Worksheet Solutions: Water - The Essence of Life | Worksheets with Solutions for Class 5 PDF Download
Q1: Choose the correct option for each question.
(i) What percentage of Earth's water is freshwater?
A) 1%
B) 10%
C) 3%
D) 5%
Ans: C) 3%(Approximately)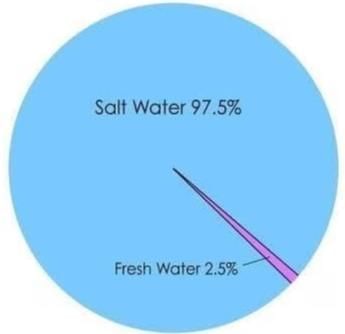 Division of Earth's Water
Division of Earth's Water
(ii) What is the process called when water turns into vapour?
A) Precipitation
B) Evaporation
C) Condensation
D) Filtration
Ans: B) Evaporation
(iii) Which of the following is NOT a type of freshwater?
A) Pond
B) River
C) Ocean
D) Lake
Ans: C) Ocean
(iv) What do we call the water that soaks into the ground?
A) Surface water
B) Groundwater
C) Rainwater
D) Tap water
Ans: B) Groundwater
(v) What is primarily responsible for the water cycle?
A) Wind
B) Sun
C) Trees
D) Animals
Ans: B) Sun
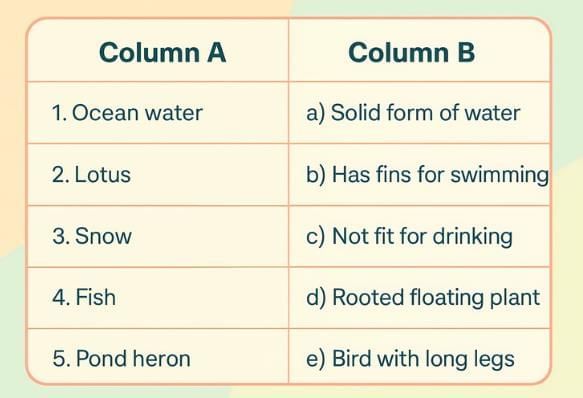
Q2: Match the items in Column A with the correct descriptions in Column B.
Ans: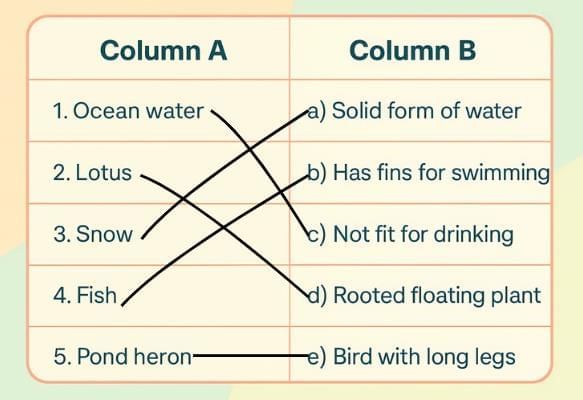
Q3: Fill in the blanks with the correct words from the chapter.
(i) The process of water falling to the ground is called __________.
(ii) Water exists in three forms: liquid, solid, and __________.
(iii) Groundwater is obtained by digging __________.
(iv) The __________ River in Rajasthan ends in the Rann of Kutch.
(v) Freshwater plants that float on the surface are called __________ plants.
Ans:
(i) The process of water falling to the ground is called precipitation.
(ii) Water exists in three forms: liquid, solid, and gas.
(iii) Groundwater is obtained by digging Wells.
(iv) The Luni River in Rajasthan ends in the Rann of Kutch.
(v) Freshwater plants that float on the surface are called floating plants.
 Floating Plant
Floating Plant
Q4: State whether the following statements are True or False. Correct the false statements.
(i) Most of the Earth's water is freshwater.
Ans: False
(ii) Rainwater is a type of surface water.
Ans: True
(iii) Water vapour can form clouds when it cools.
Ans: True
(iv) Water cannot exist in solid form.
Ans: False
(v) Planting trees helps in groundwater recharge.
Ans: True
Q5: Answer the following questions in 2-3 sentences each.
(i) Where does freshwater come from?
Ans: Freshwater comes from rivers, lakes, groundwater, and rain. It is a small part of all the water on Earth, which is mostly salty ocean water.
(ii) What are the three forms of water?
Ans: Water exists in three forms: liquid (like rain), solid (like ice), and gas (like steam). These forms change depending on temperature.
(iii) What is the water cycle?
Ans: The water cycle is how water moves around. It evaporates from oceans, forms clouds, and falls back to Earth as rain or snow. This keeps water moving.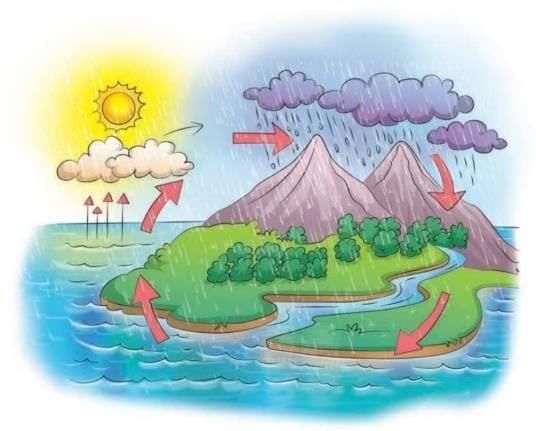 Movement of Water in atmosphere
Movement of Water in atmosphere
(iv) How do we get groundwater?
Ans: We get groundwater by digging wells or using pumps. It is the water that soaks into the ground after it rains.
(v) Why are rivers important?
Ans: Rivers are important because they provide water for drinking, farming, and help plants and animals live. They flow into seas and have smaller rivers, known as tributaries.
