Weekly Current Affairs (15th to 21st April 2025) | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
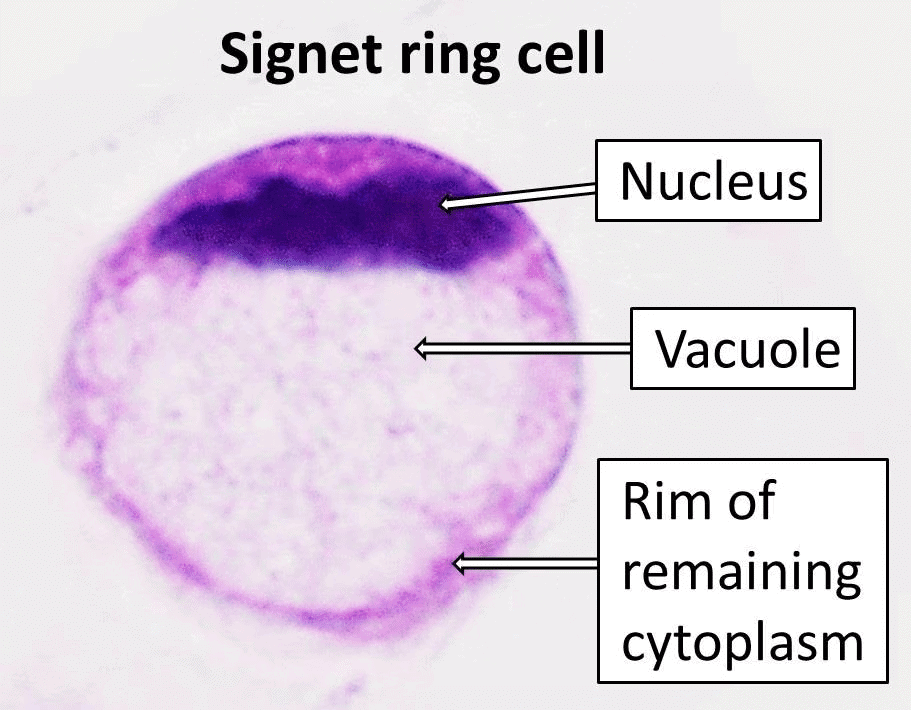
Signet Ring Cell Carcinoma
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Signet ring cell carcinoma (SRCC) is gaining attention due to its rarity and aggressive nature, particularly within the gastrointestinal tract, most notably the stomach. Its unique cellular morphology, resembling a signet ring, complicates treatment and highlights the need for advanced research methodologies to improve patient outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- SRCC is a rare subtype of colorectal cancer, accounting for approximately 1% of cases globally.
- It has a higher prevalence in India, particularly affecting younger populations.
- Diagnosis often occurs at advanced stages, limiting effective treatment options.
- Recent research utilizing patient-derived organoids (PDOs) and xenografts (PDXs) is uncovering new therapeutic vulnerabilities.
Additional Details
- Nature and Prevalence: SRCC is recognized for its aggressive behavior and is increasingly common in certain regions, notably central and northern India, where it presents significant public health challenges.
- Diagnosis Challenges: Due to its rapid progression, patients often present with advanced disease, complicating management and leading to a poor prognosis.
- Research Innovations: The development of PDOs and PDXs has allowed researchers to study SRCC more effectively, revealing specific molecular characteristics that contribute to the cancer's resistance to conventional chemotherapy.
- Therapeutic Advances: Recent findings suggest a promising three-drug combination that has shown efficacy in reducing tumor size and preventing cancer spread in laboratory models.
- Future Directions: Ongoing research is expected to lead to Phase 1 clinical trials to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new treatment options, potentially improving outcomes for patients with SRCC.
The ongoing exploration of SRCC through innovative research holds promise for developing targeted therapies, which could significantly enhance the management and prognosis of this challenging cancer type.
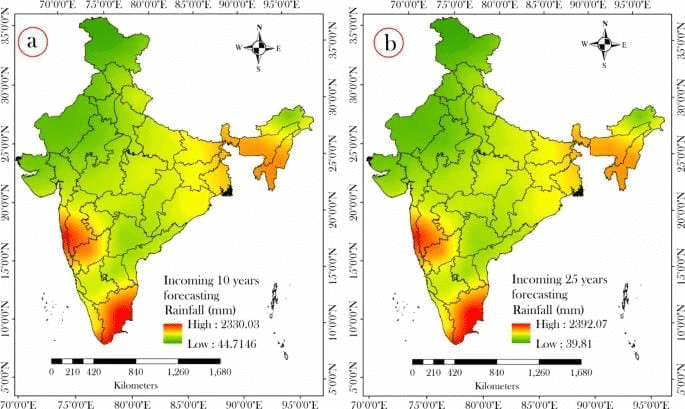
Rainfall Trends and Vegetation Changes in India
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Recent studies have highlighted significant changes in rainfall patterns across India from 2011 to 2020. These findings are based on data collected from the Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP-ISRO), a joint effort between the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA).
