Class 7 Social Science Chapter 1 Worksheet Solutions - Geographical Diversity of India
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
| Match the Following |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1: What is the meaning of the word 'Himalaya' in Sanskrit?
a) Frozen peaks
b) Land of snowstorms
c) Abode of snow
d) Cold mountains
Ans: c) Abode of snow
'Himalaya' is derived from Sanskrit where 'Hima' means snow and 'Alaya' means abode or home.
 Himalayas
Himalayas
Q2: Which of the following is India’s only active volcano?
a) Mount Abu
b) Barren Island
c) Kanchenjunga
d) Deomali
Ans: b) Barren Island
Barren Island in the Andaman Sea is home to India’s only active volcano.
Q3: The Gangetic Plains are considered ideal for agriculture because of:
a) Rocky terrain
b) Mineral-rich soil from rivers
c) Frequent snowfall
d) Presence of deserts
Ans: b) Mineral-rich soil from rivers
Rivers like the Ganga bring mineral-rich soil from the Himalayas, making the plains very fertile.
Q4: Which desert festival is celebrated in the Thar region?
a) Diwali
b) Pushkar Mela
c) Losar
d) Pongal
Ans: b) Pushkar Mela
Pushkar Mela is a popular camel and cultural fair held in Rajasthan's Thar Desert region.
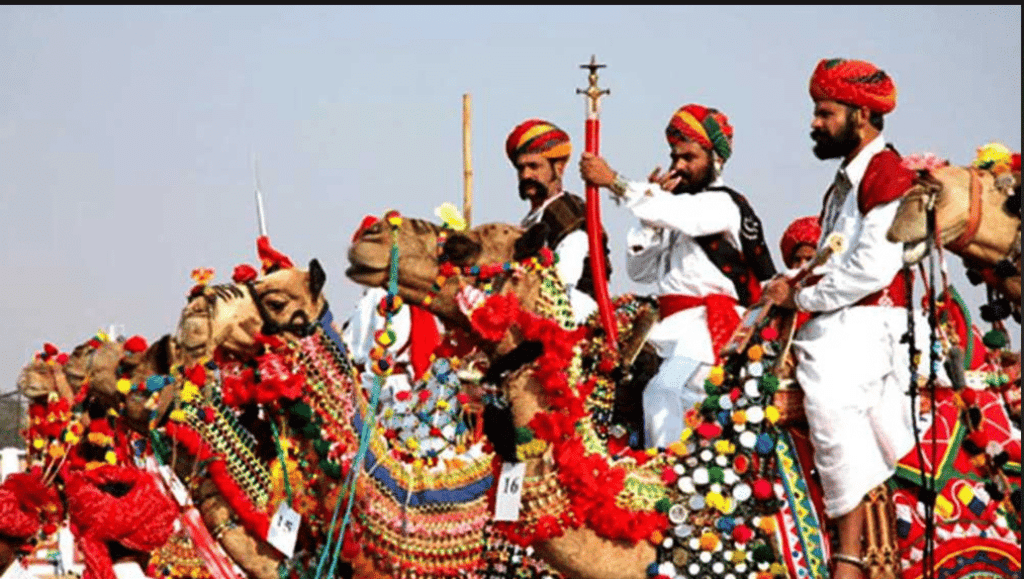 Pushkar Mela
Pushkar Mela
Q5: Which river flows westward into the Arabian Sea instead of eastward into the Bay of Bengal?
a) Godavari
b) Krishna
c) Narmada
d) Kaveri
Ans: c) Narmada
Unlike most rivers, Narmada flows west into the Arabian Sea.
Q6: What kind of landform is the Peninsular Plateau?
a) Flat desert
b) High mountain
c) Elevated flat land with steep slopes
d) River valley
Ans: c) Elevated flat land with steep slopes
Plateaus are high flat areas with steep sides.
Q7: Which Indian region is called a cold desert?
a) Ladakh
b) Sundarbans
c) Sikkim
d) Arunachal Pradesh
Ans: a) Ladakh
Ladakh has extremely cold weather and very little rainfall, making it a cold desert.
Q8: Which Indian mountain range helps stop the spread of the Thar Desert?
a) Himalayas
b) Western Ghats
c) Vindhyas
d) Aravallis
Ans: d) Aravallis
The Aravalli range acts as a natural barrier to prevent the eastward spread of the Thar Desert.
Q9: Which plateau region is known for heavy rainfall and root bridges?
a) Deccan Plateau
b) Bundelkhand Plateau
c) Meghalaya Plateau
d) Malwa Plateau
Ans: c) Meghalaya Plateau
The Meghalaya Plateau experiences heavy rainfall and has famous living root bridges.
Q10: Which animal is important for transport and daily life in Ladakh?
a) Tiger
b) Yak
c) Camel
d) Elephant
Ans: b) Yak
Yaks are vital in Ladakh for transport, milk, wool, and dung.
