NCERT Summary: Why do we need a Constitution- 1 | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
The first function of a constitution is to provide a set of basic rules allow for minimal coordination amongst members of society.
Specification of Decision-Making Powers
Well, the first question you will have to decide is:
- You may want to rule X, but others may want to rule Y.
- You may think the rules you want everyone to live by are the best but others think that their rules are the best.
In principle, this question, who gets to decide, can be answered in many ways:
- In a monarchical constitution, a monarch decides, in some constitutions like the old Soviet Union, one single party was given the power to decide.

- But in democratic constitutions, broadly speaking, the people get to decide.
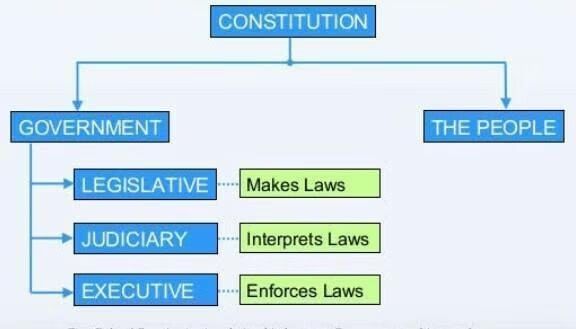
But this matter is not so simple, Because even if you answer that the people should decide, it will not answer the question: how should the people decide? For something to be law, should everyone agree to it? Should the people directly vote on each matter as the ancient Greeks did? Or should the people express their preferences by electing representatives? But if the people act through their representatives be elected? How many should there be? - This is the function of the constitution. It is an authority that constitutes government in the first place.
- In the Indian Constitution, for example, it is specified that in most instances, Parliament gets to decide laws and policies and that Parliament itself be organised in a particular manner before identifying what the law in any given society is, you have to identify who has the authority to enact it. If Parliament has the authority to enact laws, there must be a law that bestows this authority on Parliament in the first place.
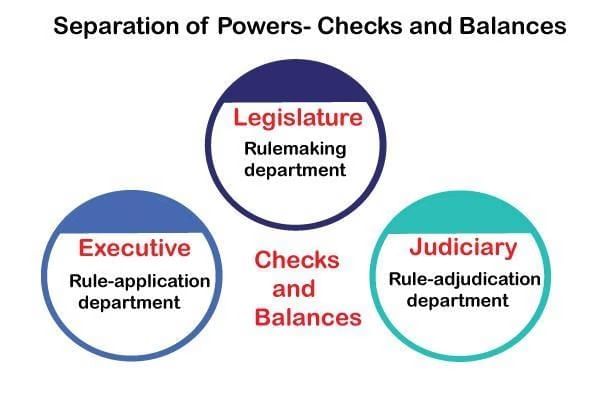
Limitations on the Powers of Government
Imagine you have assigned authority to a group to make decisions, but this authority enacts laws that you find obviously unjust. For example, they might ban your religious practices, outlaw certain colors of clothing, restrict singing specific songs, or impose rules that require individuals from certain castes or religions to serve others without the right to own property. Additionally, they could enable arbitrary arrests or restrict access to basic resources, like wells, based on skin color.
- You might think these laws are unfair and unjust. And even though they were passed by a government that followed certain rules to come into power, there is something wrong about that government enforcing these laws.
- The Constitution places limits on how much power the government can have in various ways.
- The most common way of limiting the power of government is to specify certain fundamental rights that all of us possess as citizens and which no government can ever be allowed to violate.
- The exact content and interpretation of these rights vary from the constitution to constitution.
- But most Constitutions will protect a basic cluster of rights. Citizens will be protected from being arrested arbitrarily and for no reason.