Key Takeaways
- West-central India has seen an increase of approximately 2 mm of rainfall per day.
- Eastern regions of India experienced a decrease of about 1 mm per day.
- The Indo-Gangetic Plain and southern regions noted slight increases in rainfall.
Additional Details
- Vegetation and Soil Moisture Correlation: The rise in rainfall in west-central India corresponds with an increase in vegetation cover, as indicated by the Normalised Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) which rose from around 0.2 to 0.4. This increase enhances transpiration rates, contributing to atmospheric moisture during the summer monsoon. Additionally, soil moisture content has also increased, supporting the observed rainfall trends.
- Shifts in Rainfall Timing: The timing of peak rainfall has shifted, with the Indo-Gangetic Plain experiencing peak rainfall 2-4 hours earlier compared to the previous decade, while west-central India has seen a delay of 1-2 hours. This variation is influenced by aerosol levels affecting atmospheric conditions.
- Impact of Aerosols on Rainfall: Higher aerosol concentrations in the Indo-Gangetic Plain are linked to the earlier peak rainfall. Aerosols interact with solar radiation, affecting atmospheric stability and rainfall timing, suggesting similar patterns may occur in other polluted regions.
The findings from this research enhance the understanding of climate dynamics in India, emphasizing the need for continuous monitoring of vegetation cover and soil moisture as indicators of changing rainfall patterns. It also highlights the necessity for ongoing studies regarding the impact of aerosols on weather phenomena.
Delhi Government Increases Minimum Wages for Workers
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Delhi government has announced an increase in minimum wages for workers across various categories, effective from April 1, 2025. This decision, made by Chief Minister Rekha Gupta, aims to relieve the financial strain on workers amidst ongoing inflation.
Key Takeaways
- The new wage rates reflect a significant increase for all worker categories.
- The wage hike is intended to safeguard workers' purchasing power in light of rising living costs.
- Workers earning below the new minimum rates can file claims with designated officials.
Additional Details
- Wage Rate Breakdown:The revised monthly wage rates are as follows:
- Unskilled workers: ₹18,456 (up from ₹18,066)
- Semi-skilled workers: ₹20,371 (up from ₹19,929)
- Skilled workers: ₹22,411 (up from ₹21,917)
- Graduates and higher qualifications: ₹24,356 (up from ₹23,836)
- Legal Provisions: The government has established a mechanism for addressing wage discrepancies. Workers who believe they are underpaid can file claims with the Joint Labour Commissioner or the Deputy Labour Commissioner in their districts, as authorized under the Minimum Wages Act of 1948.
- The increase in wages is a proactive measure to ensure workers can manage the effects of inflation.
This wage revision underscores the Delhi government's commitment to improving the living standards of workers, particularly those in low-paying jobs, and aims to protect them from exploitation while ensuring adherence to the new wage standards.
Safety Protocols in Human Spaceflight Missions
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The recent return of NASA astronauts Sunita Williams and Barry Wilmore underscores the critical importance of safety protocols in human spaceflight. Their nine-month mission aboard the International Space Station (ISS) exemplifies the effectiveness of rigorous safety measures. In light of this, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is adopting similar safety protocols for its Gaganyaan mission, drawing insights from previous incidents and ongoing research to ensure the safety of its astronauts.
Key Takeaways
- Human spaceflight involves three main phases: launch, orbit, and reentry, each requiring distinct safety protocols.
- The implementation of advanced safety measures has been informed by historical incidents.
Additional Details
- Safety During Launch:Safety measures commence on the launchpad, informed by past tragedies like the Apollo-1 fire in 1967. ISRO has equipped its launch pad with ziplines and fireproof lifts to enhance emergency preparedness. Key features include:
- An emergency exit device crucial for rapid evacuation.
- A human-rated launch vehicle with a tower-like structure for quick crew module detachment in emergencies.
- The Crew Escape System, which includes the Low-altitude Escape Motor (LEM) and High-altitude Escape Motor (HEM), activates based on altitude during emergencies.