 Yak at Ladakh
Yak at Ladakh
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: India is a part of the __________ Subcontinent.
Ans: Indian
India along with its neighboring countries forms the Indian Subcontinent.
Q2: The highest peaks of the Himalayas are located in the __________ Himalayas.
Ans: Himadri
Himadri or Greater Himalayas contain the tallest peaks like Mount Everest.
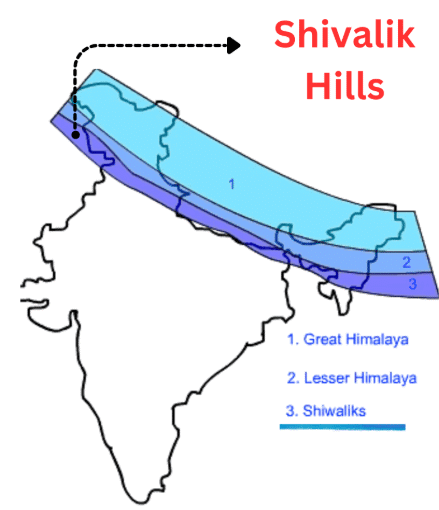
Q3: The outermost range of the Himalayas is called the __________ Hills.
Ans: Shivalik
The Shivalik Hills are the lowest and outermost part of the Himalayan range.
Q4: The Thar Desert covers states like Rajasthan and __________.
Ans: Gujarat
The Thar Desert spans across western India, including Gujarat.
Q5: Ladakh is also called the __________ desert of India.
Ans: Cold
Ladakh is a cold desert due to its icy weather and dry climate.
Q6: __________ and Tapti are the two major west-flowing rivers of India.
Ans: Narmada
Both Narmada and Tapti flow westwards into the Arabian Sea.
Q7: The peacock, India’s national bird, is found in the __________ Plains.
Ans: Gangetic
The fertile Gangetic Plains support rich wildlife including the peacock.
Q8: The Western Ghats are recognized as a __________ World Heritage Site.
Ans: UNESCO
The Western Ghats are a biodiversity hotspot declared by UNESCO.
Q9: The Sundarbans are known for their __________ forests.
Ans: Mangrove
Sundarbans are famous for mangrove trees growing in salty coastal areas.
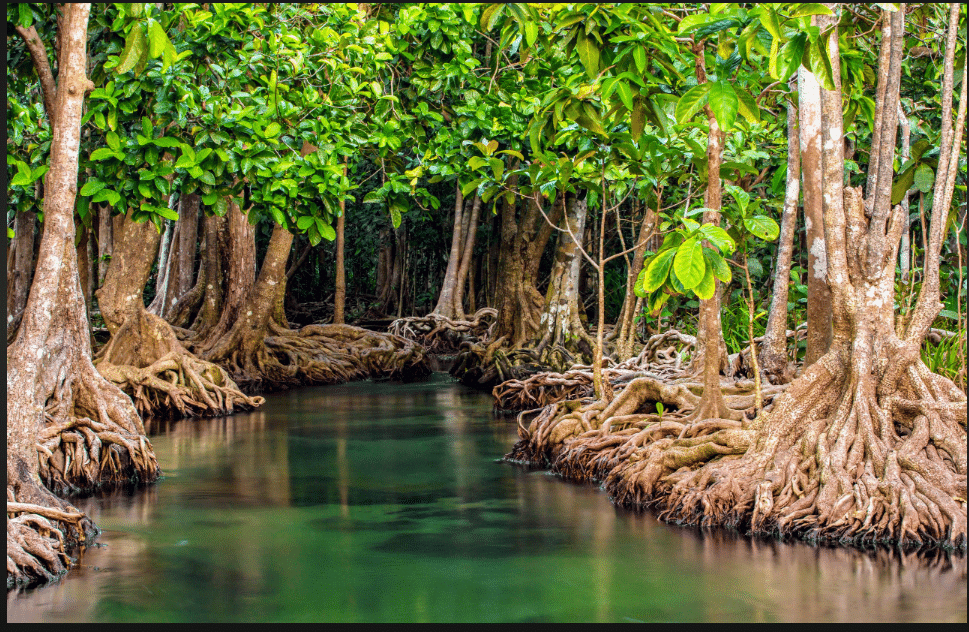 Mangroves
Mangroves
Q10: An __________ is a group or chain of islands.
Ans: Archipelago
Lakshadweep is an archipelago consisting of 36 coral islands.
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: What is the approximate length of the Himalayas?
Ans: About 2,500 km.
