Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 Previous Year Questions - Minerals and Energy Resources
Previous Year Questions 2025
Q1: Two statements are given below. They are Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read both the statements carefully and choose the correct option:
Assertion (A): Minerals are an indispensable part of our lives.
Reason (R): All living things need minerals.
Options:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Assertion (A):
Minerals are an indispensable part of our lives. This is true. Minerals are vital for building and maintaining healthy bones, teeth, and other tissues, as well as for proper nerve and muscle function and enzyme activation. They are also essential components of many biological molecules and play a role in various metabolic processes.
Reason (R):
All living things need minerals. This is also true. Both plants and animals require minerals for their survival and proper functioning. For example, plants need minerals like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium for growth, while animals need minerals like calcium, iron, and zinc for various bodily functions.
Thus, option (a) is correct.
Q2: Match Column I with Column II and choose the correct option: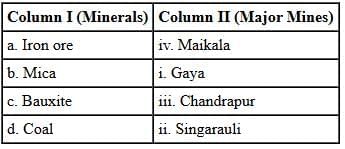 Options:
Options:
(a) a-iii, b-i, c-iv, d-ii
(b) a-iii, b-i, c-ii, d-iv
(c) a-ii, b-iii, c-i, d-iv
(d) a-ii, b-iii, c-iv, d-i
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- a. Iron ore – iii. Chandrapur: Chandrapur in Maharashtra is associated with iron ore mining, as the chapter mentions iron ore deposits in the Chhota Nagpur plateau and nearby regions, including parts of Maharashtra.
- b. Mica – i. Gaya: Gaya in Bihar is a major center for mica mining. The chapter highlights the Koderma-Gaya-Hazaribagh belt in Jharkhand and Bihar as a key mica-producing region.
- c. Bauxite – iv. Maikala: The Maikala hills in Chhattisgarh (part of the Amarkantak plateau) are known for bauxite deposits, as noted in the chapter for central India’s bauxite mining areas.
- d. Coal – ii. Singarauli: Singarauli, located in Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh, is a major coal mining area, part of the northern coalfields, as described in the chapter.
Thus, the correct option is (a) a-iii, b-i, c-iv, d-ii.
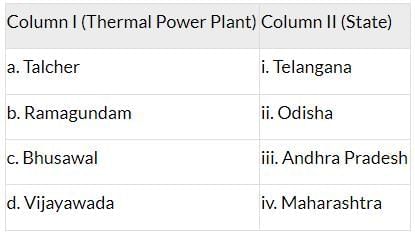
Q3: Match Column I with Column II and choose the correct option:
(A) a-ii, b-i, c-iv, d-iii
(B) a-iii, b-iv, c-i, d-ii
(C) a-iv, b-iii, c-ii, d-i
(D) a-ii, b-i, c-iii, d-iv
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) a-ii, b-i, c-iv, d-iii
The table below shows the correct matching of thermal power plants with their respective states: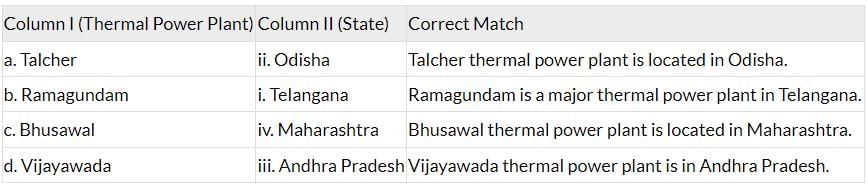
Correct Matches:
a-ii (Talcher - Odisha)
b-i (Ramagundam - Telangana)
c-iv (Bhusawal - Maharashtra)
d-iii (Vijayawada - Andhra Pradesh)
Thus, option (A) is correct.
Q4: Read the given source and answer the questions that follow:
Iron Ore
Iron ore is the basic mineral and the backbone of industrial development. India is endowed with fairly abundant resources of iron ore. India is rich in good quality iron ores. Magnetite is the finest iron ore with a very high content of iron up to 70 per cent. It has excellent magnetic qualities, especially valuable in the electrical industry. Hematite ore is the most important industrial iron ore in terms of the quantity used, but has a slightly lower iron content than magnetite (50 - 60 per cent). In 2018 - 19, almost the entire production of iron ore (97%) accrued from Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Karnataka, and Jharkhand. The remaining production (3%) was from other states.
(i) In which iron ore is the maximum iron content found?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Magnetite
Magnetite’s Iron Content: The source states that magnetite has a very high iron content, up to 70%, making it the finest iron ore.
Comparison with Hematite: Hematite, while widely used, has a lower iron content (50-60%), confirming magnetite as the ore with the maximum iron content.
Significance: Magnetite’s high iron content and magnetic properties make it valuable, especially in the electrical industry, as per the chapter.
(ii) Which is the most important industrial iron ore?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Hematite
Hematite’s Industrial Importance: The source specifies that hematite is the most important industrial iron ore due to the large quantity used in industries, particularly for steel production.
Quantity vs. Quality: Despite its lower iron content (50-60%) compared to magnetite (70%), hematite is more abundant and widely mined, making it the primary choice for industrial applications.
Production Context: The chapter notes that India’s iron ore production, largely hematite, comes from states like Odisha and Chhattisgarh.
(ii) "Iron ore is a basic mineral." Support the statement.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Iron ore is a basic mineral as it is essential for industrial development, particularly in steel production, which supports infrastructure and manufacturing.