- Historical incidents such as the Soyuz T-10 emergency and Blue Origin’s NS-23 mission highlight the effectiveness of these systems.
- Safety in Orbit: The Gaganyaan crew capsule consists of two modules: the crew module for living quarters and the service module for essential systems. In case of emergency, the propulsion system can launch the crew module onto a sub-orbital trajectory. Although Gaganyaan will not dock with a space station, crew members will be trained in docking procedures. The capsule can also function as a lifeboat during emergencies, similar to NASA's protocols during the Williams and Wilmore mission. The ISS includes designated safe areas for occupants to escape hazards like fires or radiation.
- Safety During Reentry: The reentry phase is the most intricate part of spaceflight. The crew module must carefully manage its descent for a safe landing, employing thrusters to control speed and trajectory. The capsule's heat shield withstands extreme temperatures, while a sophisticated parachute system is activated for landing. The Gaganyaan capsule will utilize a 10-parachute system, with a precisely timed deployment sequence to ensure a controlled descent to the designated splashdown area.
The advancements in safety protocols reflect an evolving understanding of the risks associated with human spaceflight. As organizations like NASA and ISRO continue to innovate, astronaut safety remains a top priority. The lessons learned from past missions will significantly influence the future of human space exploration.
SC Ruling on Waqf Amendment Act 2025
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Waqf (Amendment) Act of 2025 has ignited significant legal and social discussions in India, as it seeks to reform the management of waqf properties—properties dedicated for Islamic religious and charitable purposes. Over 70 petitions have been lodged against the Act by various religious and political factions, who argue that it infringes on the rights protected under Articles 25 and 26 of the Constitution, which guarantee religious freedom.
Key Takeaways
- The Act amends the Waqf Act of 1995, enhancing the central government's regulatory authority over waqf properties.
- Critics claim the Act undermines judicial authority by allowing district collectors to determine the status of waqf properties.
- Concerns have been raised about the feasibility of mandatory registration for waqf properties that have existed for centuries.
Additional Details
- Articles 25 and 26: These articles ensure that every citizen has the freedom of religion and the right for religious groups to manage their affairs and properties.
- Waqf by User: This term refers to properties considered waqf due to their continuous religious use, even if not formally registered. The Supreme Court indicated that properties already declared as waqf should retain that status under the new law.
- Collector's Inquiry Powers: The Act states that if a collector initiates an inquiry, the property cannot be treated as waqf during this period. The Supreme Court found this provision unfair, advocating that the inquiry should not freeze a property's waqf status.
- Non-Muslim Membership in Waqf Boards: The Act allows non-Muslims to serve on Waqf Councils, prompting the Supreme Court to question whether this principle would apply inversely in Hindu religious trusts.
The Supreme Court's deliberation on the Waqf Amendment Act is poised to have significant implications for the governance of religious properties in India, influencing the balance between religious rights and state authority in property and charitable trust management.
Jammu and Kashmir’s Controversial Reservation Policy Amendments
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Jammu and Kashmir government is currently facing significant backlash regarding its reservation policy, which determines the quotas for jobs and educational institutions for various social groups. Recently, the National Conference (NC) government supported an amended version of this policy in court, despite a prior assurance to review it before the upcoming elections. This move has sparked criticism from opposition parties and internal dissent.
Key Takeaways
- The Jammu and Kashmir Reservation Act of 2004 initially set quotas for Scheduled Tribes (ST), Scheduled Castes (SC), and residents of backward areas (RBA).
- Recent amendments increased the overall reservation in government jobs from 43% to 70%, with the Pahari community receiving ST status.
- Opposition highlights concerns over the policy's compliance with Supreme Court guidelines regarding reservation limits.
- The NC government has faced accusations of inconsistency and failing to address public concerns adequately.
Additional Details
- Reservation Policy Background: The original policy allocated 10% for ST, 8% for SC, and 20% for RBA, summing up to a total of 43% reservations in jobs, with an additional 50% quota in educational institutions. Horizontal reservations were also established for ex-servicemen and the physically challenged.
- Amendments by the Lieutenant Governor: In March 2024, the reservation was adjusted significantly, increasing the quotas and creating contention among various community groups, particularly the Gujjar and Bakerwal communities.
- Numerous petitions against the amendments have been filed in the J&K High Court, challenging their legality.
The current situation remains dynamic, with ongoing debates and protests from various stakeholders, raising questions about the government's transparency and commitment to fair representation.
