Climate - 1 Class 11 Geography
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Unity And Diversity In The Monsoon Climate |

|
| Factors Determining The Climate Of India |

|
| The Nature Of Indian Monsoon |

|
Introduction
Climate refers to the average weather conditions measured over a long period, while weather represents the current state of the atmosphere. Weather can change rapidly, often within a day or a week, but climate changes are usually gradual and may only be noticed after 50 years or longer. Variations in weather occur in different seasons due to changes in elements such as temperature, pressure, wind direction and speed, humidity, and precipitation. Weather Images
Weather Images
Unity And Diversity In The Monsoon Climate
Unity of the Climate
- The monsoon regime emphasizes the unity of India with the rest of the Southeast Asian region.
- This view of broad unity of the monsoon type of climate should not, however, lead one to ignore its regional variations, which differentiate the weather and climate of different regions of India.
- The climate of Kerala and Tamil Nadu in the south is so different from that of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar in the north, and yet all of these have a monsoon type of climate.
Diversity of Climate
The climate of India has many regional variations expressed in the pattern of:
- Winds
- Temperature
- Rainfall
- Rhythm of seasons
- Degree of wetness or dryness
Temperature Variation
- While in the summer the mercury occasionally touches 55°C in western Rajasthan, it drops to as low as minus 45°C in winter around Leh.
- Churu in Rajasthan may record a temperature of 50°C or more on a June day, while the mercury hardly touches 19°C in Tawang (Arunachal Pradesh) on the same day.
- On a December night, the temperature in Drass (Jammu and Kashmir) may drops to minus 45°C, while Thiruvananthapuram or Chennai on the same night records 20°C or 22°C.
- In Kerala and in the Andaman Islands, the difference between day and night temperatures may be hardly seven or eight degree Celsius. But in the Thar desert, if the day temperature is around 50°C, at night, it may drop considerably up to 15 °C–20°C.
The Regional Variations In Precipitation
- While snowfall occurs in the Himalayas, it only rains over the rest of the country.
- While Cherrapunji and Mawsynram in the Khasi Hills of Meghalaya receive rainfall over 1,080 cm in a year, Jaisalmer in Rajasthan rarely gets more than 9 cm of rainfall during the same period.
- Tura, situated in the Garo Hills of Meghalaya, may receive an amount of rainfall in a single day which is equal to 10 years of rainfall at Jaisalmer.
- While the annual precipitation is less than 10 cm in the northwest Himalayas and the western deserts, it exceeds 400 cm in Meghalaya.
- The Ganga delta and the coastal plains of Odisha are hit by strong rain-bearing storms almost every third or fifth day in July and August, while the Coromandal coast, a thousand km to the south, goes generally dry during these months.
- Most parts of the country get rainfall during June-September, but in the coastal areas of Tamil Nadu, it rains at the beginning of the winter season.
Factors Determining The Climate Of India
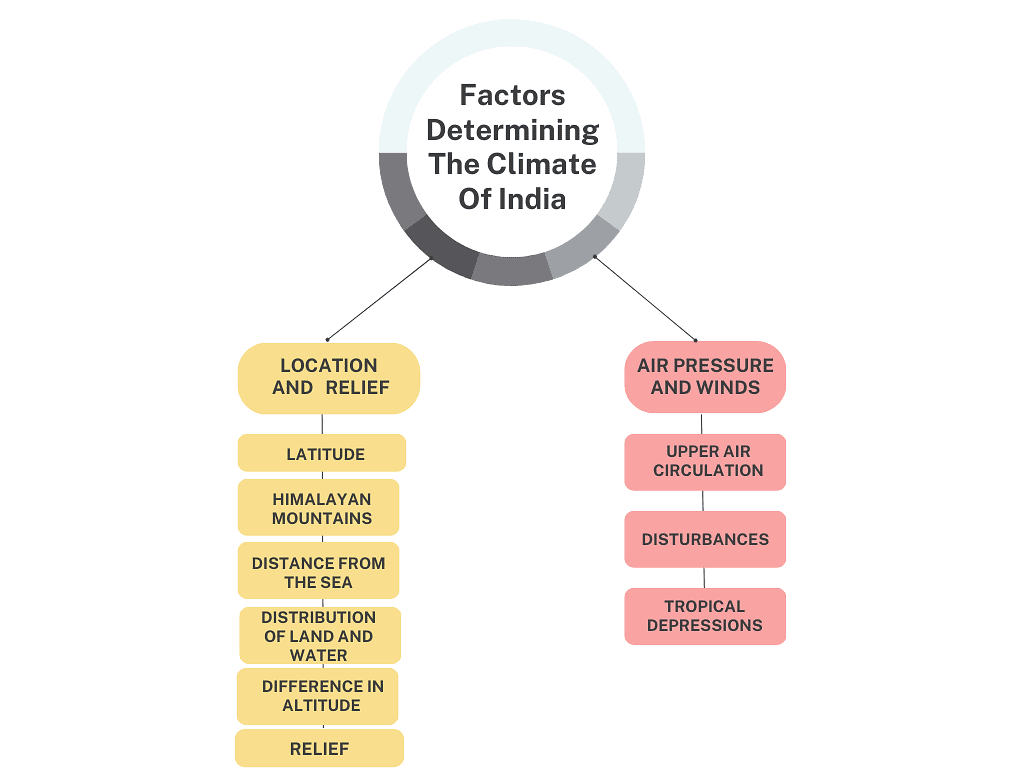
It can be broadly divided into two groups of factors:
- Factors related to location and relief
- Factors related to air pressure and winds
Factors related to Location and Relief
1. Latitude:
- The northern part of India lies in the sub-tropical and temperate zone, and the part lying south of the Tropic of Cancer falls in the tropical zone.
- The tropical zone, being nearer to the equator, experiences high temperatures throughout the year with a small daily and annual range.
- Areas north of the Tropic of Cancer, being away from the equator, experiences an extreme climate with high daily and annual range of temperature.
2. The Himalayan Mountains:
- The lofty Himalayas in the north along with their extensions, act as an effective climatic divide. The towering mountain chain provides an invincible shield to protect the subcontinent from the cold northern winds.
- The Himalayas also trap the monsoon winds, forcing them to shed air pressure, causing reversal in the direction of monsoon winds.
3. Distance from the Sea:
- With a long coastline, large coastal areas have an equable climate. Areas in the interior of India are far away from the moderating influence of the sea.
- Such areas experience extreme climate due to the lack of moisture from the sea.
4. Distribution of Land and Water:
- India is flanked by the Indian Ocean on three sides in the south and girdled by a high and continuous mountain-wall in the north. As compared to the landmass, water heats up or cools down slowly.
- This differential heating of land and sea creates different air pressure zones in different seasons in and around the Indian subcontinent.
5. Difference in Altitude:
- Temperature decreases with height.