Backbone of Industry: The source describes iron ore as the backbone of industrial development, as it is the primary raw material for steel, used in construction, machinery, and transportation (e.g., railways, vehicles).
Abundant Resources: India’s rich deposits of high-quality iron ore (magnetite and hematite) in states like Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Karnataka, and Jharkhand ensure its availability for industrial growth, as noted in the chapter.
Thus, iron ore’s critical role in industrial processes underscores its status as a basic mineral.
Q5: Match Column I with Column II and choose the correct option: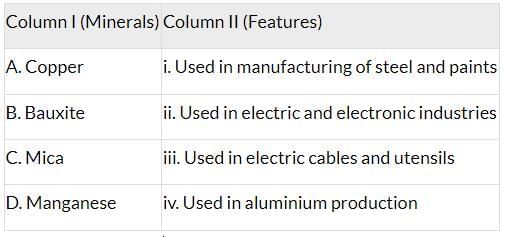
(a) A-i, B-iii, C-iv, D-ii
(b) A-ii, B-iv, C-iii, D-i
(c) A-iv, B-ii, C-iii, D-i
(d) A-iii, B-iv, C-ii, D-i
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) A-iii, B-iv, C-ii, D-i
The table below shows the correct matching of minerals with their uses: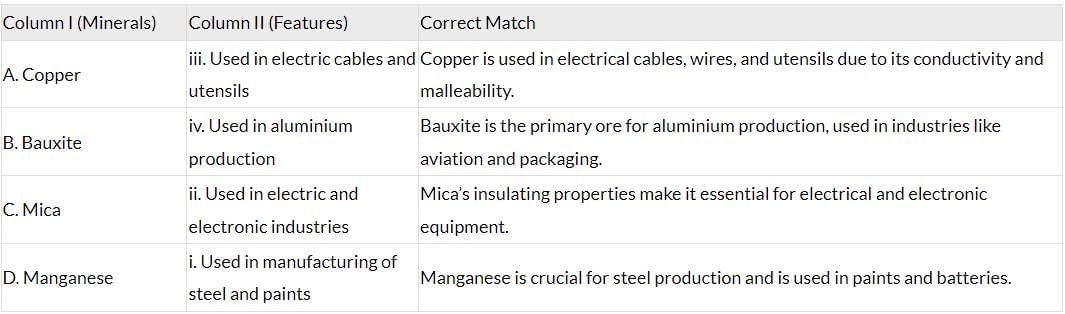
Correct Matches:
A-iii (Copper - electric cables and utensils)
B-iv (Bauxite - aluminium production)
C-ii (Mica - electric and electronic industries)
D-i (Manganese - steel and paints)
Thus, option (d) is correct.
Q6: "It would be beneficial to develop sustainable ways to meet the growing energy demand in India." Support the statement by giving suitable arguments.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Developing sustainable ways to meet India’s growing energy demand is beneficial as it ensures long-term energy security, reduces environmental degradation, and promotes economic and social development.
Energy Security: India’s energy demand is rising due to population growth and industrialization. Sustainable sources like solar, wind, and hydropower are renewable, unlike finite conventional sources (coal, oil), ensuring long-term availability, as emphasized in the chapter.
Environmental Protection: Conventional energy sources like coal cause pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Non-conventional sources (e.g., solar, wind) are cleaner, reducing air pollution and combating climate change, aligning with sustainable development goals.
Economic Benefits: Investing in renewable energy creates jobs (e.g., solar panel manufacturing) and reduces dependence on imported fuels like oil, saving foreign exchange and boosting the economy.
Rural Electrification: Sustainable energy sources like solar and biogas can provide electricity to remote areas, improving living standards and supporting inclusive development, as noted in the chapter.
Resource Conservation: Using renewables reduces the depletion of non-renewable resources like coal and oil, preserving them for future generations, a key concern in the chapter.
Q7: "We have to use a planned and sustainable manner to conserve our minerals." Support the statement by giving suitable arguments.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Using a planned and sustainable manner to conserve minerals is essential to ensure their availability for future generations, reduce environmental damage, and support economic stability.
Finite Resources: Minerals like iron ore, coal, and bauxite are non-renewable and will eventually deplete. Planned extraction and sustainable practices, such as recycling, ensure their availability, as highlighted in the chapter.
Environmental Protection: Unplanned mining causes deforestation, soil erosion, and water pollution. Sustainable practices like controlled mining and land reclamation minimize environmental degradation.
Economic Efficiency: Efficient use of minerals through technologies like ore beneficiation reduces waste, lowers production costs, and supports industries like steel and aluminium, crucial for India’s economy.
Future Generations: Sustainable mining ensures that future generations have access to essential minerals, preventing overexploitation, a key concern in the chapter.
Alternative Materials: Promoting substitutes (e.g., recycled metals) and reducing dependence on scarce minerals supports sustainable resource management.
Q8: Study the given table and answer the question that follows:
CRUDE OIL RESERVES
Read the following possible outcomes from the table and choose the correct option:
I. If crude oil continues to be extracted at the present pace, it would be exhausted in about 50 years.
II. In Middle Eastern Countries it may take longer than average of the world.
III. To ensure the availability of crude oil in future, its reuse and recycle policy should be adopted.
IV. In United States of America, Crude oil is likely to run out in just about 10 years.
(A) Only I, III and IV are correct.
(B) Only I, II and III are correct.
(C) Only II, III and IV are correct.
(D) Only I, II and IV are correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (D) Only I, II and IV are correct.
