Unit Test (Solutions): Rhythms of Nature | Our Wondrous World Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download
Time: 45 Minutes
M.M.: 20
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 6 carry 1 mark each.
Question numbers 7 to 9 carry 3 marks each.
Question number 10 carries 5 marks.
Q1. The globe is a model of –
(a) Moon
(b) Earth
(c) Sun
(d) Star
Ans: (b) Earth
Earth
Q2. Fill in the blanks:
In India, the six seasons are Vasanta (Spring), Grishma (Summer), Varsha (Monsoon), Sharad (Autumn), Hemant (Pre-winter), and ______ (Winter).
Ans: Shishir
Q3. True or False:
The Sun moves around the Earth in one day.
Ans: False
Q4. Name any sign in nature that farmers might use to know rain is coming.
Ans: Koel singing (or ants carrying eggs to higher ground)
Q5. Match the following: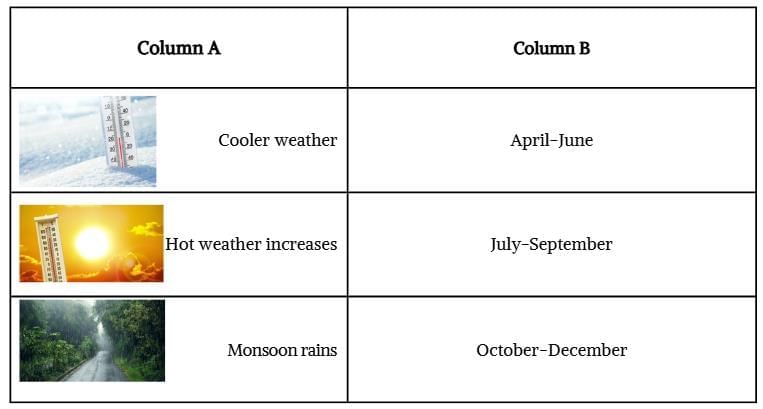
Ans:
Q6. Which activity helps students observe seasonal patterns?
(a) Single-day quiz
(b) Seasons’ journal
(c) One-time field trip
(d) Only textbook reading
Ans: (b) Seasons’ journal
Q7. Write three ways seasons influence people’s daily lives.
Ans: 1. Clothes (cotton in summer, wool in winter).
2. Food (seasonal fruits/vegetables, festive foods).
3. Activities (planting/harvesting, outdoor/indoor events).
Q8. Explain the torch-and-globe demonstration that shows day and night in three steps.
Ans:
1. Shine a torch (Sun) at one side of the globe (Earth) to show day; the opposite side is night.
2. Rotate the globe slowly; different places move into/out of light.
3. Concludes that Earth’s rotation causes day and night.
Q9. Why can winter in Kerala feel different from winter in Kashmir? Give three reasons.
Ans: 1. Different latitudes and altitudes (Kerala low and coastal; Kashmir high mountains).
2. Proximity to the sea moderates temperature in Kerala.
3. Snowfall and much lower temperatures in Kashmir due to the Himalayan climate.
Q10. Create a mini season’s chart for your region with observations for any three themes (plant life, birds/animals, air/heat/light, water bodies, human activities). Present one season in detail.
Ans: Example (Monsoon):
- Plant life: New leaves, many flowers; rapid growth.
- Birds/animals: More insects; birds are active; frogs croaking.
- Air/heat/light: Cloudy, humid; lower daytime heat; earlier sunsets.
- Water bodies: Ponds fill; streams flow; puddles form.
- Human activities: Raincoats/umbrellas; paddy planting; monsoon festivals.
Mini Season chart (all seasons)
|
11 videos|218 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Rhythms of Nature - Our Wondrous World Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the main themes explored in "Rhythms of Nature"? |  |
| 2. How does the concept of biodiversity relate to the rhythms of nature? |  |
| 3. What role do seasons play in the rhythms of nature? |  |
| 4. Can you explain how human activities disrupt the natural rhythms of nature? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to study the rhythms of nature? |  |