MacGregor Memorial Medal Awards
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The MacGregor Memorial Medal is a distinguished award that recognizes outstanding contributions in military reconnaissance and adventurous endeavors. Recently, five military personnel were honored for their exceptional achievements during the years 2023 and 2024. The award ceremony was held at the United Service Institution of India, with Chief of Defence Staff General Anil Chauhan presiding over the event.
Key Takeaways
- The medal was established on July 3, 1888, in memory of Major General Sir Charles Metcalfe MacGregor.
- It initially honored military reconnaissance and exploratory activities but expanded its criteria in 1986.
- Recent awardees include distinguished members from the Air Force and Navy for their contributions.
Additional Details
- Award Criteria: The medal is awarded for valuable military intelligence obtained through reconnaissance, exploration, or similar activities of national importance. All ranks from various branches of the Armed Forces, including the Territorial Army, Reserve Forces, Rashtriya Rifles, and Assam Rifles, are eligible.
- Notable Recipients: Since its inception, a total of 127 medals have been awarded, with 103 given prior to India's Independence. Some prominent recipients include Captain F.E. Younghusband and Major General Orde Charles Wingate.
- The medal's criteria have evolved to include a broader range of adventure activities such as mountain expeditions and polar explorations, reflecting modern military challenges.
The MacGregor Memorial Medal continues to be a symbol of honor within the Indian Armed Forces, highlighting the significance of reconnaissance and adventure in military operations. It serves as an encouragement for personnel to participate in activities that enhance national security.
Flue Gas Desulphurisation
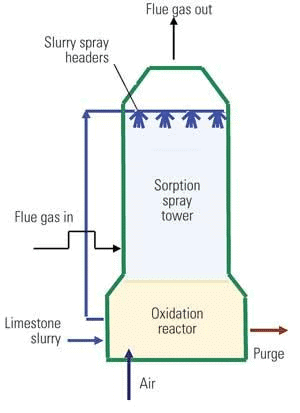 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Union Environment Ministry is re-evaluating its 2015 directive regarding Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD) across all coal-fired power plants in India. A recent study conducted by the National Institute of Advanced Studies indicates that FGD should primarily be mandated for plants utilizing imported or high-sulphur coal. This reconsideration stems from an analysis of the coal types used in India and their subsequent impact on air quality.
Key Takeaways
- FGD technology is designed to eliminate sulphur dioxide (SO2) from exhaust emissions.
- SO2 is a significant pollutant produced from burning fossil fuels, contributing to acid rain and environmental degradation.
- Current compliance with FGD mandates is low, with only 8% of coal-fired plants having implemented the technology as of the 2018 deadline.
- Environmental trade-offs exist, such as increased CO2 emissions associated with widespread FGD installation.
- The study suggests focusing on particulate matter (PM) pollution as a more effective air quality strategy.
Additional Details
- Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD): FGD is a process that can remove up to 95% of SO2 from emissions, utilizing absorbents such as ammonia, sodium sulphite, or limestone slurry.
- Impact of SO2: Sulphur dioxide contributes to acid rain, harming ecosystems, freshwater resources, and infrastructure.
- Current Implementation Status: Despite an initial deadline, many plants are still in the process of installation, with costs estimated at ₹1.2 crore per megawatt.
- Coal Quality Analysis: The majority of coal used in Indian power plants has low sulphur content (0.3%-0.5%), with existing regulations helping to mitigate SO2 emissions.
- Environmental Concerns: FGD installation could increase power and water consumption, potentially resulting in higher CO2 emissions while only modestly reducing SO2 levels.
The findings from the NIAS study urge the Environment Ministry to reconsider the FGD mandate, advocating for a shift in focus towards reducing particulate matter emissions instead, which may yield greater benefits for air quality improvement.
Article 142: Tensions Between Judiciary and Executive in India
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Recent events in Indian politics have highlighted escalating tensions between the judiciary and the executive branches. Vice President Jagdeep Dhankhar has expressed concerns regarding a Supreme Court ruling that set a deadline for the President to assent to bills passed by state assemblies. This ruling stems from the Tamil Nadu versus the governor case and has raised alarms about potential encroachments on executive powers, leading Dhankhar to advocate for greater judicial accountability.
Key Takeaways
- Supreme Court's ruling mandates President's timely assent to state assembly bills.
- Concerns about the balance of power among government branches have been amplified.
- Article 142 grants the Supreme Court authority for "complete justice," but its powers are not absolute.