Statement I: The table states the world average crude oil reserves will last 50.2 years, which aligns with “about 50 years” at the current extraction rate. This is correct.
Statement II: The Middle East’s reserves (808 thousand million barrels) will last 70 years, longer than the world average (50.2 years), making this statement correct.
Statement III: Crude oil is a non-renewable resource and cannot be reused or recycled once consumed (unlike metals). The chapter does not support a reuse/recycle policy for crude oil, so this statement is incorrect.
Statement IV: The table indicates U.S. crude oil reserves will last 10.5 years, which aligns with “just about 10 years,” making this statement correct.
Thus, option (D) is correct as I, II, and IV are accurate, but III is not.
Q9: Two statements are given below. They are Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read both the statements and choose the correct option:
Assertion (A): Certain minerals may occur as alluvial deposits in sands of valley floors and the base of hills.
Reason (R): These are usually minerals, that are not corroded by water.
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(C) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(D) (A) is false but (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Assertion (A): The chapter states that certain minerals, like gold and platinum, occur as alluvial deposits (placer deposits) in sands of valley floors and hill bases, formed by the action of water. This is true.
Reason (R): These minerals are found in alluvial deposits because they are resistant to corrosion by water, allowing them to be transported and deposited by rivers without degrading. This is true.
Evaluation: The resistance to corrosion (R) explains why these minerals (e.g., gold) are found in alluvial deposits (A), as water erodes other materials but leaves these intact. Thus, (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Therefore, option (A) is correct.
Q10: Match Column I with Column II and choose the correct option: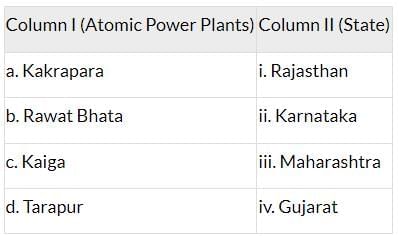
(A) a-i, b-ii, c-iii, d-iv
(B) a-ii, b-iii, c-iv, d-i
(C) a-iv, b-i, c-ii, d-iii
(D) a-iv, b-i, c-iii, d-ii
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (C) a-iv, b-i, c-ii, d-iii
The table below shows the correct matching of atomic power plants with their states: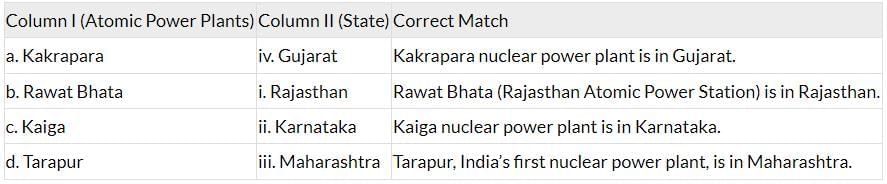
Correct Matches:
a-iv (Kakrapara - Gujarat)
b-i (Rawat Bhata - Rajasthan)
c-ii (Kaiga - Karnataka)
d-iii (Tarapur - Maharashtra)
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Q11: Attempt any three questions:
(i) Name the leading state in production of rice.
(ii) Name the place where coal-mines are located in Tamil Nadu.
(iii) Name the place where major sea port is located in Karnataka.
(iv) Name the oil field located in Maharashtra.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(i) West Bengal
(ii) Neyveli
(iii) New Mangalore
(iv) Mumbai High
(i) Leading state in rice production: West Bengal is the leading state for rice production in India, as it has fertile alluvial soils and a monsoon climate suitable for rice, as per the Contemporary India - II textbook (though this relates to agriculture, not minerals).
(ii) Coal mines in Tamil Nadu: Neyveli is known for its lignite coal mines, a significant source of coal used for thermal power generation, as mentioned in the chapter.
(iii) Major sea port in Karnataka: New Mangalore (Mangalore Port) is a major port on Karnataka’s coast, handling exports like iron ore, as noted in the textbook.
(iv) Oil field in Maharashtra: Mumbai High, located in the Arabian Sea off Maharashtra’s coast, is India’s largest offshore oil field, a key petroleum resource in the chapter.
Q12: Read the characteristics given in the box and identify the type of coal from the options given below:
This is low grade brown coal.
The principal reserves are in Neyveli in Tamil Nadu.
It is soft with high moisture content.
(A) Pit Coal
(B) Anthracite Coal
(C) Lignite Coal
(D) Bituminous Coal
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (C) Lignite Coal
Characteristics Match: The chapter describes lignite as a low-grade brown coal with high moisture content, soft texture, and major reserves in Neyveli, Tamil Nadu, used for thermal power generation.
Other Options:
Pit Coal: Not a standard term in the chapter; likely a distractor.
Anthracite Coal: High-grade coal with low moisture and high carbon content, found in Jammu & Kashmir, not Neyveli.
Bituminous Coal: Medium-grade coal, harder and with less moisture than lignite, found in places like Jharia (Jharkhand).
Conclusion: The described characteristics (low-grade, brown, high moisture, Neyveli) align with lignite coal, making (C) the correct answer.
Q13: Why is the conservation of conventional sources of energy significant? Explain any two reasons.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Conservation of conventional energy sources is significant to ensure their availability for future generations and to minimize environmental damage.
Finite Resources: Conventional energy sources like coal, petroleum, and natural gas are non-renewable and will deplete over time. Conserving them through efficient use (e.g., energy-efficient technologies) ensures they last longer, as emphasized in the chapter.
