UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Polity for UPSC CSE > Mind Map: Making of the Constitution
Mind Map: Making of the Constitution | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
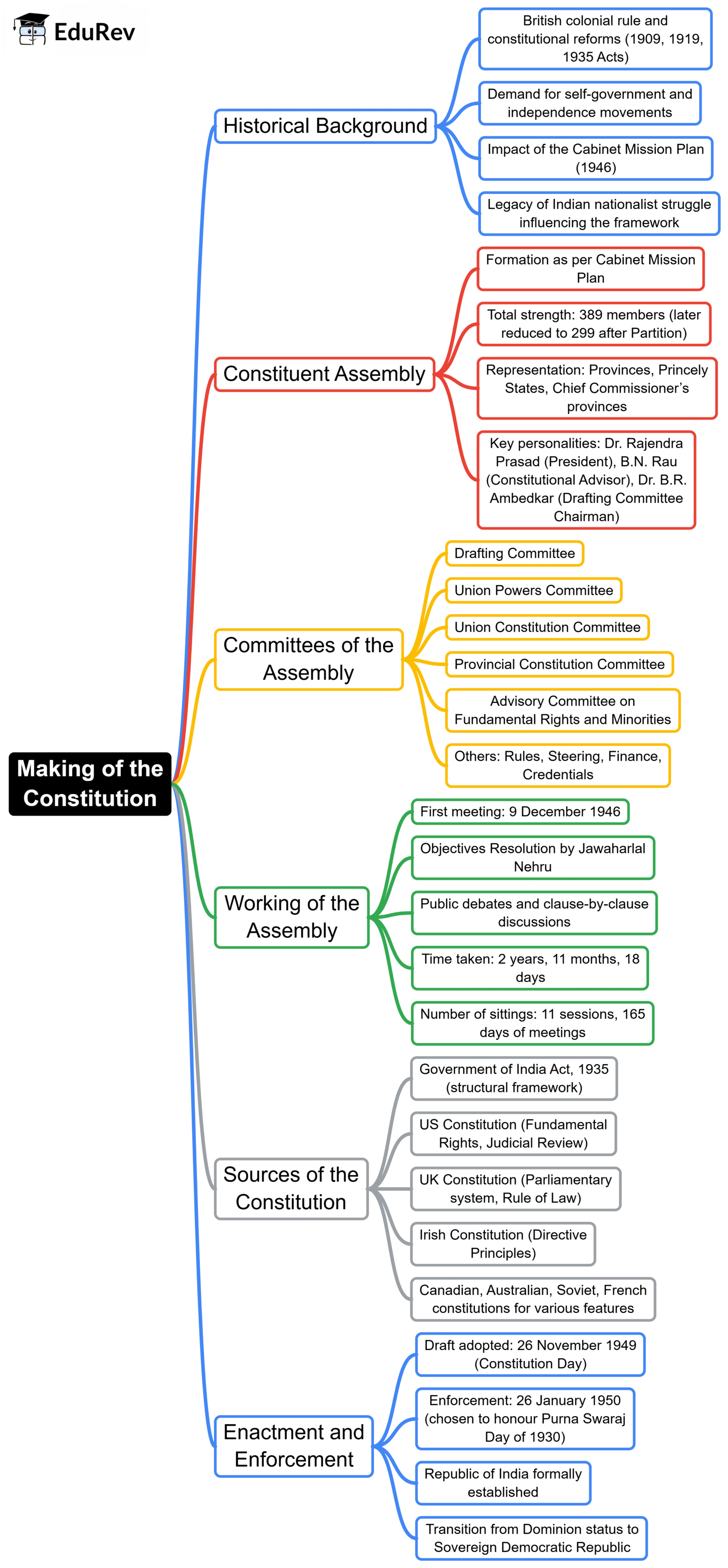
The document Mind Map: Making of the Constitution | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Polity for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
154 videos|985 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Making of the Constitution - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the significance of the Constitution? |  |
Ans. The Constitution is significant as it serves as the fundamental law of the land, providing the framework for governing a country. It establishes the rights and responsibilities of citizens, the structure of the government, and the distribution of powers among different branches and levels of government.
| 2. Who were the key individuals involved in the making of the Constitution? |  |
Ans. The key individuals involved in the making of the Constitution were the delegates who attended the Constitutional Convention in 1787. Notable figures include George Washington, James Madison, Benjamin Franklin, Alexander Hamilton, and Thomas Jefferson. These delegates debated and drafted the Constitution, bringing their diverse perspectives and experiences to the process.
| 3. How long did it take to draft the Constitution? |  |
Ans. The drafting of the Constitution took approximately four months. The Constitutional Convention began on May 25, 1787, and the final draft of the Constitution was signed on September 17, 1787. During this period, the delegates engaged in intense debates and negotiations to shape the provisions of the Constitution.
| 4. What were the major compromises made during the Constitutional Convention? |  |
Ans. Two significant compromises made during the Constitutional Convention were the Great Compromise and the Three-Fifths Compromise. The Great Compromise resolved the issue of representation in the legislative branch by creating a bicameral legislature, with the House of Representatives based on proportional representation and the Senate granting equal representation to each state. The Three-Fifths Compromise addressed the contentious issue of counting enslaved individuals for determining a state's population and representation.
| 5. How does the Constitution protect individual rights? |  |
Ans. The Constitution protects individual rights through the inclusion of the Bill of Rights, which consists of the first ten amendments. These amendments guarantee various civil liberties and protections, such as freedom of speech, religion, and assembly, the right to bear arms, protection against unreasonable searches and seizures, the right to a fair trial, and protection against cruel and unusual punishment. Additionally, the Constitution establishes a system of checks and balances that helps safeguard individual rights by preventing any one branch of government from becoming too powerful.
Related Searches

