Additional Details
- Article 142(1): Empowers the Supreme Court to issue orders necessary for complete justice, enforceable throughout India, based on Parliament laws or presidential directives in the absence of such laws.
- Article 142(2): Grants the Court authority to summon individuals, request documents, and enforce penalties for contempt of court, guided by parliamentary legislation.
- Important Cases Using Article 142:
- Chandigarh Mayoral Election (2024): The Supreme Court utilized Article 142 to declare AAP’s Kuldeep Kumar as Mayor after finding evidence of tampered ballots.
- Ayodhya Verdict (2019): The Court allocated the disputed land to the Ram temple trust and provided 5 acres to the Sunni Waqf Board for mosque construction, under Article 142.
- Implications of the Ruling: The ruling from April 8 requires the President to assent to Tamil Nadu assembly bills within a specified timeframe, asserting state legislative power while raising questions about separation of powers.
- Limits of Article 142:The Supreme Court's powers under Article 142, while significant, are constrained by existing laws and the Constitution. Notable limitations include:
- In the Supreme Court Bar Association Case (1998): The Court clarified that Article 142 cannot disregard prevailing laws.
- In State of Karnataka v. Umadevi (2006): It was established that Article 142 cannot be used to perpetuate illegal actions.
- In High Court Bar Association, Allahabad v. State of U.P. (2024): Guidelines were set that the powers of Article 142 should respect valid orders from other courts and adhere to principles of natural justice.
In conclusion, while Article 142 provides essential powers to the Supreme Court to ensure justice, the recent ruling underscores the ongoing debate regarding judicial overreach and the need to maintain a balance of power within the Indian government framework.
Maharashtra’s New Education Policy
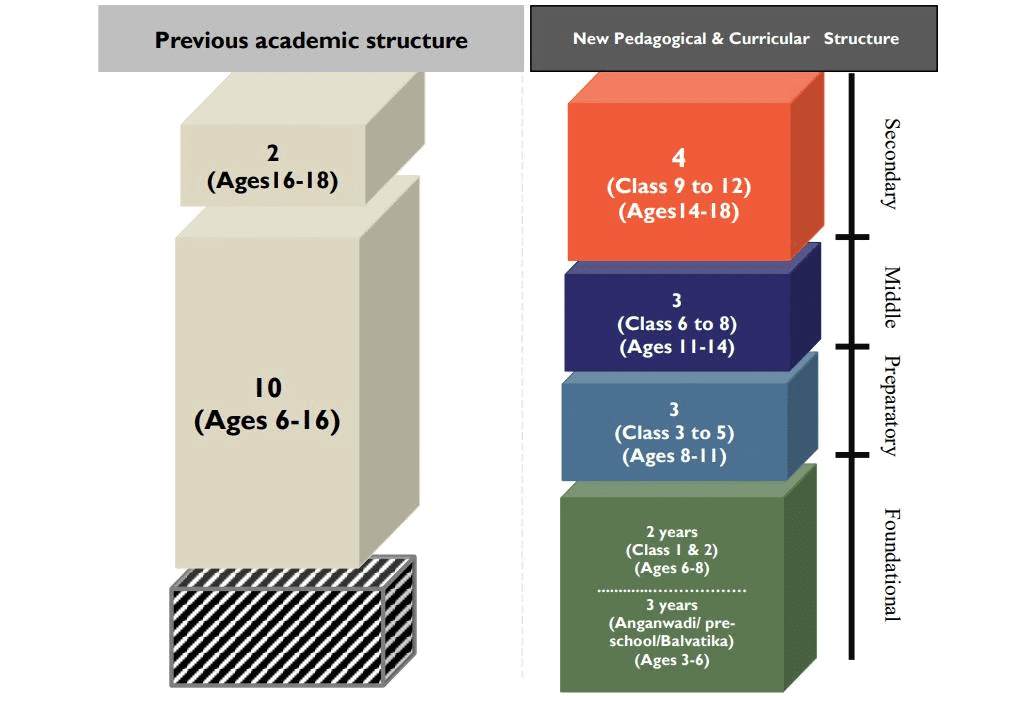 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Maharashtra government has recently mandated the teaching of Hindi as a third language in schools, aligning with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020. This change will affect both Marathi and English medium schools for students in classes 1 to 5, with the aim of enhancing language skills and promoting inclusivity.
Key Takeaways
- Hindi will be taught as a compulsory third language from Grade 1.
- The new curriculum follows a 5+3+3+4 educational structure.
- Emphasis on local context within the syllabus, particularly in History and Geography.