Environmental Protection: Extraction and use of conventional sources cause pollution (e.g., coal burning releases CO2, leading to air pollution and climate change). Conservation reduces environmental degradation, promoting cleaner ecosystems, a key concern in the chapter.
Q14: Why is it necessary to adopt non-conventional sources of energy? Explain.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Adopting non-conventional sources of energy is necessary to ensure sustainable energy supply and reduce environmental degradation.
Sustainability: Non-conventional sources like solar, wind, and biogas are renewable, unlike finite conventional sources (coal, oil), ensuring long-term energy security, as highlighted in the chapter.
Environmental Benefits: Non-conventional sources produce minimal pollution compared to coal or petroleum, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and environmental damage, supporting sustainable development goals.
Q15: Suggest any two ways for the conservation of minerals.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Two ways to conserve minerals are recycling metals and using alternative materials.
Recycling Metals: Recycling minerals like aluminium and copper reduces the need for fresh mining, conserving mineral reserves and reducing environmental damage, as suggested in the chapter.
Using Alternative Materials: Substituting scarce minerals with alternatives (e.g., using composites instead of metals) reduces dependence on non-renewable minerals, promoting sustainable use.
Q16: Attempt any three questions:
(i) Name the place where an International Airport is located in Punjab.
(ii) Name the place where major sea port is located in Gujarat.
(iii) Name an oil field of India located in Arabian Sea.
(iv) Name the place where nuclear power plant is located in Uttar Pradesh.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(i) Amritsar
(ii) Kandla
(iii) Mumbai High
(iv) Narora
(i) International Airport in Punjab: Amritsar hosts the Sri Guru Ram Dass Jee International Airport, a major airport in Punjab, as per general geographical knowledge in the textbook.
(ii) Major sea port in Gujarat: Kandla (Deendayal Port) is a major sea port in Gujarat, handling mineral exports like bauxite, as noted in the chapter.
(iii) Oil field in Arabian Sea: Mumbai High, located off Maharashtra’s coast in the Arabian Sea, is India’s largest offshore oil field, a key petroleum resource in the chapter.
(iv) Nuclear power plant in Uttar Pradesh: Narora is home to the Narora Atomic Power Station, as mentioned in the chapter’s discussion of nuclear energy.
Previous Year Questions 2024
Q1: Match Column-I with Column-II and choose the correct option. (CBSE 2024)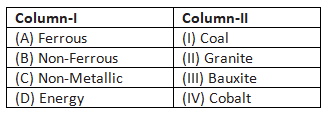 (a) (A)-(II), (B)-(IV), (C)-(III), (D)-(I)
(a) (A)-(II), (B)-(IV), (C)-(III), (D)-(I)(b) (A)-(IV), (B)-(III), (C)-(II), (D)-(I)
(c) (A)-(I), (B)-(II), (C)-(IV), (D)-(III)
(d) (A)-(III), (B)-(IV), (C)-(II), (D)-(I)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
(A) Ferrous matches with (IV) Cobalt, as ferrous materials are related to iron and cobalt is a metal used in various alloys.
(B) Non-Ferrous matches with (III) Bauxite, since bauxite is a non-ferrous ore primarily used to produce aluminum.
(C) Non-Metallic matches with (II) Granite, because granite is a type of rock and not a metal.
(D) Energy matches with (I) Coal, as coal is a major source of energy.
Q2: (A) How is energy a basic requirement for economic development? Explain. (CBSE 2024)
OR
(B) How are conventional sources of energy different from non- conventional sources? Explain.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) Energy is a fundamental requirement for economic development because it powers industries, transportation, communication, and daily life.
Here’s how energy drives economic growth:
- Industrial Growth: Industries rely on energy to operate machinery, manufacture goods, and process raw materials. Without a stable energy supply, industrial productivity declines, hindering economic growth.
- Infrastructure Development: Energy is essential for building and maintaining infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and buildings. Construction equipment and materials production depend heavily on energy.
- Transportation and Trade: Energy fuels transportation systems, including cars, trucks, ships, and airplanes, enabling the movement of goods and people. Efficient transportation networks are vital for trade and commerce, which are key components of economic development.
- Technological Advancement: Modern technologies, including computers, telecommunications, and medical equipment, require energy to function. Technological innovation drives productivity and economic growth, making energy indispensable.
- Agriculture and Food Production: Energy is crucial for agricultural activities, such as irrigation, harvesting, and food processing. It also powers the transportation and storage of food, ensuring food security and supporting rural economies.
- Employment and Income Generation: The energy sector itself creates jobs in production, distribution, and maintenance. Additionally, reliable energy access enables the growth of other sectors, leading to increased employment opportunities and income generation.
- Quality of Life: Energy improves the quality of life by powering homes, schools, hospitals, and public services. Access to electricity enhances education, healthcare, and overall well-being, which are essential for a productive workforce.
In summary, energy is a cornerstone of economic development as it supports industrial activities, infrastructure, transportation, technology, agriculture, employment, and quality of life. Without adequate and reliable energy, economic progress would be severely constrained.
OR
(B) Conventional sources of energy and non-conventional sources of energy are different in the following ways:
1. Source:
- Conventional Sources: These are traditional sources of energy that have been used for a long time, such as coal, petroleum (oil), natural gas, and hydropower.
- Non-Conventional Sources: These are newer or alternative sources of energy that are not widely used yet, like solar energy, wind energy, biomass, tidal energy, and geothermal energy.
2. Renewability:
- Conventional Sources: These sources are mostly non-renewable, meaning they are finite and can run out over time. For example, coal and petroleum are limited and take millions of years to form.
