, conduct research, and solve problems.
Limitations of Group Discussion Method
- Time-Consuming and Stressful: The method can be time-consuming and may cause stress to participants.
- Requires High Attainment Level: Needs a group of trainees with a fairly high level of attainment.
Advantages of Panel Discussion
- Engaging Format: When conducted well, panel discussions are often more interesting to the audience than single-speaker forums.
- Social Relevance: Typically held on socially relevant issues, making them pertinent to the audience.
Limitations of Panel Discussion
- Expert Coordination: Bringing experts together for a panel can be challenging.
- Audience Engagement: The audience is not actively involved in the discussion.
Advantages of Brainstorming
- Fostering Creativity: Encourages creativity and helps participants think and explore ideas.
- Broad Participation: Allows for larger participation from group members.
- Cost-Effective: Requires minimal preparation, making it economical.
Limitations of Brainstorming
- Lack of Systematic Approach: Not a very systematic way of studying a subject.
- Participant Reluctance: Some participants may be reluctant to engage.
Advantages of Project Method
- Development of Critical Thinking: Students are likely to develop critical thinking skills.
- Teamwork Skills: Encourages the habit of working in teams.
Limitations of Project Method
- Need for Continuous Monitoring: May require continuous monitoring of students.
- Resource Intensive: Additional resources may be necessary.
Advantages of Role Playing
- Real-Life Simulations: Mimics real-life situations, making it relatable.
- Interactive Engagement: Involves participation from every group member, making it interesting.
- Immediate Feedback: Provides instant feedback to participants.
- Skill Development: Helps develop social, decision-making, problem-solving, negotiating, and manipulating skills.
- Attitude Change: Effective in changing participants' attitudes.
Limitations of Role Playing
- Unpredictable Outcomes: The results of role playing can be unpredictable.
- Complexity of Real Situations: Real-life situations are often more complex than the scenarios presented.
- Resource Requirements: Requires a significant amount of resources to implement.
Advantages of Simulation
- Long-Term Cost Efficiency: Economical in the long run.
- Safety Considerations: Safety aspects are prioritized and ensured.
Limitation of Simulation
- High Initial Investment: Requires substantial initial investment in machinery, equipment, etc.
Advantages of Tutorial Method
- Focused Attention: Allows for focused attention on individual students.
- Idea Generation: Generates more ideas and insights.
- Pace Control: Provides better control over the pace of teaching and learning.
Limitations of Tutorial Method
- Varying Ability Paces: Difficult to find a suitable pace if trainees vary greatly in ability.
- Time-Consuming: Can be time-consuming to implement.
Advantages of Demonstration Method
- Effective Explanation: Useful for explaining materials, objects, and ideas effectively.
- Abstract Concept Clarification: Helps in explaining abstract concepts.
- Diverse Objective Achievement: Useful for achieving cognitive, psychomotor, and affective objectives due to mental and physical participation.
Limitation of Demonstration Method
- Limited Participation: Only a few participants get opportunities to participate in the experimental process.
Learner Centred Teaching Methods
The learner-centred teaching methods aim to accommodate the differences displayed between the learners. The main teaching methods include assignments, case study approach, computer-based learning, open learning, personalized system of instruction and programmed instructions.
Assignments
- Assignments are given to students for a number of purposes, such as for acquiring additional information, surveying, application of knowledge and solving numerical problems.
- The teacher has to plan the assignments and guide the student regarding references for collecting relevant information.
- The assignments should be open-ended and should promote creativity among the students.
Advantages of Assignments:
- Helps students work independently.
- Sharpens the student’s comprehension, analytical, and problem-solving abilities.
- Inculcates creativity among students.
Limitations of Assignments:
- Students may copy each other’s material unless the assignments are carefully planned.
Case Study
- A case is usually a ‘description of an actual situation, commonly involving a decision, a challenge, an opportunity, a problem, or an issue faced by a person or persons in a social set up such as an organization’.
- By allowing students to gain hands-on experience of the real world and shifting the work focus from professor to the student, the case-study method becomes an efficient tool for the creation of a learner-centred education rather than teacher-centred education.
- The cases can be short, from brief classroom discussions, to long and elaborate semester-long projects.
Advantages of Case Study:
- Provides opportunity to the participants to analyse, critically examine, evaluate and express reasoned opinions.
- Enhances decision-making and problem-solving skills.
- Ensures active participation, which may lead to innovative solutions.
Limitations of Case Study:
- Requires training for the teachers to use this method.
- Is not useful for all subjects and situations.
Programmed Instruction
- Programmed Instruction (PI) is a general term for a highly structured system of learning, which is based on logical sequence of self-paced, learning steps with feedback between each step.
- The learner gets immediate feedback after each step.
Advantages of Programmed Instruction:
- Regular feedback.
- Active participation of the learner.
- Can be used for any subject.
Limitations of Programmed Instruction:
- Learner motivation may get diminished after some time.
Personalized System of Instruction
- Personalized System of Instruction (PSI) can be used for all subject matters except where the students are to select the content.
- Learners must achieve mastery of a series of written mastery units, assisted by teachers, proctors and enriching lectures before proceeding to the final test.
- PSI consists of five basic elements: mastery learning, self-pacing, stress on written material, proctors, and lectures.
Advantages of Personalized System of Instruction:
- Based on mastery learning.
- Facilitates self-paced learning.
Limitations of Personalized System of Instruction:
- Not suitable for rapidly changing course contents.
- Not suitable for psychomotor and affective domains.
Computer-assisted Learning
- Computer-assisted Learning (CAL) is concerned with the use of a computer to mediate the flow of information in a learning process.
- A computer has the ability to process information very quickly, accurately and to adapt and respond to the learner’s needs, difficulties, and progress, which is much greater than that of a book or video tape.