- Due to the thin air, places in the mountains are cooler than places on the plains.
- For example, Agra and Darjiling are located on the same latitude, but the temperature in January in Agra is 16°C, whereas it is only 4°C in Darjiling.
6. Relief:
- The physiography or relief of India also affects the temperature, air pressure, direction and speed of wind and the amount and distribution of rainfall.
- The windward sides of Western Ghats and Assam receive high rainfall during June-September, whereas the southern plateau remains dry due to its leeward situation along the Western Ghats.
Factors Related to Air Pressure and Wind
- Distribution of air pressure and winds on the surface of the Earth.
- Upper air circulation is caused by factors controlling global weather and the inflow of different air masses and jet streams.
- Inflow of western cyclones, generally known as disturbances during the winter season and tropical depressions during the south-west monsoon period, into India creates weather conditions favourable to rainfall.
The ITCZ is a low-pressure area near the equator where winds from both sides meet and rise. In July, it moves to 20°–25°N (over northern India), forming the monsoon trough, which creates low pressure in north India. Winds from the southern hemisphere cross the equator and turn into southwest monsoon winds. In winter, the ITCZ shifts south, and winds reverse direction, blowing as the northeast monsoon.
The Nature Of Indian Monsoon
Onset of the Monsoon
- During April and May, when the sun shines vertically over the Tropic of Cancer, the large landmass in the north of the Indian Ocean gets intensely heated. This causes the formation of an intense low-pressure in the northwestern part of the subcontinent.
- Since the pressure in the Indian Ocean in the south of the landmass is high as water gets heated slowly, the low-pressure cell attracts the southeast trades across the Equator.
- These conditions help in the northward shift in the position of the ITCZ. The southwest monsoon may thus be seen as a continuation of the southeast trades deflected towards the Indian subcontinent after crossing the Equator. These winds cross the Equator between 40°E and 60°E longitudes.
 Monsoon
Monsoon
Entry of Monsoon into India
- The southwest monsoon sets in over the Kerala coast by 1st June and moves swiftly to reach Mumbai and Kolkata between 10th and 13th June.
- By mid-July, the southwest monsoon engulfs the entire subcontinent.
Rain-bearing Systems and Rainfall Distribution
- Bay of Bengal Branch
- Arabian Sea branch
The rainfall distribution is based on two factors:
- The offshore meteorological conditions.
- The position of the equatorial jet stream along the eastern coast of Africa.
EI-Nino and the Indian Monsoon
- EI-Nino is a complex weather system that appears once every three to seven years, bringing drought, floods and other weather extremes to different parts of the world.
- The system involves oceanic and atmospheric phenomena with the appearance of warm currents off the coast of Peru in the Eastern Pacific and affects weather in many places, including India.
- El-Nino is a periodic warming of the central and eastern Pacific Ocean near Peru, replacing the usual cold Humboldt Current, which affects atmospheric circulation and causes irregular rainfall in India. This results in:
i) The distortion of equatorial atmospheric circulation;
ii) Irregularities in the evaporation of sea water;
iii) reduction in the amount of plankton, which further reduces the number of fish in the sea - EI-Nino is used in India for forecasting long range monsoon rainfall. In 1990-91, there was a wild EI-Nino event and the onset of southwest monsoon was delayed over most parts of the country ranging from five to twelve days.Question for Revision Notes: Climate - 1Try yourself:What does the term "El-Nino" mean and why is it called so?View Solution
Break in the Monsoon
- During the south-west monsoon period after having rains for a few days, if rain fails to occur for one or more weeks, it is known as break in the monsoon.
- These dry spells are quite common during the rainy season. These breaks in the different regions are due to different reasons:
1. In northern India, rains are likely to fail if the rain-bearing storms are not very frequent along the monsoon trough or the ITCZ over this region.
2. Over the west coast, the dry spells are associated with days when winds blow parallel to the coast.
|
70 videos|347 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Climate - 1 Class 11 Geography
| 1. What are the factors that determine the climate of India? |  |
| 2. What is the nature of Indian monsoon? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of unity and diversity in the monsoon climate? |  |
| 4. How does altitude affect the climate of India? |  |
| 5. What are the main pressure and wind systems that influence the monsoon climate of India? |  |
