- Non-Conventional Sources: These are usually renewable, meaning they can be replenished naturally and are not likely to run out, like solar and wind energy.
3. Environmental Impact:
- Conventional Sources: They often cause pollution and harm the environment. Burning fossil fuels like coal and petroleum releases harmful gases, contributing to air pollution and climate change.
- Non-Conventional Sources: These sources are generally cleaner and have less impact on the environment. Solar and wind energy, for example, produce little to no pollution.
4. Availability:
- Conventional Sources: These sources are available in specific regions. For example, coal is found in large quantities in some countries, while oil is concentrated in others.
- Non-Conventional Sources: These sources can be found anywhere, as long as the natural conditions are right, like sunlight for solar energy or wind for wind energy.
5. Cost:
- Conventional Sources: They tend to be cheaper initially but can lead to higher long-term costs due to pollution, health effects, and resource depletion.
- Non-Conventional Sources: They may be expensive to set up initially (like installing solar panels or wind turbines), but they have lower operational costs and are more sustainable in the long run.
In summary, conventional sources are traditional, non-renewable, and polluting, while non-conventional sources are modern, renewable, and environmentally friendly.
 Sustainable Energy
Sustainable Energy
Previous Year Questions 2023
Q3: Which one of the following is an example of the Ferrous Metal? (CBSE 2023)(a) Copper
(b) Tin
(c) Bauxite
(d) Nickel
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Nickel is considered a ferrous metal because it is often used in the production of alloys with iron, which enhances the strength and resistance of steel. In contrast, copper and tin are non-ferrous metals, and bauxite is an ore of aluminum, not a metal itself.
Q4: Read the given case and answer the questions that follow: (2023)
CONSERVATION OF ENERGY RESOURCES
Energy is a basic requirement for economic development. Every sector of the national economy - agriculture, industry, transport, commercial and domestic - needs inputs of energy. The economic development plans implemented since independence necessarily required increasing amounts of energy to remain operational. As a result, consumption of energy In all forms has been steadily rising all over the country. In this background, there is an urgent need to develop a sustainable path of energy development. Promotion of energy conservation and increased use of renewable energy sources are the twin planks of sustainable energy. India is presently one of the least energy-efficient countries in the world. We have to adopt a cautious approach for the judicious use of our limited energy resources. For example, as concerned citizens, we can do our bit by using public transport systems instead of individual vehicles; switching off electricity when not in use, using power-saving devices and using non-conventional sources of energy. At last "Energy Saved is energy produced”.
(i) Why is sustainable energy a key to sustainable development?
(ii) Why is consumption of energy rising in all over India?
(iii) Explain 'Energy saved is energy produced.’
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(i) Sustainable energy is a key to sustainable development, as sustainability demands that resource reserves including exhaustible, natural and environmental resources, be maintained.
(ii) After getting independence development of all sectors like agriculture, industry, transport, domestic needs etc. necessarily required to remain in operation, hence consumption of energy in all forms has increased all over India.
(iii) Energy saved is energy produced. We cannot keep on producing non-renewable energy like petrol, diesel and electricity. So the need of the hour is the better utilisation of existing resources. We have to adopt cautions approach for the judicious use of our limited energy resources.
Previous Year Questions 2020
Q5: Classify metallic minerals with an example of each. (2020 C) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Ferrous minerals: Iron ore, manganese
- Non-ferrous minerals: Copper, lead, bauxite
- Precious minerals: Gold, silver, platinum
Q6: "Minerals occur in various forms". Support this statement with examples. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Minerals can occur in igneous and metamorphic rocks as veins and lodes. Examples include tin, copper, zinc, and lead.
- Minerals can also occur in sedimentary rocks as beds or layers. Examples include gypsum, potash salt, and sodium salt.
- Some minerals are formed through the decomposition of surface rocks, leaving behind residual material. Bauxite is an example.
- Alluvial deposits in sands can also contain minerals. Gold, silver, tin, and platinum are examples.
Q7: "Minerals are an indispensable part of our lives". Support this statement with examples. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Minerals are used in the construction of buildings and infrastructure, such as iron ore for steel.
- Minerals are used in transportation systems, such as copper for electrical wiring.
- Minerals are used in electronic devices, such as lithium for batteries.
- Minerals are used in everyday items, such as gold and silver for jewelry.
 Minerals
Minerals
Q8: Differentiate between anthracite and bituminous coal on the basis of quality. (2020 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Anthracite coal is of higher quality, while bituminous coal is comparatively lower grade in quality.
- Anthracite coal has a higher carbon content, causing less pollution compared to bituminous coal.
- Anthracite coal is available in small quantities in India, while bituminous coal is available in abundance.
Q9: In which of the following states is Kalpakkam nuclear power plant located ? (2020)
(a) Gujarat
(b) Odisha
(c) Kerala
(d) Tamil Nadu
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The Kalpakkam nuclear power plant is located in Tamil Nadu, near the town of Kalpakkam, which is close to Chennai. This plant is significant as it contributes to India's energy needs by generating electricity through nuclear power.
Q10: In which of the following States is Narora Nuclear Power Plant located? (2020)
(a) Karnataka
(b) Kerala
(c) Tamil Nadu
(d) Uttar Pradesh
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The Narora Nuclear Power Plant is located in Uttar Pradesh, near the town of Narora, which is about 200 kilometers from Delhi. This plant plays an important role in generating nuclear energy to meet the electricity demands of the region.