- The educational framework is built on the principles of inclusiveness, equity, quality, affordability, and accountability.
Additional Details
- Implementation of the New Curriculum Framework: The Maharashtra school education department issued a Government Resolution on April 16, 2025, to implement NEP 2020 recommendations in phases.
- Language Policy Changes: Previously, only Marathi and English were mandatory languages for classes 1 to 4. With the new policy, students will be expected to be proficient in three languages by the end of primary education.
- The syllabus will be developed based on NCERT guidelines while incorporating Maharashtra's local context.
- This educational reform supports the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) that aim to be achieved by 2030.
This significant policy shift underscores Maharashtra's commitment to enhancing language proficiency and creating an inclusive educational environment that values both regional and national languages.
India-US Trade Agreement Negotiations
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Recent developments indicate that India and the United States are making progress towards a Bilateral Trade Agreement (BTA). Negotiations are set to commence in Washington, DC, focusing on an "early tranche" of discussions aimed at a limited scope of issues, with the goal of reaching a conclusion before the fall deadline.
Key Takeaways
- The BTA targets doubling bilateral trade in goods and services to USD 500 billion by 2030.
- Negotiations will cover 19 chapters, addressing key areas like digital taxation, tariff reductions, and non-tariff measures.
Additional Details
- Early Tranche: This term refers to the initial phase of the trade agreement, concentrating on specific issues such as market access for select goods and the reduction of non-tariff barriers. This approach is intended to lay the groundwork for more complex discussions in later phases.
- 90-Day Tariff Pause: This pause allows India to negotiate without the immediate pressure of US tariffs, initially announced by President Trump, and excludes tariffs on China. It provides India a unique opportunity to secure beneficial trade terms while avoiding high tariffs on exports.
- Terms of Reference (ToRs): These outline the scope and objectives of the BTA, covering tariffs, customs procedures, and rules of origin to facilitate clear and efficient negotiations.
- Strategic Significance for India: The trade agreement is vital for protecting Indian exports from potential US tariffs and aims to enhance economic ties and market access for Indian products, contributing to a more balanced trade relationship.
- Future Prospects: In-person negotiations are scheduled for April 23, 2025, with an ambitious timeline to conclude the first phase by fall 2025, emphasizing the need for continued engagement for desired outcomes.
The ongoing negotiations between India and the US for a Bilateral Trade Agreement represent a significant step towards enhancing bilateral trade relations. With a focus on strategic sectors and the intent to double trade volumes, the outcomes of these discussions could reshape economic interactions between the two nations.
Jal Jeevan Mission Funding Controversies
Why in News?
- The Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) has recently come under scrutiny due to rising costs and funding requirements. Initiated in 2019, the mission aimed to provide tap water connections to 16.36 crore rural households by the end of 2024. However, by early 2025, only approximately 12.17 crore connections had been established. In light of this, the Jal Shakti Ministry is now proposing to extend the timeline to 2028, along with a revised financial outlay of Rs 9.10 lakh crore, significantly higher than the initial estimate of Rs 3.60 lakh crore.
Key Takeaways
- The JJM was launched on August 15, 2019, to ensure clean drinking water access for rural households.
- As of early 2025, the progress has been slower than expected, leading to a proposed extension of the mission's timeline.
- The cost per connection has dramatically increased from Rs 30,000 to Rs 1,37,500.
Additional Details
- Funding Challenges: The Finance Ministry has expressed concerns regarding the increased costs associated with tap connections, attributing them to factors such as inflation, price volatility, and delays related to the COVID-19 pandemic and the Ukraine conflict.
- Revised Cost Estimates: The Jal Shakti Ministry's revised estimates indicate an additional cost of Rs 5.5 lakh crore to connect the remaining 4 crore households, with contributions required from both the Centre and state governments.
- The Expenditure Finance Committee (EFC) has recommended a reduction in the Central funding assistance from Rs 2.08 lakh crore to Rs 1.51 lakh crore, which may affect states that have already incurred expenses related to the project.
- The increase in costs has raised suspicions about potential inflated contracts and inefficiencies in project execution, as well as concerns about the financial burden being shifted to the states.
The future of the Jal Jeevan Mission hinges on securing necessary funding and addressing the Finance Ministry's concerns regarding cost overruns and project delays. The Jal Shakti Ministry is advocating for a one-time settlement of additional liabilities incurred by states to facilitate the mission's objectives.
|
194 videos|844 docs|2239 tests
|
















