Worksheet: Globalisation | Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: Globalization refers to the movement of ____________, ____________, ____________, and ____________ among various regions of the world.
Q2: One of the causes of globalization is ____________, which enables easier global movement of people and ideas.
Q3: Economic globalization has led to increased ____________ among nations, both voluntary and compelled by international organizations.
Q4: ____________ is an international platform for those opposed to neoliberal globalization.
Q5: India started its economic reform program in ____________ to deregulate industries and promote trade and foreign investment.
Q6: Globalization has led to the rise of a uniform culture, also known as ____________.
Q7: The World Social Forum focuses on issues related to ____________, ____________, ____________, and ____________.
Q8: Globalization reduces the ____________ of the government, leading to a more minimalist state.
Q9: Cultural globalization has both ____________ and ____________ effects on the world.
Q10: Globalization has faced opposition from both the ____________ and the ____________ in India.
Match the Column
Q1: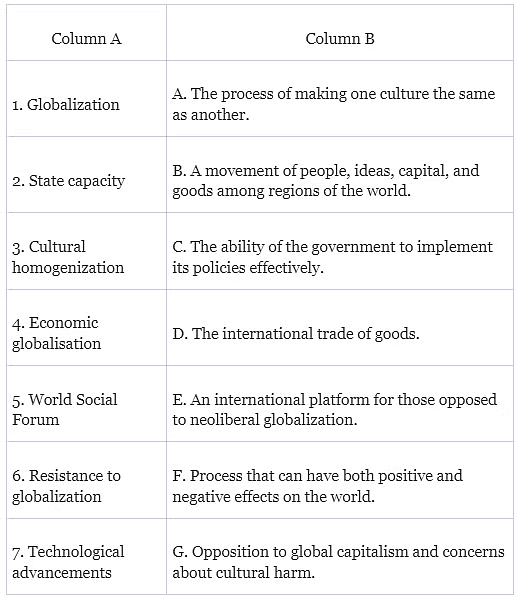
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: Globalization reduces state capacity.
Reason: The market takes over the role of the government in determining economic and social priorities.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Q2: Assertion: The World Social Forum opposes neoliberal globalization and advocates for human rights and environmental issues.
Reason: The World Social Forum is a platform for promoting capitalist globalization.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Q3: Assertion: India started an economic reform program in 1991 to become economically self-sufficient.
Reason: Economic liberalization and trade promotion were key goals of India's reform program.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Q4: Assertion: Cultural globalization leads to cultural homogenization.
Reason: Cultural globalization promotes diverse cultural influences.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What are the different dimensions of globalization?
Q2: How has technology contributed to globalization?
Q3: What is cultural homogenization?
Q4: Name one international platform opposing neoliberal globalization.
Q5: When did India initiate its economic reform program?
Q6: What is the role of the market in state capacity reduction due to globalization?
Q7: Give an example of a resistance movement against globalization.
Q8: What does economic globalization involve?
Q9: How has globalization affected the role of the government?
Q10: Why do some people oppose globalization culturally?
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the concept of cultural homogenization and provide an example.
Q2: Discuss the economic consequences of globalization, highlighting both positive and negative aspects.
Q3: How has technology facilitated the movement of people and ideas globally?
Q4: Describe the role of the World Social Forum in opposing globalization and promoting specific issues.
Q5: What were the goals of India's economic reform program initiated in 1991?
Q6: Explain the relationship between state capacity and globalization.
Q7: Discuss the reasons behind the opposition to globalization in India from both the political left and right.
Q8: How do resistance movements against globalization form international alliances?
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the Political Consequences of Globalisation.
Q2: Discuss the Economic Consequences of Globalisation.
Q3: Describe the Cultural Consequences of Globalisation.
Q4: Explain India’s Role in Globalisation and the Resistance It Faced.
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
34 videos|433 docs|77 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Globalisation - Political Science Class 12 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is globalization and how does it impact societies? |  |
| 2. What are the positive effects of globalization? |  |
| 3. What are the negative consequences of globalization? |  |
| 4. How does globalization influence cultural exchange? |  |
| 5. What role do international organizations play in globalization? |  |




















