Notes: Individual Differences | Teaching Aptitude for Teaching Exam - B.Ed Entrance PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Types of Individual Differences |

|
| Reasons for Individual Differences |

|
| Educational Implications of Individual Differences |

|
| Syllabus and Curriculum |

|
Introduction
Individual difference is a universal phenomenon. It is said that no two individuals are exactly alike. They differ from each other in some way or the other. Such a similarity or difference between persons reveals individual differences.
- According to Drever James: Individual Differences are variations or deviations from the average of the group, with respect to the mental or physical characters, occurring in the individual member of the group.
- According to Carter B. Good: Individual Difference is the the variation or deviations among individual in regard to a single characteristics or a number of characteristics, those differences which in their totality distinguish one individual from another.
- According to Skinner, C.E.: Today we think of individual differences as including any measurable aspect of the total personality.
- According to R.S. and Marquis , D.G.: Individual differences are found in all psychological characteristics physical mental abilities, knowledge, habit, personality and character traits.
Types of Individual Differences
1. Physical Differences:
- Stature: This refers to whether a person is short or tall.
- Complexion: This involves the color of a person's skin, such as being dark or fair.
- Body Type: This includes variations like obesity (being overweight), thinness (being underweight), or general weakness.
2. Differences in Intelligence:
- Individuals vary in their levels of intelligence, with some being highly intelligent and others having lower intellectual capacities.
3. Differences in Attitudes:
- People possess different attitudes towards other individuals, as well as varying opinions on objects, institutions, and authority figures.
4. Variations in Motor Ability:
- Individuals exhibit differences in their motor abilities.
- Some individuals find mechanical tasks easy to perform, while others may struggle with the same tasks, even if their skill levels are similar.
5. Variations in Skills and Abilities:
- Women tend to excel in memory tasks, whereas men often demonstrate greater proficiency in motor abilities.
- Women typically have better handwriting skills, while men are more skilled in mathematics and logic.
- Some research suggests that women may possess greater sensitivity in certain sensory distinctions, whereas men are more attuned to size-weight illusions.
- Women may perform better in language tasks, while men might excel in subjects like physics and chemistry.
6. Racial Differences
- Racial differences are evident, with environmental factors playing a crucial role.
- Research by Karl Brigham indicated variations in intelligence among individuals who migrated to the United States.
- He emphasized that assessing mental age based on race is impractical due to the impact of environmental influences.
7. Differences due to Economic Status:
Economic disparities contribute to differences in children's interests, tendencies, and character.
8. Differences in Interests:
Various factors such as sex, family background, developmental level, race, and nationality influence individuals' interests.
9. Personality Differences:
Individuals exhibit diverse personalities, leading to various personality classifications.
Reasons for Individual Differences
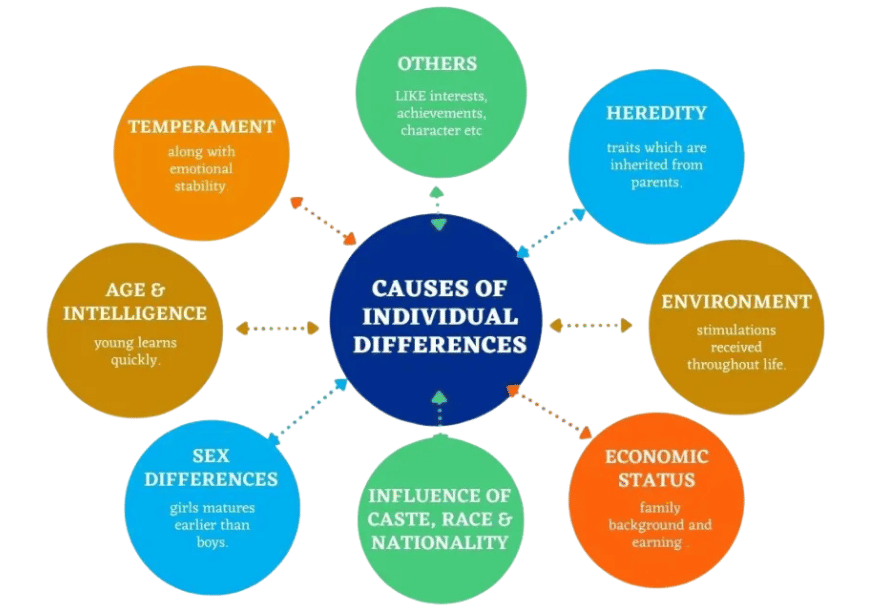 Individual Differences
Individual Differences
- Heredity: Individual differences stem significantly from heredity. Genetic traits result in variations among individuals. Hereditary characteristics such as height, size, shape, hair color, facial features, and overall body structure play a crucial role in distinguishing people.