Q11: Fill in the blank: ________ is well known for effective use of wind energy in Rajasthan. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Jaisalmer is well known for the effective use of wind energy in Rajasthan.
Q12: Suggest any one way to enhance the use of natural gas in India. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Use of natural gas:
Making people aware about the importance of using this clean energy resources because this gas is considered environment friendly.
Q13: Fill in the blanks: 'Gobar gas plants’ provide twin benefits to the farmers in the form of_______and________ (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 'Gobar gas plants' provide twin benefits to the farmers in the form of energy and manure.
Q14: Suggest any one way to maximize the use of nuclear energy in the field of medicine. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Nuclear medicine use radio-active substances, mostly to diagnose cancer as well as cardiac and other diseases.
Previous Year Questions 2019
Q15: In which of the following state is the Narora Nuclear Power Plant located ?(a) Karnataka
(b) Kerala
(c) Tamil Nadu
(d) Uttar Pradesh (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The Narora Nuclear Power Plant is located in the state of Uttar Pradesh in India. It is situated on the banks of the Ganges River in the Bulandshahr district. This plant is one of India's key nuclear power facilities, generating electricity through nuclear energy.
Thus, the correct answer is (d) Uttar Pradesh.
Q16: “India has fairly rich and varied mineral resources across different regions”. Support the statement with examples. (CBSE 2019)
OR
“Minerals occur in various forms.” Support this statement with examples. (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (1) Minerals occur in the cracks, crevices, faults or joints in igneous rocks and metamorphic rocks in the form of small occurrences of veins and large occurrences called lodes. Tin and zinc are obtained from veins and lodes.
(2) Sedimentary Rocks are found in nodes and layers. Minerals like gypsum, coal, iron ore are formed.
(3) Minerals are also formed by decomposition of surface rocks, and the removal of soluble constituents, leaving a residual mass of weathered material containing ores. For example, bauxite
Q17: ‘Energy saved is energy produced.’ Assess the statement. (CBSE 2019, 17)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: This statement can be supported in the following ways:
(1) Promotion of energy conservation and increased use of renewable energy sources is an important measure to save resources for the upcoming generations.
(2) A judicious use in using our limited energy resources is of utmost significance to encourage development without any threat to survival in the future generations.
(3) Public transport systems can help save fuel and other important energy resources. Fuel will last for a longer time.
(4) Using power-saving devices and using nonconventional sources of energy helps in preventing excessive usage of conventional energy resources.
Previous Year Questions 2017
Q18: Describe any three characteristics of the Ballari-Chitradurga, Chikkamagaluru-Tumakuru iron-ore belt in India. (Foreign 2017) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- The Ballari-Chitradurga, Chikkamagaluru-Tumakuru iron-ore belt is located in Karnataka.
- The Kudremukh mines in this belt, located in the Western Ghats, are a 100% export unit.
- The Kudremukh deposits are known to be one of the largest in the world.
- The ore from these mines is transported as slurry through a pipeline to a port near Mangaluru.
Q19: Describe any three characteristics of the Durg-Bastar-Chandrapur iron-ore belt in India. (AI 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- The Durg-Bastar-Chandrapur iron-ore belt is located in Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra.
- It provides very high-grade hematite iron ore from the famous Bailadila range of hills in the Bastar district of Chhattisgarh.
- The iron ore deposits in this belt have the best physical properties needed for steel making.
- Iron ore from these mines is exported to Japan and South Korea via Vishakhapatnam port.
Q20: Describe any three characteristics of the 'Odisha-Jharkhand belt' of iron ore in India. (Delhi 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- The Odisha-Jharkhand belt is known for high-grade haematite ore.
- In Odisha, the iron ore is found in Badampahar mines in the Mayurbhanj and Kendujhar districts.
- In Jharkhand, haematite iron ore is mined in Gua and Noamundi.
- These mines supply iron ore to the steel industry in the eastern and other parts of India.
Q21: Why is it necessary to conserve mineral resources? Explain any four ways to conserve mineral resources. (AI2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: It is necessary to conserve mineral resources because they are limited in availability and the process of mineral formation is slow. Additionally, minerals are non-renewable and exhaustible.
Four ways to conserve mineral resources are:
1. Using minerals in a planned and sustainable manner.
2. Evolving improved technology to allow the use of low-grade ore at a low cost.
3. Practicing recycling of minerals.
4. Using alternative renewable substitutes.
Q22: 'Energy saved is energy produced.’ Assess the statement. (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The statement "Energy saved is energy produced" emphasizes the importance of conserving energy. By reducing energy wastage and using energy-efficient practices, we can save energy and reduce the need for additional energy production. This approach is beneficial for the environment as it reduces the consumption of fossil fuels and decreases greenhouse gas emissions.
Q23: Why should we use renewable energy resources? Explain with arguments. (Foreign 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: There are several reasons why we should use renewable energy resources:
1. Non-renewable resources are limited and will eventually get exhausted. In contrast, renewable energy resources such as solar power and wind energy are inexhaustible, making them a sustainable choice for long-term energy needs.
2. The depletion of non-renewable resources like coal and petroleum has taken millions of years to occur. By using renewable energy resources, we can avoid further depletion and preserve these non-renewable resources for future generations.
3. Fossil fuels, which are non-renewable resources, contribute to pollution and environmental degradation. Renewable energy sources, on the other hand, are cleaner and emit fewer greenhouse gases, thus mitigating the impact of climate change.
