Research - Meaning & Characteristics - Research Aptitude Notes
Meaning and Concept
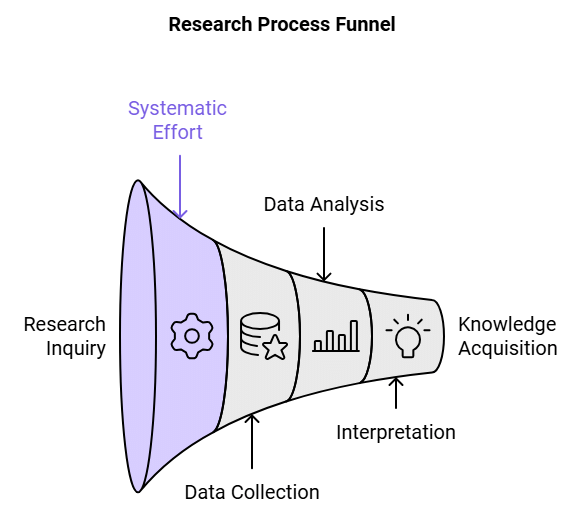
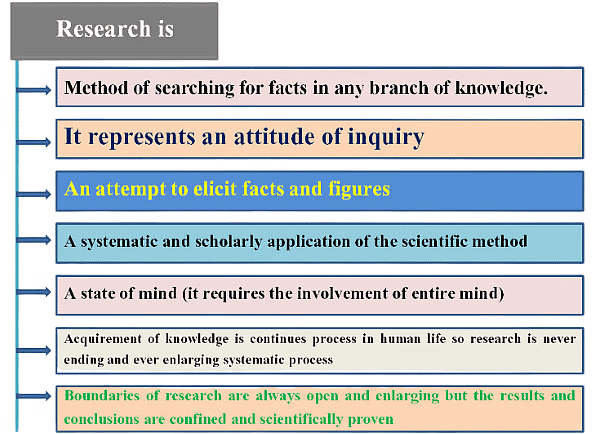
Research basically means an art of scientific investigation. The definition of research varies according to different researchers. One such definition of research, according to Redman and Mory is “research is a systematized effort to gain new knowledge” This basically means Research is a walking from known thing towards unknown thing. It is basically a systematized process of discovery.
According to John W. Best “research is considered to be the more formal, systematic intensive process of carrying on the scientific method of analyses. It involves a more systematic structure of investigation, usually resulting in some sort of formal record of procedure and a report of results or conclusions”. The meaning of research is totally confined inside the word RESEARCH. If we analyze letter by letter, we will get
R : Rational way of thinking
E : Expert and exhaustive
S : Search for solution
E : Exactness
A : Analytical analyses of adequate data
R : Relationships of facts
C : Careful recording, critical observation and constructive attitude
H : Honesty
Definition of Research
- Redman and Mory define research as a "Systematic effort to gain new knowledge.
- According to Webster, "Research is a studious inquiry or examination, critical and exhaustive investigation or experimentation, having its aim for discovery of new facts and their correct interpretation
- .According to J W Best, "Research is considered to be the more formal, systematic, intensive process of carrying on the scientific methods of analysis. It involves a more systematic structure of investigation, usually resulting in some sort of formal record of procedures and report of results or conclusions."
- According to John Creswell, "Research is a process of steps used to collect and analyse information to increase our understanding of a topic or an issue."
- According to Morley, "Research is a process of arriving at dependable solutions to problems through the planned and systematic collection, analysis and interpretation of data."
Objectives of Research
Objectives are the goals that researchers aim to achieve in their studies. They communicate what the researcher intends to accomplish through their research work.
Categories of Research Objectives
- Theoretical Objectives: These objectives lead to the development of new theories and fundamental knowledge by investigating the relationship between different variables.
- Factual Objectives: These objectives involve studies focused on discovering new facts.
- Application Objectives: These objectives propose applying existing theories to new situations.
- Variable Objectives: These objectives are philosophical in nature, where the end result is based on philosophy.
- Practical Objectives: These objectives are classified as developmental research, and functional research is conducted to achieve them.
Research objectives represent the outcomes that researchers seek to attain by the end of their research study. While each research study has its unique purpose, research objectives vary based on the desired achievements.
Characteristics of Research
1. Objectivity: It means the research is being free from all bases. In other words it means, observation is unaffected by the observer’s values, beliefs and preferences to the possible extent.
2. Reliability: If the similar research is carried by time and again in a similar setting it must give similar result. So, the researcher must frame the research questions to make it reliable and provide similar outcomes. For example, if a respondent gives out a response to a particular item, he/she is expected to give the same response to that item even if he/she is asked repeatedly. If he/she is changing his/her response to the same item, the consistency will be lost.
3. Validity: The meaning of validity in research is accuracy in research procedure and research instruments. There are multiple measuring tools available for research design but valid measuring tools are those which help a researcher in determining results according to the objective of research. Any measuring device can said to be valid if it measures what it is expected to measure and nothing else.
- Internal Validity: It is the most basic type of validity because it concerns the logic of the relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable. This type of validity is an estimate of the degree to which inferences about causal relationship can be drawn based on the measure employed and research design.
- External Validity: It means the external factors that can affect study must be controlled. It concerns whether results of the research can be generalised to another situation, different subjects settings and so on.
4. Accuracy: It means truth or correctness of a statement or describing things exactly as they are and avoiding jumping to unwarranted conclusions either by exaggeration or fantasising.
5. Credibility: It refers to the extent to which a research account is believable and appropriate, with particular reference to the level of agreement between participants and the researchers.
6. Systematisation: It means attempting to find all the relevant data or collecting data in a systematic and organised way so that the conclusions drawn are reliable.
7. Empirical research is based on direct experience or observation by the researcher.
8. Logical research is based on valid procedures and principles.
9. Cyclical research starts with a specific problem, finds a solution for that problem and paves the way to arise new problems.
10. Generalisation: It is closely related to validity. It refers to the degree to which research findings can be applied to a larger population. Here, the sample considered is the representative of the whole population, so the findings should be applicable to the whole population.
- Analytical research utilises proven analytical procedures in gathering data; whether historical, descriptive, experimental and case study.
- Critical research exhibits careful and precise judgements.
- Methodological research is conducted in a methodological manner without biasness, using systematic method and procedures.
- Replicability research design and procedures are repeated to enable the researcher to arrive at valid and conclusive results.
11. Importance of cause and effect: Establishing cause and effect is a central goal of most researches. It demonstrates that a particular independent variable (the cause) has no effect on the dependent variable of interest (effect).
|
12 videos|40 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on Research - Meaning & Characteristics - Research Aptitude Notes
| 1. What is the meaning of research in the context of academia? |  |
| 2. What are the main objectives of conducting research? |  |
| 3. What are the key characteristics of effective research? |  |
| 4. How does research contribute to knowledge advancement? |  |
| 5. Why is it important for researchers to adhere to ethical standards? |  |






















