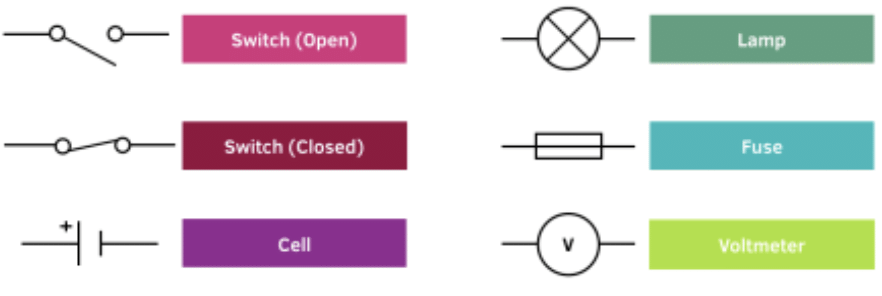
Q.12. What is a switch, and how does it control an electric circuit?
Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Worksheet Solutions - Electricity: Circuits and their Components
Q.1. True/False
(i) The human body is a good conductor of electricity.
True
Explanation: That is why touching live wires is dangerous.
(ii) An incandescent lamp will not glow if connected with the wrong terminals.
False
Explanation: It glows regardless of which terminal is connected to which side.
(iii) Circuit diagrams use symbols to show real components in a circuit.
True
Explanation: Standard symbols make diagrams easy to understand.
(iv) A battery produces alternating current (AC).
False
Explanation: Batteries produce direct current (DC).
(v) LEDs can work even if the positive and negative terminals are reversed.
False
Explanation: LEDs only work when connected in the correct direction.
Q.2. Fill in the blanks.
(i) Longer line in the symbol for a cell represents its ____ terminal.
positive
The longer line in the symbol for a cell indicates the positive terminal, while the shorter line represents the negative terminal.
(ii) The combination of two or more cells is called a ____.
battery
A battery is formed when two or more cells are connected together to provide a higher voltage or capacity.
(iii) When current is switched ‘on’ in a room heater, it ____.
produces heat
- When the current is switched on in a room heater, it:
- Produces heat as the electric current flows through the wire.
(iv) The safety device based on the heating effect of electric current is called a ____.
fuse
A fuse is designed to protect electrical circuits by melting and breaking the circuit when excessive current flows, preventing damage or fire.
Answer the following Questions
Q.3. What is electric current?
Electric current is the flow of electrons through a conductor, such as a wire.
- It is measured in amperes.
- Electric current can produce heat when it flows through a wire.
- This heating effect is used in many appliances, like heaters and toasters.
- When current flows, it can also create a magnetic field, making wires behave like magnets.
Q.4. Write some uses of battery.
Battery Uses
- Torches for lighting
- Transistors for amplifying signals
- Toys for operation
- TV remote controls for convenience
Q.5. What is filament?
In the bulb there is a thin wire, called the filament, which glows when an electric current passes through it.
Q.6. What are the uses of heating effect of electric current?
The heating effect of electric current is utilised in various electrical appliances, including:
- Immersion heaters
- Hotplates
- Irons
- Geysers
- Electric kettles
- Hair dryers
Q.7. Name any two effects of electric current.
The two effects of electric current are:
(i) Heating effect of electric current
(ii) Magnetic effect of the electric current
Q.8. What is an
An electric circuit is a closed path that allows electricity to flow between the two terminals of an electric cell. Key points include:
- The circuit must be closed for current to flow.
- A bulb will only glow when the current is flowing through the circuit.
- If the circuit is open (e.g., when a switch is off), no current flows.
In the bulb, a thin wire called the filament glows when electric current passes through it. If the filament is broken, the circuit becomes incomplete, and the bulb will not glow.
Q.9. Explain the symbol of electric cell.
In the symbol of an electric cell, the representation consists of:
- The longer line indicates the positive terminal.
- The thicker, shorter line represents the negative terminal.
Q.10. Why a fused bulb does not glow?
A fused bulb does not glow due to a break in its filament. This break interrupts the flow of current between the bulb's terminals. As a result:
- The circuit becomes incomplete.
- No current passes through the filament.
- Thus, the bulb remains unlit.
Q.11. Sometimes the cells are placed side by side. Then how are the terminals of the cells connected?
Cells are typically connected using:
- A thick wire or a metal strip that links the positive terminal of one cell to the negative terminal of the next.
- This connection allows the cells to work together as a battery.
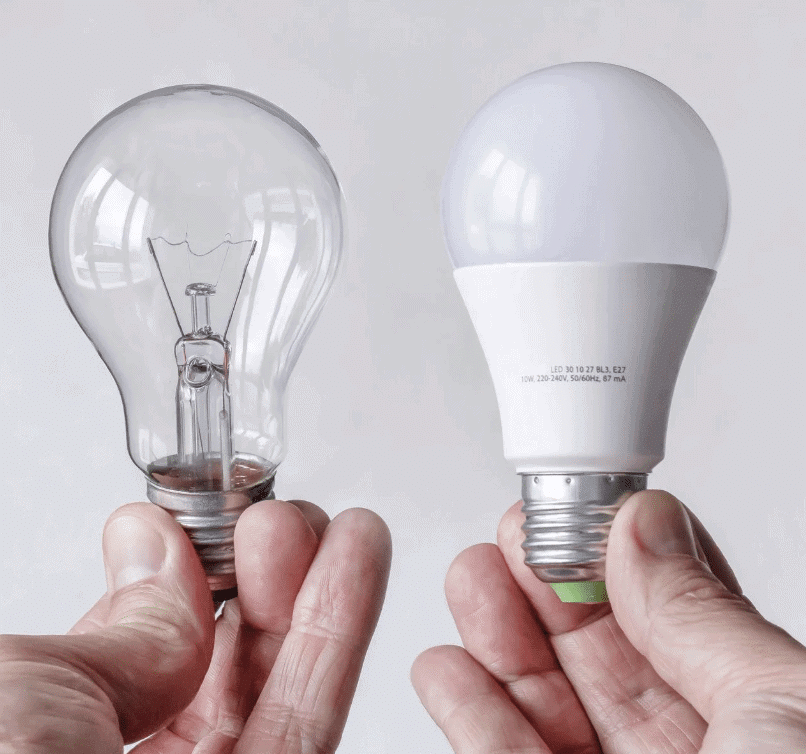
Q.14. Describe the difference between an incandescent lamp and an LED.
An incandescent lamp has a filament that glows when current passes through it and can work in either direction of connection. An LED does not have a filament; it only glows when connected correctly, with the longer wire to the positive terminal and the shorter wire to the negative. LEDs are energy-efficient and long-lasting.
Q.15. What are conductors and insulators? Give examples and their uses.
Conductors are materials that allow electricity to pass easily, like copper and aluminum, used in wires and plugs. Insulators block current and include rubber, plastic, and glass. They are used to cover wires, make switches, and ensure electrical safety by preventing shocks.
|
1 videos|107 docs
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Worksheet Solutions - Electricity: Circuits and their Components
| 1. What are the basic components of an electric circuit? |  |
| 2. How does a series circuit differ from a parallel circuit? |  |
| 3. What is the role of a switch in an electric circuit? |  |
| 4. What safety precautions should be taken when working with electric circuits? |  |
| 5. How can we measure electric current in a circuit? |  |