4. The cost of extracting and using non-renewable resources is increasing as these resources become harder to find. In contrast, the cost of renewable energy technologies, such as solar panels and wind turbines, has been decreasing over time. Investing in renewable energy can help reduce energy costs in the long run.
Q24: Why is energy needed? Write one reason. (CBSE 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Energy is required for all kinds of activities like cooking, lighting and heating, propelling vehicles and enabling smooth working of machinery in industries.
Q25: “Natural gas is an important source of energy.” Support the statement. (CBSE 2017)
Ans: Natural gas is an important source of energy because:
(1) It is an industrial raw material in the petrochemical industry.
(2) It helps build fertiliser plants and encourages the use of fertilisers. It can boost agricultural production.
(3) It can be easily transported through pipelines
Q26: Which state is the largest producer of manganese in India? Mention any two uses of manganese. (CBSE 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The nation's top producer of manganese is Madhya Pradesh.
(1) Manganese manufactures steel and ferro-manganese alloy. Nearly 10 kgs of manganese is used in manufacturing one tonne of steel.
(2) It is used in the production of bleaching powder, insecticides and paints
Q27: “Minerals are an indispensable part of our lives.” Support the statement with examples. (CBSE 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (1) Minerals are used to create or produce almost everything we use everyday. This includes our technology, equipment etc., which are made of steel, silicon, aluminium, copper, gold, silver. Needles, Utensils, Clothes, Jewellery, and containers are all made of minerals.
(2) Transportation was made possible because of minerals. The railway lines and tarmac (paving) of the roads, cars, buses, trains, airplanes are manufactured from minerals.
(3) Even the food that we eat contains minerals. Minerals are produced when we digest it and even when we excrete it.
Q28: “There is a pressing need for using renewable energy sources in India.” Justify the statement. (CBSE 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: There is a pressing need to use renewable energy resources because:
(1) The growing consumption of energy has resulted in the country becoming increasingly dependent on fossil fuels such as coal, oil and gas.
(2) The rising prices of oil and gas and their potential shortages have raised uncertainties about the security of energy supply in future.
(3) It has serious repercussions on the growth of the national economy.
(4) The increasing use of fossil fuels also causes serious environmental problems.
(5) Non-renewable energy resources take millions of years to regenerate.
Previous Year Questions 2016
Q29: Why are there a wide range of colours, hardness, crystal forms, lustre and density found in minerals? (Delhi 2016) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The varied colours, hardness, crystal forms, lustre, and density found in minerals are due to their chemical composition and the parameters such as temperature, pressure, rate of cooling, etc., present during their formation.
Q30: How is iron-ore transported from Kudremukh mines to a port near Mangaluru? (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Iron ore is transported from Kudremukh mines to a port near Mangaluru as slurry through pipelines.
Q31: Why should the use of cattle cake as fuel be discouraged? (Al 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The use of cattle cake as fuel should be discouraged because it creates pollution and by burning it, a valuable manure resource is destroyed, which could otherwise improve soil fertility.
Q32: How are 'Gobar Gas Plants' beneficial to the farmers? (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 'Gobar Gas Plants' are beneficial to the farmers in two ways. Firstly, they provide a clean fuel for domestic cooking and lighting. Secondly, they produce high-quality manure that can be used to enhance soil fertility.
Q33: "India is an important iron and steel producing country in the world. Yet we are not able to perform to our full potential." Suggest and explain any three measures to reach our full potential. (Foreign 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Modernizing technology and machinery in the iron and steel industry to improve efficiency and productivity.
- Streamlining the supply of inputs such as iron ore and coke to ensure a steady and sufficient availability.
- Developing a supportive infrastructure, such as adequate electricity capacity, to meet the demands of the industry.
- Implementing effective customer demand and supply management strategies to optimize production and distribution.
Q34: 'Consumption of energy in all forms has been rising all over the country. There is an urgent need to develop a sustainable path of energy development and energy saving.' Suggest and explain any three measures to solve this burning problem. (AI 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Increase the use of renewable energy resources like solar power, wind power, biogas, tidal energy, and geothermal energy. This will reduce dependence on non-renewable sources and promote sustainable energy development.
- Promote energy conservation by encouraging the judicious use of energy resources. This can be achieved through awareness campaigns, energy-efficient practices, and the use of power-saving devices.
- Improve energy efficiency in industries, transportation, and buildings by adopting energy-saving technologies and practices. This can be done through government regulations, incentives, and public-private partnerships.
Q35: "There is a pressing need to use renewable energy resources." Justify the statement with suitable arguments. (AI 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- The growing consumption of energy has led to increased dependence on fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gas, which are finite resources. The use of renewable energy resources can help reduce this dependence and ensure a sustainable energy future.
- Rising prices and potential shortages of fossil fuels have raised concerns about the security of energy supply. Renewable energy resources are more abundant and can provide a more reliable and secure source of energy.
- The use of renewable energy resources can help mitigate the adverse environmental impacts of fossil fuel use, such as air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power are cleaner and have a lower carbon footprint.
- Investing in renewable energy technologies can stimulate economic growth and create jobs in sectors like manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
Q36: Which minerals are used to obtain nuclear energy? Name all the six nuclear power stations of India. (AI 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- The minerals used to obtain nuclear energy are uranium and thorium.
- The six nuclear power stations in India are: Narora Nuclear Power Station, Kakrapara Nuclear Power Station, Tarapur Nuclear Power Station, Kaiga Nuclear Power Station, Rawat Bhata Nuclear Power Station, and Kalpakkam Nuclear Power Station.