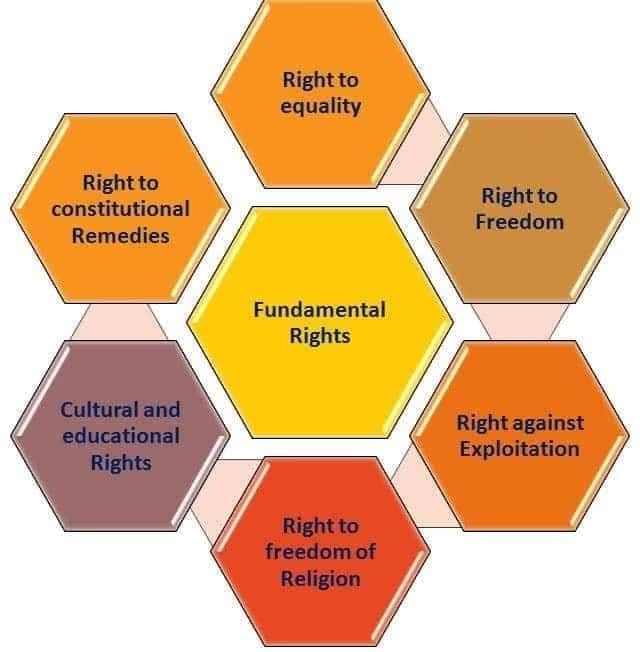
This is one basic limitation upon the power of government. Citizens will normally have the right to some basic liberties: to freedom of speech, freedom of conscience, freedom of association, freedom to conduct a trade or business etc. and practice, these rights can be limited during times of national emergency and the constitution specifies the circumstances under which these rights may be withdrawn.
So, the third function of a constitution is to set some limits on what a government can impose on its citizens. These limits are fundamental in the sense that government may never trespass them.
Aspirations and Goals of Society
- Most of the older constitutions limited themselves largely to allocating decision making power and setting some limits to government power. But many twentieth-century constitutions, of which the Indian Constitution is the finest example, also provide an enabling framework for the government to do certain positive things, to express the aspirations and goals of society. The Indian Constitution was particularly innovative in this respect.
- Societies with deeply entrenched inequalities of various kinds, will not only have to set limits on the power of government, but they will also have to enable and empower the government to take positive measures to overcome forms of inequality or deprivation.
Example: India aspires to be a society that is free of caste discrimination. If this is our society’s aspiration, the government will have to be enabled or empowered to take all the necessary steps to achieve this goal. In a country like South Africa, which had a deep history of racial discrimination, its new constitution had to enable the government to end racial discrimination.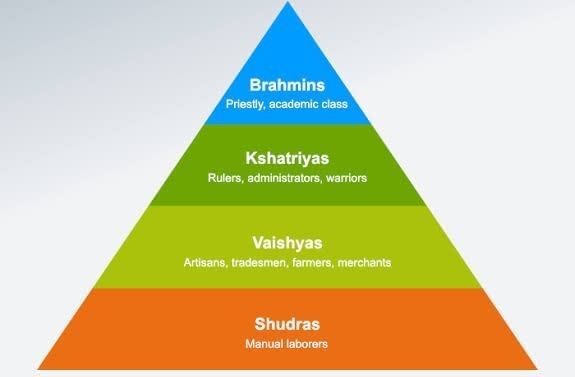 Indian Caste System
Indian Caste System - A constitution can reflect the dreams and goals of a society in a positive way.
- The creators of the Indian Constitution believed that every person in society should have what they need to live a life of basic dignity and self-respect.
- This includes having enough material resources, access to education, and more.
- The Indian Constitution allows the government to implement welfare measures that are sometimes legally required.
- As we study the Indian Constitution, we will see that these provisions are supported by the Preamble of the Constitution.
- These important provisions are also mentioned in the section on Fundamental Rights.
- Additionally, the Directive Principles of State Policy instruct the government to achieve certain goals that reflect the desires of the people.
The Fundamental Identity of a People
- Finally, and perhaps even most importantly, a constitution expresses the fundamental identity of a people.
- The fourth function of a constitution is to enable the government to fulfil the aspirations of a society and create conditions for a just society.
- This means the people as a collective entity comes into being only through the basic constitution. It is by agreeing to a basic set of norms about how one should be governed, and who should be governed that one forms a collective identity. One has many sets of identities that exist before a constitution. But by agreeing to certain basic norms and principles one constitutes one’s basic political identity.