- Age: With age, individuals typically enhance their learning and adaptability. Older adults often exhibit improved emotional regulation and social skills, contributing to their individuality.
- Sex: Inherent differences between sexes contribute to individual variations. Physical development can vary, with some girls maturing more quickly than boys and vice versa. Additionally, there are fundamental behavioral differences between the sexes that influence individual traits.
- Environment: The environment significantly shapes individual differences. Changes in a person’s surroundings can directly impact their personality. Various factors such as physical, intellectual, social, moral, political, economic, and cultural aspects of the environment play crucial roles in this regard.
- Education: Education is a vital factor in individual differences. The behavior of educated individuals often contrasts sharply with that of uneducated individuals, highlighting education’s influence in shaping personalities and skills.
Educational Implications of Individual Differences
- Tailoring Educational Goals and Methods: The objectives of education, the curriculum, and teaching methods should be customized to accommodate the unique individual differences of students, taking into account their varying abilities and characteristics.
- Diverse Teaching Approaches: Teachers should use a range of teaching methods that cater to the different interests and needs of students. For example, methods such as play-based learning, project-based learning, and storytelling can be employed to observe how students respond to various tasks and challenges.
- Co-curricular Activities: Co-curricular activities like drama, music, and literary pursuits should be offered to students based on their individual interests.
- Curriculum Modification: The curriculum should be adjusted to meet the diverse needs of all students.
- Educational Guidance: Teachers should provide educational guidance that reflects the individual differences among students, ensuring that each student receives support tailored to their unique needs.
- Home Assignments: Home assignments should be assigned with consideration of individual differences, ensuring that they are appropriate for each student's capabilities and interests.
- Flexible Learning Pace: Students should have the flexibility to learn at their own pace in each subject, allowing for personalized learning experiences.
Syllabus and Curriculum
Syllabus: The syllabus comprises topics or content covered in a specific subject. It is created by professors and provided to students, guiding them on the subject matter, expectations, rules, assignments, projects, and more.
Curriculum: The curriculum outlines the academic content and chapters included in a program. It not only covers knowledge but also focuses on students' attitudes, behaviors, skills, and overall development. Curricula are meticulously planned by educational institutions or governments to enhance students' learning experiences.
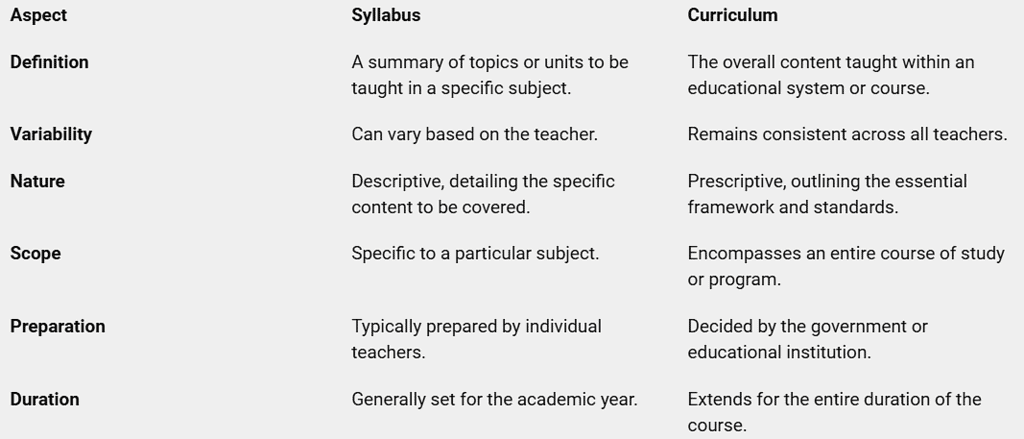 Differences between Syllabus & Curriculum
Differences between Syllabus & Curriculum|
29 videos|48 docs|11 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Individual Differences - Teaching Aptitude for Teaching Exam - B.Ed Entrance
| 1. What are some common types of individual differences in educational settings? |  |
| 2. How do individual differences impact student performance in the classroom? |  |
| 3. Can individual differences be changed or modified through education? |  |
| 4. How can teachers accommodate individual differences in a diverse classroom? |  |
| 5. What are some strategies that educators can use to address individual differences in the classroom? |  |