Q37: Explain the importance of conservation of minerals. Highlight any three measures to conserve them. (AI2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Conservation of minerals is important for the following reasons:
1. Minerals are the backbone of the economy and are essential for various industries.
2. The total volume of workable mineral deposits is very limited, representing only 1% of the Earth's crust.
3. Mineral resources are being consumed at a rapid rate, while the geological processes of mineral formation are slow. This means that the rate of consumption far exceeds the rate of replenishment.
Three measures to conserve minerals are:
1. Using minerals in a sustainable manner by planning their extraction and usage.
2. Developing improved technologies that allow the use of low-grade ore at a lower cost.
3. Promoting recycling and reuse of minerals to reduce the demand for new extraction.
Q38: Highlight the importance of petroleum. Explain the occurrence of petroleum in India. (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The importance of petroleum can be highlighted as follows:
1. Petroleum is a major source of energy in India, providing fuel for heat, lighting, and transportation.
2. It serves as a lubricant for machinery, ensuring their smooth operation.
3. Petroleum is a crucial raw material for various manufacturing industries.
4. Petroleum refineries play a significant role in supporting industries such as synthetic, textile, fertilizer, and chemical industries.
In India, petroleum occurs in the following ways:
1. Most petroleum reserves in India are associated with anticlines and fault traps.
2. In regions of folding anticlines or domes, petroleum is trapped in the crust of the upfold.
3. Petroleum is also found in fault traps between porous and non-porous rocks.
Q39: Suggest and explain any three measures through which every citizen can help to conserve energy resources. (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Three ways in which citizens can help conserve energy resources are:
(1) Reduction in usage of individual vehicles.
(2) Minimisation of electricity usage.
(3) Reduction in usage of water resources
Previous Year Questions 2015
Q40: Why does aluminium metal have great importance? (2015) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Aluminium metal has great importance because it combines the properties of great strength, lightness, malleability, and conductivity.
Q41: "Natural gas is considered an environment-friendly fuel." Explain the statement in two points. (AI 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Natural gas is considered an environment-friendly fuel because it causes less pollution compared to other fossil fuels like coal and oil. It has a lower carbon content and emits fewer greenhouse gases when burned, reducing the impact on climate change.
- Natural gas is a clean-burning fuel that produces fewer air pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxide, and particulate matter. This improves air quality and reduces the health risks associated with pollution.
Q42: How is geothermal energy produced? Explain. (AI 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Geothermal energy is produced by harnessing the heat from the Earth's interior.
- In areas with high geothermal gradients, where temperatures increase with depth, groundwater absorbs heat from the rocks and becomes hot.
- This hot water or steam rises to the Earth's surface and can be used to drive turbines and generate electricity.
Q43: How can biogas solve the energy problem mainly in rural India? Give your suggestions. (AI 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Biogas can solve the energy problem in rural India by providing a renewable source of energy that is readily available.
- The raw materials for biogas production, such as agricultural waste, animal manure, and kitchen waste, are abundant in rural areas.
- By promoting the use of biogas plants, rural communities can generate their own energy for cooking, lighting, and other domestic uses, reducing their dependence on traditional sources like firewood and kerosene.
- Biogas production also has environmental benefits, as it helps in waste management by converting organic waste into a useful energy resource and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
 Biogas Energy
Biogas Energy
Q44: Describe any three features of ferrous minerals found in India. (Foreign 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Ferrous minerals in India account for approximately three-fourths of the total value of metallic mineral production.
- They provide a strong foundation for the expansion of metallurgical industries in the country.
- India is a leading exporter of ferrous minerals, with magnetite and hematite being some of the common ferrous minerals.
- States like Odisha, Chhattisgarh, and Maharashtra are rich in ferrous mineral deposits.
Q45: How is the mining activity injurious to the health of the miners and the environment? Explain. (Delhi 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Mining activities can lead to respiratory diseases and other health issues for miners due to the inhalation of dust and toxic fumes.
- The roofs and walls of mines can pose a risk of collapsing, leading to accidents and injuries.
- Flooding and fire hazards are common risks in mining operations.
- Mining can result in the contamination of water bodies with mineral dust, affecting aquatic life and human consumption.
- The dumping of waste and slurry from mining operations can degrade the land and contribute to environmental pollution.
Q46: How can solar energy solve the energy problem to some extent in India? Give your opinion. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Solar energy can contribute to solving the energy problem in India in the following ways:
1. India receives abundant sunlight throughout the year, especially in rural and remote areas. Harnessing solar energy through solar panels and solar power plants can provide a reliable source of electricity in these areas.
2. Establishing solar plants in rural and remote areas can help minimize the dependence on traditional sources of energy such as firewood and dung cakes. This, in turn, contributes to environmental conservation and reduces indoor air pollution.
3. Solar energy can provide electricity for various applications, including lighting, cooking, and powering electronic devices. By utilizing solar energy, India can reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and decrease greenhouse gas emissions, thereby mitigating climate change.
|
66 videos|793 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 Previous Year Questions - Minerals and Energy Resources
| 1. What are the major types of minerals found in India? |  |
| 2. How does energy resource distribution affect India's economy? |  |
| 3. What are the renewable energy resources available in India? |  |
| 4. What role do minerals play in India's industrial sector? |  |
| 5. What are the environmental impacts of mining minerals in India? |  |






