Q6: Answer the following questions in 4-6 sentences each. Use examples from the chapter to support your answers.
(i) Describe the water cycle in detail, including how water changes forms and moves through nature. Explain why it is important for life on Earth.
Ans: Heat causes water from different sources, like oceans and rivers, to become water vapour.
Water vapour forms the clouds, which come down as rain, snow and hail. This water goes back into rivers, lakes and oceans.
This constant circular movement of water in nature is called the water cycle.
Water keeps moving through the water cycle, changing its form as it travels through the air, land, and sky.
This reminds us how essential freshwater is for supporting life on Earth.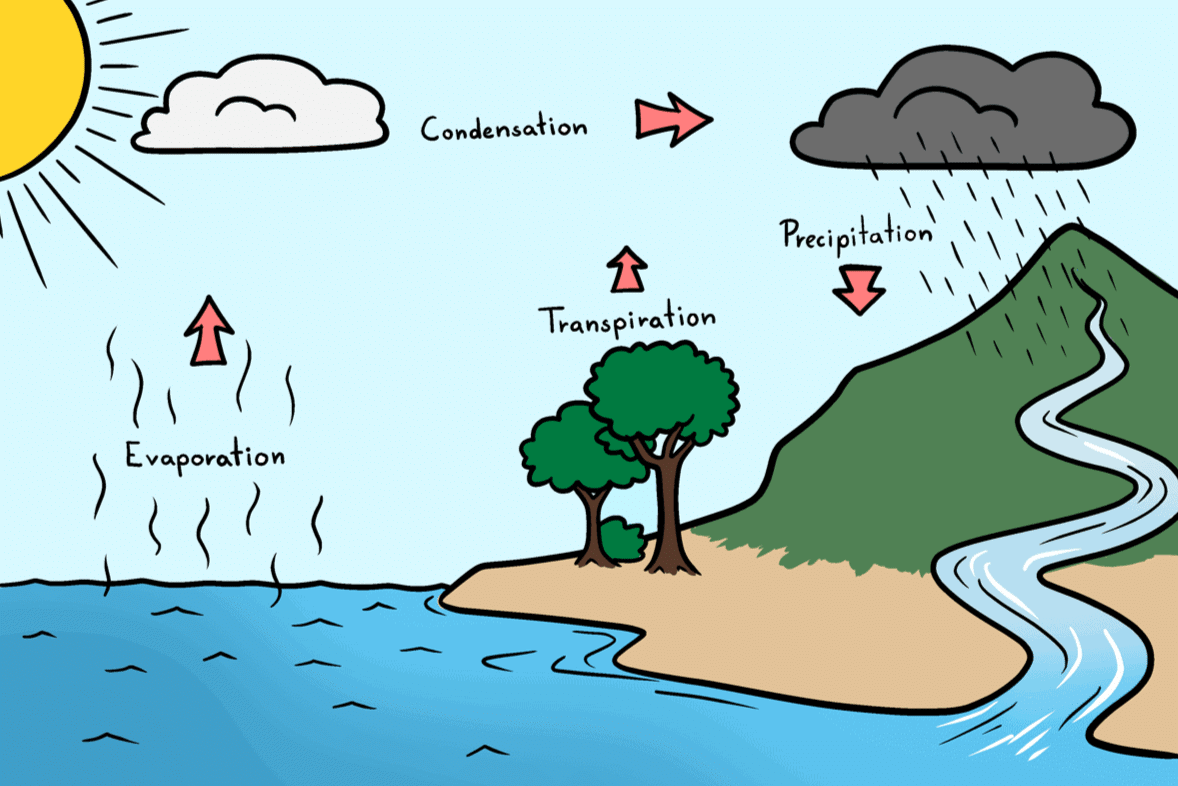 Water Cycle
Water Cycle
(ii) Explain the difference between freshwater and saltwater sources. Discuss why freshwater is essential for humans, plants, and animals, and what challenges we face in accessing it.
Ans: Although most of the Earth's surface is covered with water, the majority of it is salty, leaving a smaller amount of freshwater. Ocean water is salty and not fit for drinking.
All living beings—people, animals, birds, and plants—depend on freshwater to survive.
It is essential for drinking, growing crops, and carrying out daily activities.
Many plants and animals also live in freshwater. Without water, life would not be possible.
(iii) How do rivers form and flow across the land? Use the mustard seed activity and examples from Indian rivers to describe how they shape the landscape and support ecosystems.
Ans: A river often begins its journey from up in the mountains and flows down across the land.
Water flows, stops or curves according to the shape of the land formations in its path.
The flow of water can also change the shape of the land. In the mustard seed activity, seeds roll down slopes and gather, like water gathers in lakes, rivers and so on.
Some rivers flow into the Bay of Bengal, and some into the Arabian Sea.
Rivers, ponds, lakes, etc., are the natural sources of freshwater.
(iv) Why is groundwater recharge important, and what happens if it doesn't occur properly? Suggest ways to conserve water and protect groundwater in cities and villages.
Ans: When it rains, some water is soaked up by the soil. This water sinks through the layers of soil and rocks.
The water that gets stored deep underground is called groundwater. In cities with many cemented surfaces, rainwater cannot go into the ground easily, which stops groundwater from getting recharged.
Soak pits, ponds, human-made lakes, and planting more trees help rainwater return underground.
Water is a limited and shared resource which must be used wisely.
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Water - The Essence of Life - Worksheets with Solutions for Class 5
| 1. Why is water considered the essence of life? |  |
| 2. What are the unique properties of water that support life? |  |
| 3. How does water contribute to the survival of ecosystems? |  |
| 4. What are the main sources of water on Earth? |  |
| 5. How can we conserve water and ensure its availability for future generations? |  |





















