Class 7 Social Science Chapter 5 Worksheet Solutions - The Rise of Empires
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
| Match the Following |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1: What is the main feature of an empire?
a) A ruler governs one kingdom.
b) A ruler controls many smaller kingdoms.
c) The kingdom is independent of others.
d) The ruler is elected by the people.
Ans: b) A ruler controls many smaller kingdoms.
An empire is a large territory where a powerful emperor governs many smaller kingdoms or regions.
Q2: What did tributary kingdoms do in an empire?
a) They were fully independent.
b) They paid tribute to the emperor.
c) They ruled their own territories.
d) They supported military campaigns.
Ans: b) They paid tribute to the emperor.
Tributary kingdoms paid money, goods, or services to the emperor in exchange for protection and loyalty.
Q3: Which of the following was a reason for the expansion of empires?
a) To maintain peace
b) To gain fame and resources
c) To form alliances
d) To promote democracy
Ans: b) To gain fame and resources
One of the main reasons for empire expansion was the desire for resources, wealth, and fame.
Q4: Who helped Chandragupta Maurya to establish the Maurya Empire?
a) Dhanananda
b) Alexander the Great
c) Kauṭilya
d) Ashoka
Ans: c) Kauṭilya
Kauṭilya, also known as Chanakya, guided Chandragupta Maurya in founding the Maurya Empire and overthrowing the Nanda dynasty.
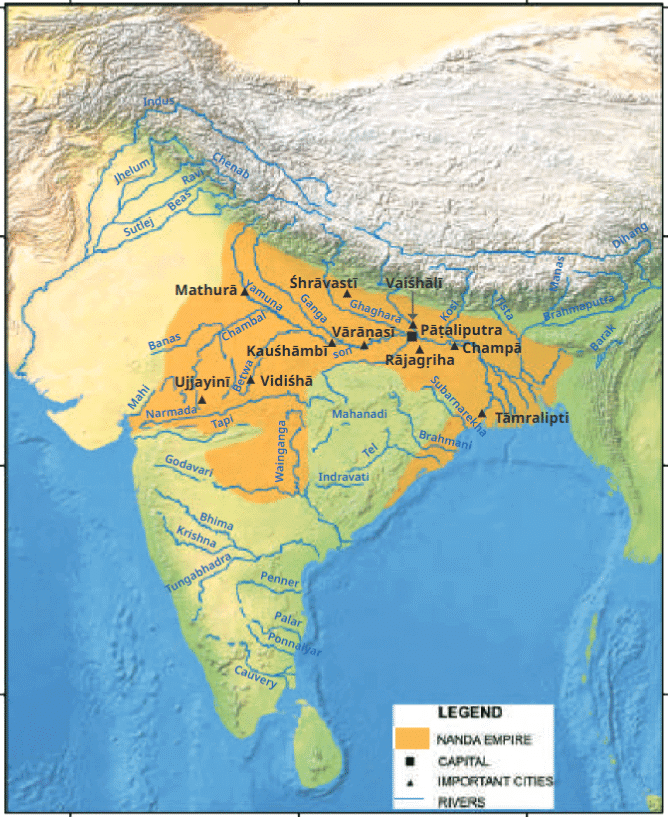 Maurya Empire
Maurya Empire
Q5: What was the capital of the Maurya Empire under Chandragupta?
a) Pataliputra
b) Rajagriha
c) Kausambi
d) Ujjain
Ans: a) Pataliputra
Pataliputra (modern-day Patna) was the capital of the Maurya Empire, strategically located for administration and trade.
Q6: What did Kauṭilya's Arthashastra primarily focus on?
a) Religion
b) Warfare and governance
c) Literature
d) Agriculture
Ans: b) Warfare and governance
Kauṭilya's Arthashastra is a treatise on statecraft, economics, and military strategy.
Q7: Who succeeded Chandragupta Maurya as emperor of the Maurya Empire?
a) Dhanananda
b) Ashoka
c) Ajatashatru
d) Mahapadma Nanda
Ans: b) Ashoka
Ashoka, the grandson of Chandragupta, succeeded him and expanded the empire significantly.