- Second, constitutional norms are the overarching framework within which one pursues individual aspirations, goals and freedoms. The constitution sets authoritative constraints upon what one may or may not do. It defines the fundamental values that we may not trespass. So the constitution also gives one a moral identity. Third and finally, it may be the case that many basic political and moral values are now shared across different constitutional traditions.
- If one looks at constitutions around the world, they differ in many respects — in the form of government they enjoy in many procedural details. But they also share a good deal. Most modern constitutions create a form of government that is democratic in some respects, most claim to protect certain basic rights. But constitutions are different in the way they embody conceptions of natural identity.
- Most nations are an amalgamation of a complex set of historical traditions; they weave together the diverse groups that reside within the nation in different ways. For example, German identity was constituted by being ethnically German. The constitution gave expression to this identity. The Indian Constitution, on the other hand, does not make ethnic identity a criterion for citizenship.
- Different nations embody different conceptions of what the relationship between the different regions of a nation and the central government should be. This relationship constitutes the national identity of a country.
The Authority of a Constitution
- We have identified several important roles that a constitution serves in society. These roles help explain why many societies adopt a constitution.
- There are three additional questions we can consider regarding the constitution:
(i) What is a constitution?
(ii) How effective is a constitution?
(iii) Is a constitution just? - In most nations, the term Constitution refers to a concise document that contains various articles about the state. It outlines how the state is to be organized and what rules it should follow.
- When we inquire about a country's constitution, we typically mean this specific document.
- However, some countries, like the United Kingdom, do not have a single document that is called the Constitution. Instead, they have multiple documents and legal decisions that collectively form what is referred to as the constitution.
- Thus, we can define a constitution as a document or a collection of documents that aim to fulfill the important roles previously mentioned.
- But many constitutions around the world exist only as written words on paper, lacking real power or effect. The key question is: how effective is a constitution?
- What factors contribute to its effectiveness? What ensures that it truly influences the lives of individuals?
- Making a constitution effective relies on various important factors.
Mode of Promulgation
- This refers to how a constitution is formed.
- It examines who created the constitution and the level of authority they possessed.
- In several nations, constitutions fail to function effectively because they are made by military leaders or unpopular leaders who lack the ability to connect with the people.
- The most successful constitutions, such as those of India, South Africa, and the United States, were established following significant popular national movements.
- India's Constitution was officially created by a Constituent Assembly between December 1946 and November 1949, but it was influenced by a long history of the nationalist movement that successfully united various groups in Indian society.
- The Constitution gained a lot of legitimacy because it was made by individuals who had great public trust, could negotiate well, and respected many different parts of society.
- These leaders were able to persuade the public that the Constitution was not just a tool for increasing their own power.
- The final document represented a broad national agreement at that time.
- Some countries have asked all their citizens to vote on whether a constitution should be accepted through a full referendum.
- Although the Indian Constitution did not go through such a referendum, it was still widely accepted because it had the support and agreement of popular leaders.
- Even without a referendum, the people embraced the Constitution by following its rules.
- Thus, the authority of those who create the constitution plays a significant role in determining its potential for success.
The Substantive Provisions of a Constitution
- It is essential for a successful Constitution to provide reasons for everyone in society to accept its rules.
(i) A constitution that allows a permanent majority to oppress minority groups would leave those minorities with no motivation to accept its terms.
(ii) Similarly, if a constitution consistently favors some individuals over others or gives power to a small group, it will lose support from the broader population. - When any group feels that their identity is being suppressed, they will not feel compelled to follow the constitution.
- No constitution can create perfect justice on its own, but it must persuade people that it offers a structure for achieving basic justice.
- Consider this thought experiment: What would be the content of some basic rules in society, such that they gave everyone a reason to go along with them?
- The more a constitution protects the freedom and equality of all its members, the higher the chances it will be successful. Does the Indian Constitution, in general, provide reasons for everyone to support its main principles?
|
154 videos|973 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: Why do we need a Constitution- 1 - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. Why is a constitution important for a society? |  |
| 2. What are the main functions of a constitution? |  |
| 3. How does a constitution reflect the aspirations of a society? |  |
| 4. What limitations are placed on the powers of government by a constitution? |  |
| 5. What is the process of promulgating a constitution? |  |

