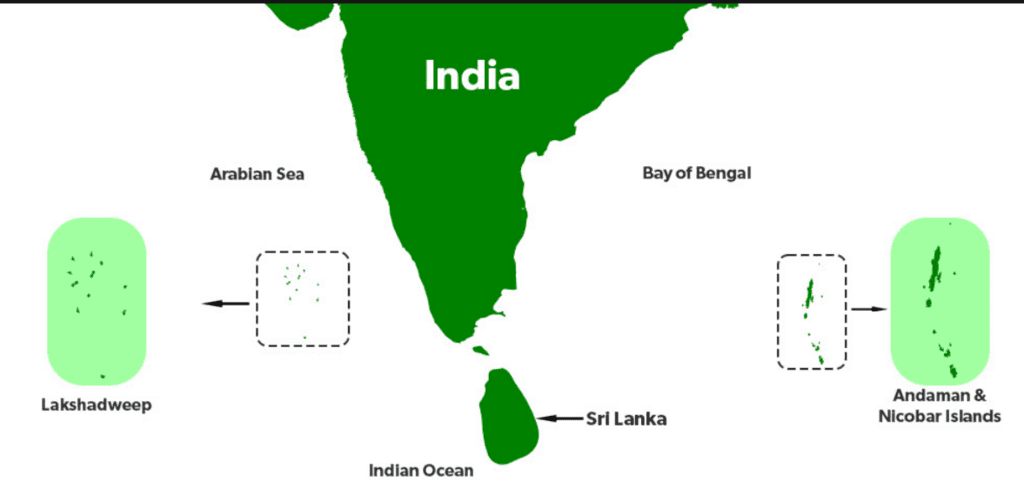
Q2: Name the two island groups of India.
Ans: Lakshadweep and Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
 Islands of India
Islands of India
Q3: What is the cleanest village in Asia?
Ans: Mawlynnong in Meghalaya.
Q4: Which hill stations are found in the Himachal range?
Ans: Shimla, Manali, Dharamshala.
Q5: Which mineral is extracted in Zawar mines of the Aravallis?
Ans: Zinc.
Short Answer Questions
Q1: Why are the Himalayas called the ‘Water Tower of Asia’?
Ans: Because they store snow and glaciers which melt in summer and feed rivers like the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Indus, providing water to millions of people.
Q2: What are some adaptations seen in the Thar Desert region?
Ans: People use camels for transport, clean utensils with sand, and harvest rainwater using tankas and kunds due to water scarcity.
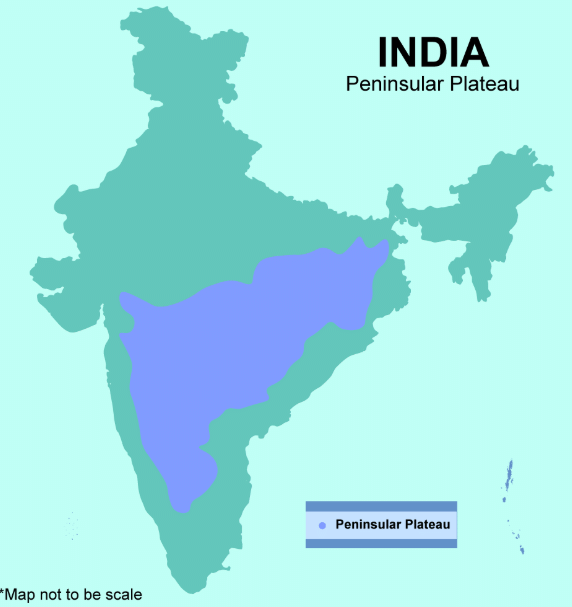
Q3: Describe two features of the Peninsular Plateau.
Ans: It is a triangular plateau surrounded by water on three sides and is rich in minerals and forests, supporting agriculture and hydroelectric power.
 Peninsular Plateau
Peninsular Plateau
Q4: How are the islands of Andaman and Nicobar ecologically important?
Ans: They have coral reefs, tropical forests, unique wildlife, and are home to some of the oldest tribes in India, contributing to biodiversity.
Q5: What makes the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers culturally special?
Ans: They are considered sacred in Indian culture and are personified as deities like Ganga and Brahmaputra, playing a role in rituals and beliefs.
Match the Following
(Match Column A with the correct option in Column B)
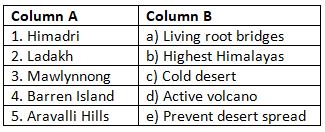
Ans: Matched Pairs and Explanations:
- 1 → b: Himadri is the highest Himalayan range with peaks over 8000 m.
- 2 → c: Ladakh is India’s cold desert with extreme winters.
- 3 → a: Mawlynnong is known for eco-tourism and root bridges.
- 4 → d: Barren Island hosts India’s only active volcano.
- 5 → e: The Aravallis block the expansion of the Thar Desert.
|
1 videos|107 docs
|
FAQs on Class 7 Social Science Chapter 1 Worksheet Solutions - Geographical Diversity of India
| 1. What are the major geographical features of India? |  |
| 2. How does geographical diversity affect the climate of India? |  |
| 3. What role do rivers play in the geographical diversity of India? |  |
| 4. How does India's topography influence its agriculture? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of geographical diversity in India's culture and traditions? |  |
