Q8: What was the significant change in Ashoka’s rule after the Kalinga War?
a) He focused on expanding the empire further.
b) He became a pacifist and embraced Buddhism.
c) He implemented stricter laws for the empire.
d) He strengthened military power.
Ans: b) He became a pacifist and embraced Buddhism.
After the brutal Kalinga War, Ashoka adopted Buddhism and promoted non-violence and peace.
 Kalinga War
Kalinga War
Q9: Which of the following was a key feature of the Maurya Empire’s governance?
a) Decentralized rule with local rulers in charge
b) Centralized administration with a strong military
c) Democracy where people voted for rulers
d) Isolation from foreign empires
Ans: b) Centralized administration with a strong military
The Maurya Empire had a strong centralized administration with a powerful military that helped maintain control over vast regions.
Q10: What was the primary purpose of Ashoka’s edicts?
a) To celebrate military victories
b) To promote Buddhism and moral values
c) To establish a monarchy
d) To create a system of taxation
Ans: b) To promote Buddhism and moral values
Ashoka’s edicts, written in Prakrit and inscribed on pillars and rocks, promoted dharma (moral duties) and Buddhist teachings.
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: An empire is ruled by a powerful __________.
Ans: Emperor
The emperor has control over many smaller kingdoms or regions within the empire.
Q2: The capital of the Maurya Empire under Chandragupta was __________.
Ans: Pataliputra
Pataliputra (Patna) was the capital city of the Maurya Empire, serving as the center of governance.
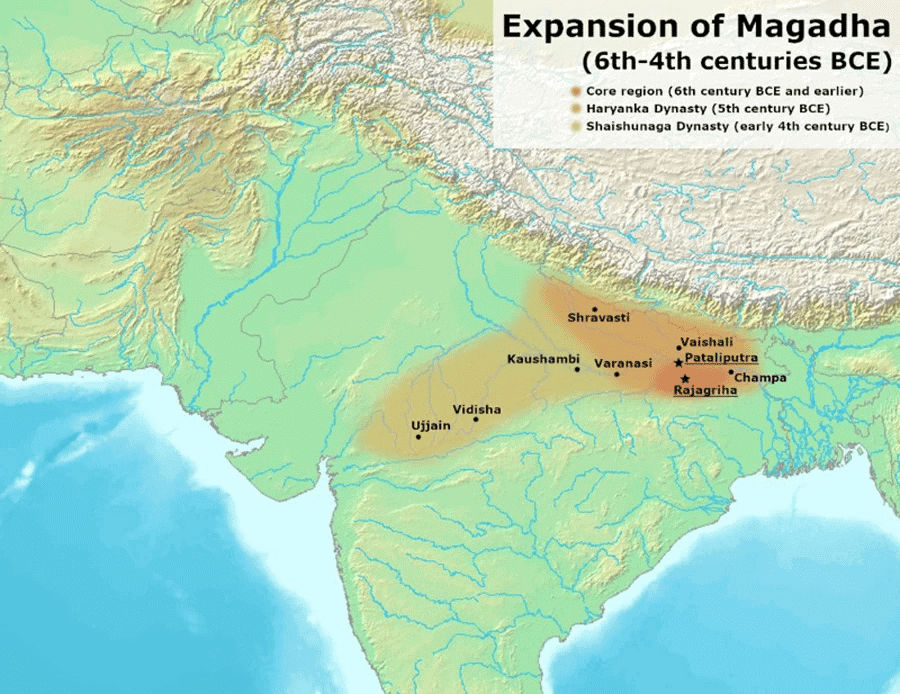
Q3: The Maurya Empire's administration was based on __________.
Ans: Centralization
The empire was centralized, with the emperor controlling all important decisions, supported by a bureaucracy.
Q4: Ashoka’s transformation after the Kalinga War led him to promote __________.
Ans: Buddhism
Ashoka embraced Buddhism and promoted its peaceful teachings after witnessing the devastation caused by the Kalinga War.
Q5: Kauṭilya, also known as Chanakya, wrote the __________ on governance and economics.