Advantages of Computer-assisted Learning:
- More flexibility and better control in comparison to other methods.
- Can be effectively used for drilling and practising, simulation and modelling.
Limitations of Computer-assisted Learning:
- Impersonal and costly.
Open Learning
- Open Learning is a flexible method of delivering the instruction, where the learner has open access to learning resources of people, material, equipment and accommodation, although regular class attendances are not necessary.
- There are no or minimal restrictions on admissions.
Advantages of Open Learning:
- Offers flexibility to the learner.
Limitations of Open Learning:
- Not suitable for achieving psychomotor and affective learning objectives.
- Requires time, expertise, resources and is hence not suitable for subjects of rapidly changing nature.
Interactive Video
- The interactive video approach to teaching can be employed to achieve cognitive, psychomotor and affective objectives.
- It allows the learner to randomly access any piece of information and provide immediate feedback regarding the consequences of their action.
Advantage of Interactive Video:
- Enhances the decision-making power of an individual.
Limitation of Interactive Video:
- This method is time-consuming and requires resources and expertise.
Heuristic Method
- In this method, the student has to find out the answer to his/her own problem by unaided efforts.
- The child becomes a discoverer of knowledge by developing a spirit of inquiry.
- The main aim of teaching by this method is not to provide much facts about science, mathematics, grammar, etc., but to teach how knowledge of these can be obtained.
Advantage of Heuristic Method:
- Self-learning approach.
Limitation of Heuristic Method:
- Not much focus on factual knowledge.
Reflective Teaching and Blended Learning
Reflective Teaching
- Classroom teaching relies on various factors like individual differences, class environment, teacher and learner abilities, and subject matter.
- There is no one-size-fits-all teaching method; teachers need to find a suitable approach for their lessons.
- Reflective teachers are knowledgeable about pedagogy but always have room for improvement.
- Reflective teaching involves self-observation and self-evaluation to enhance teaching quality by examining classroom actions, their reasons, and effectiveness.
- It is about gaining a better understanding of problems and finding solutions through suggestions, problems, hypotheses, reasoning, and testing.
- Reflective teaching questions the practices of the teaching profession.
- Examples include peer observation, self-reports, journal writing, and student feedback.
- Reflective teaching is beneficial for pre-service teachers' professional development, involving training, practice, and feedback.
Blended Learning
- Blended learning, originating in the USA, combines online and face-to-face learning.
- It involves multiple pedagogical approaches like self-paced, collaborative, and inquiry-based study to create an effective learning experience.
- The aim is to provide efficient and effective instruction by integrating different delivery modalities.
Differentiated Instruction
- Differentiated instruction is a proactive and flexible teaching approach that involves planning and using various methods to meet diverse learning needs.
- It includes a mix of whole group, small group, and individual instruction, focusing more on qualitative aspects than quantitative ones.
- This method accommodates multiple intelligences and is student-centered, ensuring lessons are engaging, relevant, and active.
- Differentiated instruction is organized and planned, aiming to create a dynamic learning environment for all students.
Gagne’s Teaching – Learning Process
Robert Gagne's Contribution to Learning
- Robert Gagne was an educational psychologist who, in the 1940s, laid the groundwork for the science of instruction.
- In his book "The Conditions of Learning," published in 1965, Gagne identified the mental conditions necessary for effective learning.
- He developed a nine-step process outlining the essential elements for successful learning.
Nine Steps for Effective Learning
- Gain Attention: Capture the learner's interest.
- Orient the Learner: Prepare the learner with objectives.
- Stimulate Recall: Help learners remember prior knowledge.
- Present Content: Deliver the learning material.
- Provide Guidance: Offer support to learners.
- Elicit Performance: Encourage practice.
- Provide Feedback: Give informative feedback.
- Assess Learning: Evaluate if objectives have been met.
- Enhance Retention: Foster long-term retention and transfer of knowledge.
Lifelong Learning Principles by Jacques Delors
- Jacques Delors from France emphasizes the importance of lifelong learning for building self-esteem and personal empowerment.
- He advocates for four pillars of learning: learning to know, learning to do, learning to live together, and learning to be.
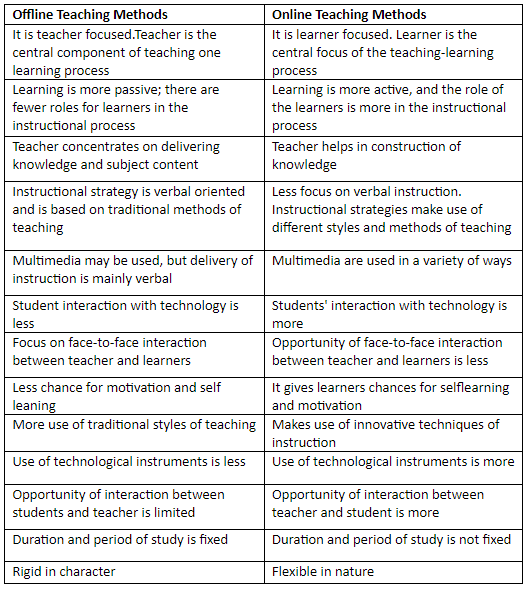
Offline vs Online Methods
|
29 videos|48 docs|11 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Methods of Teaching - Teaching Aptitude for Teaching Exam - B.Ed Entrance
| 1. What are the main advantages of using mixed group teaching methods? |  |
| 2. How does Gagne’s Teaching-Learning Process enhance student learning? |  |
| 3. What are the key differences between offline and online teaching methods? |  |
| 4. What are some effective strategies for implementing mixed group teaching in the classroom? |  |
| 5. How can teachers assess the effectiveness of their teaching methods? |  |