Ans: Arthashastra
The Arthashastra provides a detailed guide on statecraft, governance, and military strategy.
Q6: The Maurya Empire used __________ as a tool for managing and expanding the empire.
Ans: Warfare
Emperors like Chandragupta used military power to expand and maintain control over large territories.
Q7: The __________ dynasty ruled Magadha before the Mauryas.
Ans: Nanda
The Nanda dynasty was overthrown by Chandragupta Maurya, marking the rise of the Maurya Empire.
Q8: Ashoka’s __________ were inscribed on pillars and rocks throughout the empire.
Ans: Edicts
Ashoka’s edicts promoted Buddhist values and moral conduct, encouraging peace and welfare.
Q9: The Maurya Empire was known for its __________, which was used to manage its vast territory.
Ans: Administration
The Maurya Empire had a highly structured administration to manage its large territory and diverse population.
Q10: __________ was a major resource for the Maurya Empire’s army, used for weapons and tools.
Ans: Iron
Iron was crucial for the Maurya Empire's military, as it was used to make weapons and tools.
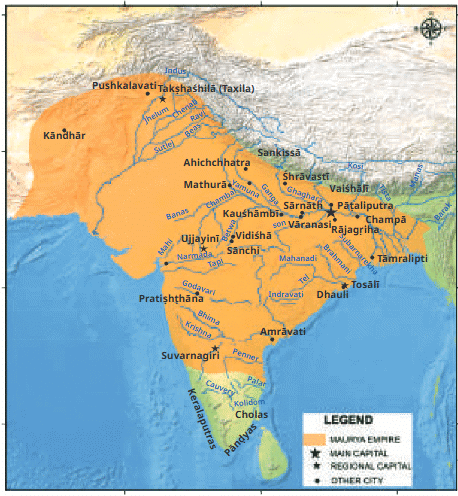 Mauryan Empire
Mauryan Empire
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: What is the Latin origin of the word 'empire'?
Ans: Imperium, meaning “supreme power.”
Q2: Who helped Chandragupta Maurya in establishing the Maurya Empire?
Ans: Kauṭilya (Chanakya).
Q3: What was the main contribution of Ashoka’s edicts?
Ans: Promoting Buddhist values and moral duties.
Q4: Which battle made Ashoka choose non-violence?
Ans: The Kalinga War.
Q5: What was the capital of the Maurya Empire?
Ans: Pataliputra.
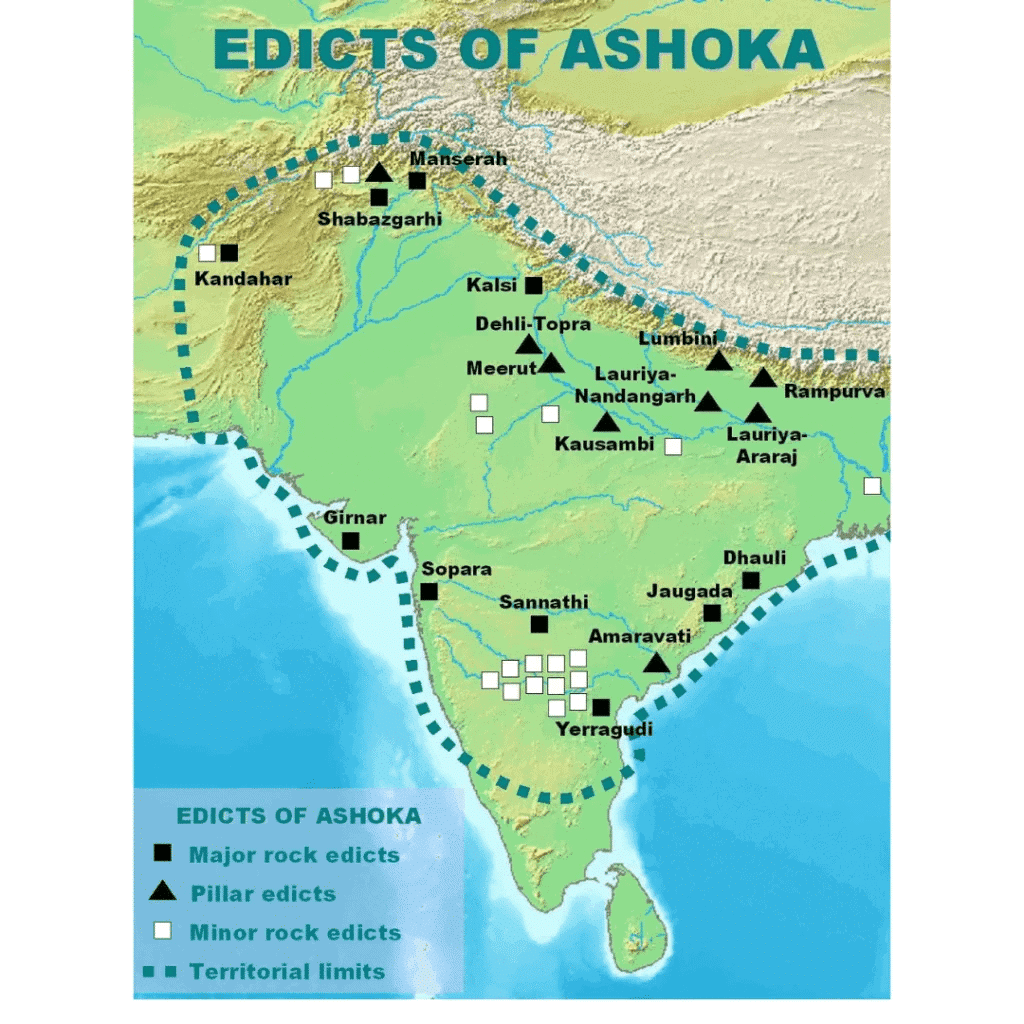 Edicts of Ashoka
Edicts of Ashoka
Short Answer Questions
Q1: How did the Nanda dynasty contribute to the rise of the Maurya Empire?
Ans: The Nanda dynasty helped consolidate the region of Magadha, making it an ideal base for Chandragupta Maurya to rise to power and expand the empire.
Q2: What was the role of Kauṭilya in the formation of the Maurya Empire?
Ans: Kauṭilya, also known as Chanakya, provided strategic advice, helped overthrow the Nandas, and guided Chandragupta in establishing and expanding the Maurya Empire.
Q3: How did the Maurya Empire impact trade and administration?
Ans: The Mauryas built a strong administrative system and protected trade routes, facilitating economic growth, especially in trade and cities.
Q4: What were Ashoka’s views on governance, as seen in his edicts?
Ans: Ashoka promoted moral governance based on dharma, emphasizing non-violence, justice, and the welfare of his people.
Q5: Why was the Kalinga War significant for Ashoka’s rule?
Ans: The Kalinga War caused massive destruction, leading Ashoka to adopt Buddhism and promote peace, non-violence, and welfare through his edicts.
Match the Following
(Match Column A with the correct option in Column B)
Ans: Matched Pairs and Explanations:
- 1 → d: The Maurya Empire had its capital in Pataliputra, from where governance was centralized)
- 2 → c: Ashoka’s edicts promoted the spread of Buddhism and moral values across the empire.
- 3 → b: Kauṭilya wrote the Arthashastra, a book on governance and strategy.
- 4 → e: Chandragupta Maurya introduced administrative reforms that helped manage the empire.
- 5 → a: Ashoka’s reign was marked by the Kalinga War, which led to his conversion to Buddhism and promotion of peace.
|
1 videos|107 docs
|
FAQs on Class 7 Social Science Chapter 5 Worksheet Solutions - The Rise of Empires
| 1. What are the main factors that led to the rise of empires in ancient history? |  |
| 2. How did empires maintain control over their vast territories? |  |
| 3. What role did religion play in the expansion of empires? |  |
| 4. Can you provide examples of significant empires and their contributions to world history? |  |
| 5. What were some of the challenges faced by empires during their rise and rule? |  |




















